
What is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit analyzes a website’s on-page, off-page, and technical optimization, searching for opportunities to improve a site’s visibility in search engines. These components affect how search engines crawl, index, and rank a website. Conducting an SEO audit is typically the first step in a larger strategy to better optimize a website for search visibility.
Why is an SEO audit important?
An SEO audit ensures your website is always up-to-**** with Google Search Essentials (formerly known as Webmaster Guidelines). Over time, these guidelines can change due to factors such as algorithm updates. Frequently auditing a website is a good way to make sure it is optimized and has the best opportunity to perform well in search engines.
What are the different types of SEO audits?
There are many website audits, but SEO audits usually fall under three main categories:
- Technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
What is a technical SEO audit?
A technical SEO audit reviews elements that affect a search engine’s ability to crawl and index a website, looking for errors or missed opportunities to keep the website competitive and possibly improve performance.
Technical SEO elements include:
- Website speed optimization
- Redirect links optimization
- Internal links optimization
- Mobile-friendliness
- URL structures optimization
- Broken links
- Indexing
- Crawlability
What is an on-page SEO audit?
An on-page SEO audit optimizes the elements on a website’s page or in its HTML to help improve page performance. This process helps users and search engines better understand the contents of a webpage.
The on-page SEO elements to be optimized include:
- Meta tag
- Header
- Site content
- Image
- Page title
- Internal link
By optimizing these elements, we can help users quickly find the answer to their query and ensure they have a good experience.
What is an off-page audit?
An off-page SEO audit refers to optimizing elements outside of your website that can impact the website’s ranking.
Off-page elements include:
- Backlinks to your site
- Social media sharing
- Branded searches
Backlinks are the main element of off-page SEO. Search engines use these backlinks to gauge the quality of your content. The idea is the better the backlinks to a website or webpage, the better it will rank.
2023 SEO AUDIT CHECKLIST
SEO audits have many aspects, and it can be challenging to know where to start. This 2023 SEO audit checklist covers on-page, off-page, and technical SEO elements that should be optimized to Google Search Essential standards. Additionally, this checklist shows how to troubleshoot common issues when conducting audits.
Technical SEO Audit Checklist
Step 1. Use an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to secure your website.
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It is a security protocol that creates a secure link between two systems, such as a server and a browser.
In 2014, Google announced that HTTPS protocol would be a ranking signal.
HTTPS (or HypertextHyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) can be located at the beginning of a URL if an SSL certificate secures a website.
A URL protected by an SSL certificate will keep your connection secure when interacting on the web. This system allows sensitive information to be shared, such as login details and credit card numbers, without the risk of criminals accessing the information.

Further Resources
How to Install an SSL Certificate
Install an SSL Certificate on Your WordPress Site
Step 2. Check that your website resolves to the correct URL.
When you use an SSL for your website, there should be four versions of your website URL:
http://example.com
https://example.com
http://www.example.com
https://www.example.com
Though the above four versions are all technically the same website, to search engines they are different. It is imperative to make sure they all 301 (or, point) to the URL (or, version) you want to be indexed.
To check if your URL is set up correctly, use a tool like serpworx. Enter your URL and click “check redirects.”
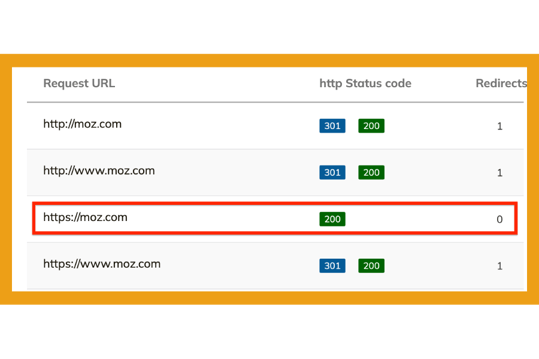
You should see all versions of your URL with a 301 and a returning 200 status code. The URL returning only a 200 status code is the URL where your website resides.
Further Resources
How to Redirect Non-www to www URLs
Step 3. Ensure your website is mobile-friendly.
In 2016, Google started experimenting with mobile-first indexing, and by 2018 they announced it would be used for the whole web.
What does mobile-first mean? It means that the mobile version of a website is crawled, indexed, and used for ranking purposes on both mobile and desktop.
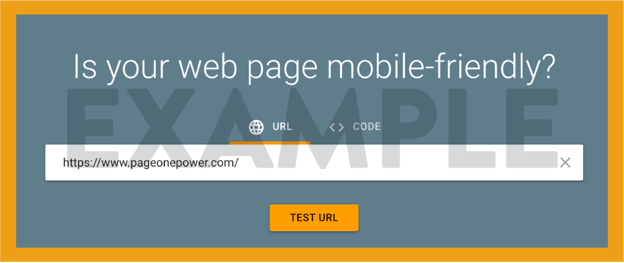
Using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Testing Tool, Google has made it simple to test your site for mobile friendliness. First, enter the webpage you want to test and click “TEST URL” to see if Google considers your page optimized for mobile.
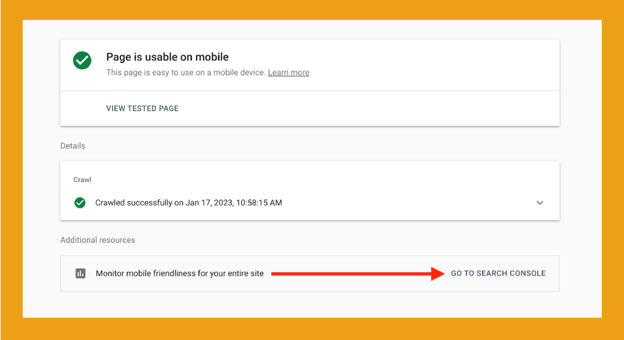
You can also monitor your whole website using Google Search Console.
Further Resources
Getting started with Search Console
Mobile-first Indexing Best Practices
Step 4. Optimize your website for speed.
In 2018, around the same time they rolled out mobile-first, Google announced that site speed would be a ranking factor in mobile search results. This made sense because waiting for a site to load was considered a bad user experience.
PageSpeed Insights is a great tool for analyzing your website’s loading speed. Enter the page URL to test and hit “Analyze.”
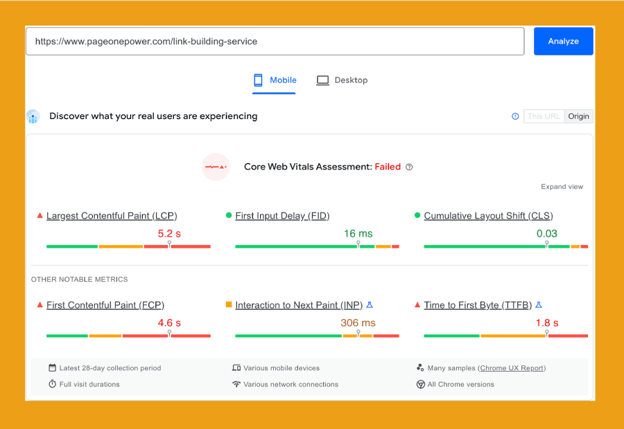
The tool gives you a granular look at what affects a page’s loading speed on mobile and desktop and offers suggestions for improving performance.
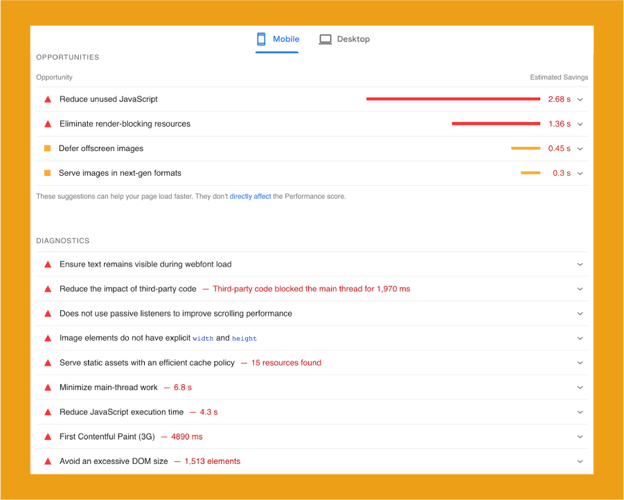
There are many tools that test actual page speed. One tool we recommend is GTmetrix, which can test different browsers, devices, and locations.
The waterfall feature is a quick way to examine what uses the most resources and helps find speed optimization opportunities.
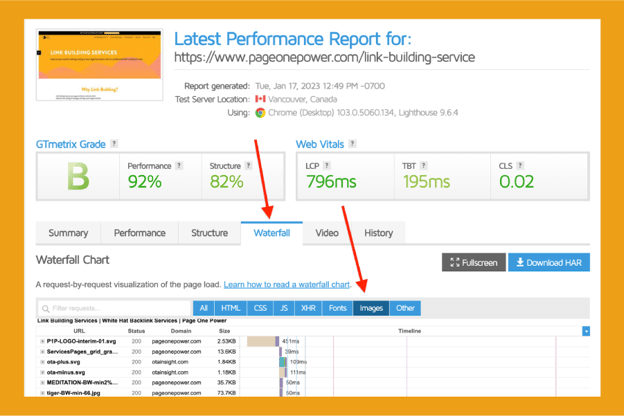
Further Resources
About PageSpeed Insights
PageSpeed Insights Guide
Step 5. Check for duplicate and thin content.
Some content management systems (CMS) automatically generate new pages. These pages can be thin on content or even contain duplicate content. Thin content is content that doesn’t adequately answer a user’s query and offers little to no value. Thin content and duplicate content can harm your SEO because Google either does not find it valuable or sees it as a manipulation.
Here are some examples of pages that can house thin or duplicate content:
- Category
- Tag
- Archive
- Search result
To find duplicate content, use a crawler like Screaming Frog. Once you crawl a website, click on the content tab and choose “Exact Duplicates.” With some configuration, you can also search for “Near Duplicates.”
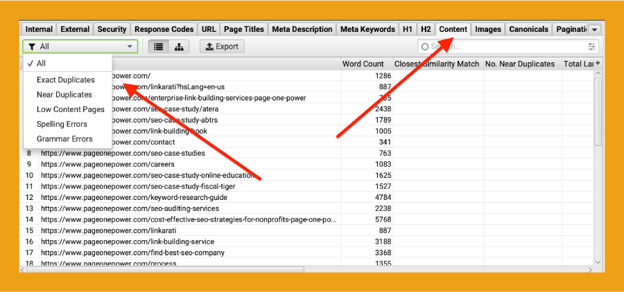
In the same drop-down, you also have the choice to view “Low Content Pages” (also known as thin content) which, by default, shows pages with less than 200 words.
You can configure this tool using whatever parameters you choose. However, keep in mind there is no set number of words used in the classification of thin content. Screaming Frog can help you find pages that might be thin on content, but you should review those pages for quality.
Further Resources
How to check for duplicate content using Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog Tab Guide
Step 6. Make sure you have an XML sitemap.
An XML (extensible markup language) sitemap is a file that contains information about websites. Search engines crawl this information to better understand the relationship between a website’s pages, images, and other files.
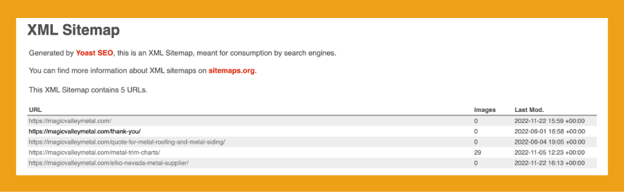
To find your sitemap, type your site’s root domain in the address bar and add “.xml” to the end. For example:
Many times it is also placed in the robots.txt file of your website. If you can’t find it there you can find it using advanced search operators. Use the guide in the “Further Resources” section to find your sitemap.
Further Resources
What is an XML sitemap and why should you have one?
How to Find Your Sitemap
Step 7. Validate any schema markup on your website.
Schema markup helps search engines better understand the content a website presents. Schema markup is also required on a page to qualify for certain rich snippets found in SERPs such as reviews, FAQs, and recipes.
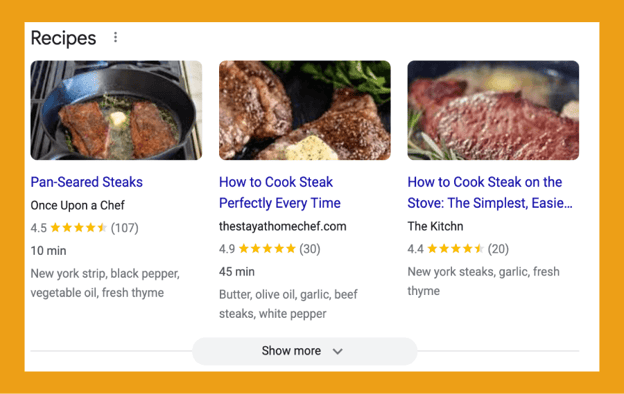
It is important to make sure there are no errors in the schema markup or you won’t qualify for the special features. There are two ways to check schema markup:
1. Enter the URL or the page HTML into the Schema.org validator tool and click “RUN TEST.”
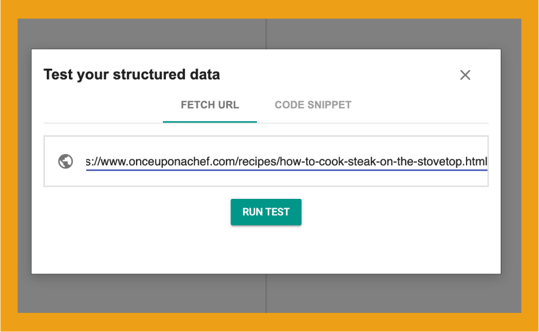
Any errors will appear in the boxes labeled “WebPage,” “VideoObject,” and “Recipe.” Clicking on those boxes will expand them to reveal the schema object with errors.
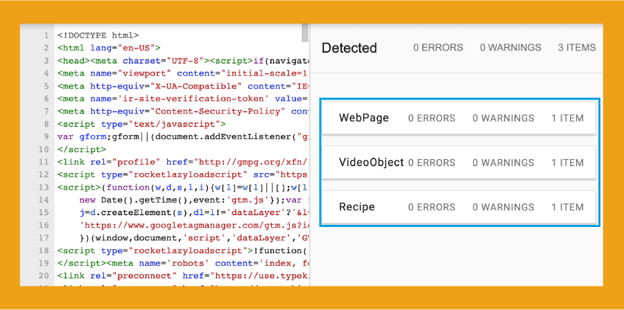
2. Enter the URL or the page HTML into Google’s Rich Results Test tool, choose the type of device, and click “TEST URL.”
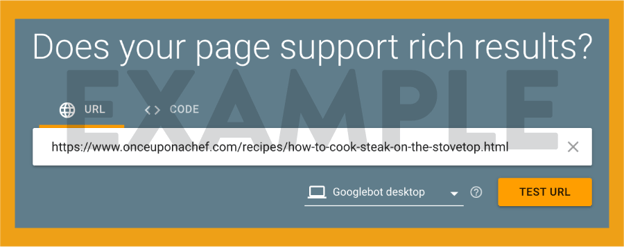
This tool shows the schema markup found on the page, along with any errors.
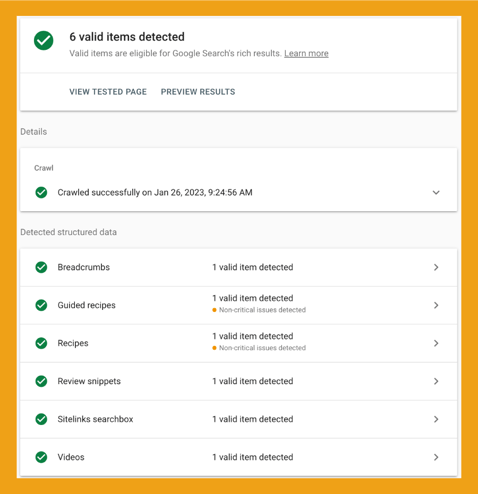
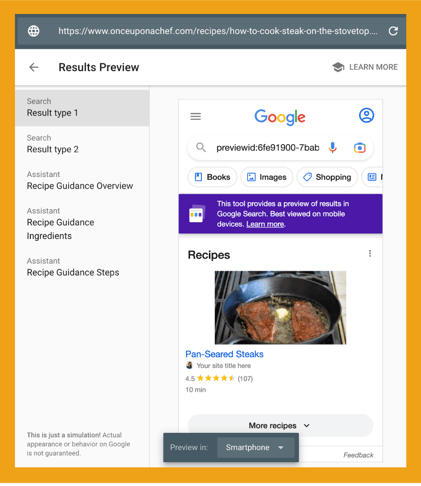
You can click “PREVIEW RESULTS” and see what your pages will look like in the SERPs.
Further Resources
How to check your schema markup
Schema Markup Validator Tool
Step 8. Fix Broken Links
Broken links are hyperlinks that return a 404 error (page not found) and are typically caused by deleted pages, removed content, or misspelled URLs.
Links, either internal or external, usually lead to relevant resources. Trying to use broken links can leave users frustrated and they may end up leaving your site. This bad user experience can have a negative impact on SEO.
Finding broken links on your website is pretty easy. You can use paid tools such as Ahrefs or Screaming Frog, or free online tools such as Broken Link Checker.
Broken Link Checker checks both internal and external URLs and reveals those that could be problematic.
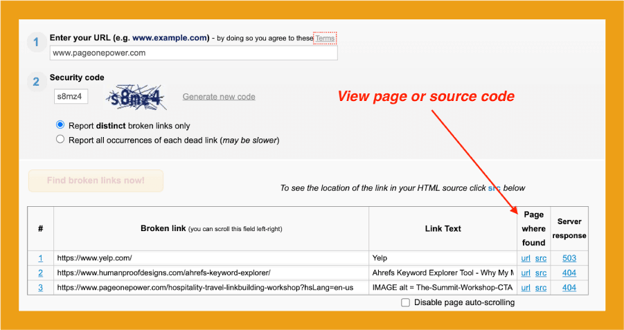
You can use the blue links under “Page where found” to visit the page or review the link in the source code to learn more about it.
Further Resources
How to check for broken links using Ahrefs
How to check for broken links using SEMrush
Step 9. Check Your Website Architecture
A website’s architecture shows how your content is organized and linked together. Site architectures are constructed in two ways:
- Flat architecture: A website whose pages are one click away from the home page.
- Deep architecture: A website whose pages are more than four clicks away from the home page.
Creating a flat site architecture makes it easy for crawlers to find all your pages.
Benefits of an optimized site architecture:
1. It helps search engine crawlers find and index all of a website’s pages.
If you have a deep architecture, crawlers may not reach some of the deeper pages.
Additionally, pages with no inbound links (orphaned) are equally hard to find.
It helps search engines understand what pages are most important.
An organized site with related subjects linked together will help search engines better understand the main topics found within your site.
2. It makes for a better user experience.
Looking at the image above, we can easily tell that each subject listed is just one click away from the main topic, “Home Remodeling.” This structure makes it simple for users of your site to find other pieces of relevant content.
Users should be able to easily navigate to any page on your website in three to four clicks. Keeping your website relatively flat ensures your website is organized and that users can quickly find content.
Tools such as SEMrush, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs can help analyze your website structure and determine whether or not you need to reorganize your pages.
Further Resources
Screaming Frog – Site Architecture & Crawl Visualisations Guide
Ahrefs – How to use the Structure Explorer report
SEMrush – Optimize Your Internal Linking with Site Audit
On-Page SEO Audit Checklist
Check Content Quality
Creating quality content is essential for SEO success because search engines reward content that is relevant and engaging to users. Quality content creates a positive user experience, builds trust, and directly impacts how well your website will rank on the search engine results page (SERPs). Poorly written content can lead to confusion, lack of engagement, and can even drive visitors away from your website.
When you evaluate your content for quality, consider the following:
- Does it add value?
- Does it solve a problem?
- Does the page have appropriate headings and subheadings?
- Does it have relevant images, videos, or other multimedia to support the content?
- Is it free of grammar and spelling errors?
- Is the content clear and easy to understand?
- Is the page organized and easy to read?
Starting with high-quality content can help build a foundation for successful SEO strategy.
Further Resource
Google Offers a Definition of Quality Content
How to Create High-Quality Content
Internal Linking Optimization
Internal links are links on a webpage that connect to other pages on the same website. These are vital for SEO optimization because they allow search engines to discover, crawl, and index your website faster.
Internal linking is beneficial because it:
- Improves internal page rankings.
- Enhances user experience by making it easier to find related content.
- Establishes a clear hierarchy and structure on your website.
- Drives more traffic to important pages or products on your website.
When internally linking your pages, it’s a good idea to ask yourself a few questions:
Is the internal link:
- Relevant to the content?
- Anchor text descriptive?
- Easy to understand?
- Used in moderation?
- Something that adds value to the user?
Further Resource
Importance of Link Architecture
Internal Linking Best Practices
Title Tag Optimization
Title tags are HTML elements that help define the title of the page or post and appear in the title bar of a web browser and search engine results pages (SERPs).
Title bar:
SERPs:

On the backend, you’ll find the title tag wrapped in an HTML meta tag <title>.
Title tags should be optimized to accurately reflect the content on your page and include relevant keywords related to your topic.
Benefits of title tag optimization include:
- Improving click-through rate (CTR) from SERPs.
- Making your title more enticing and relevant.
- Increasing visibility in (SERPs).
- Providing a better user experience for visitors.
Title tag best practices:
1. Keep It Short and Sweet
A good rule of thumb is to keep your title tags 60 characters or less. This is the maximum character count displayed in the SERPs. Titles longer than this may be cut off.
2. Use Keywords Wisely
Include your keywords in your title tag and put the most important ones first. Focus on keywords relevant to both your content and the words your target audience is likely to use in search.
3. Use Unique Titles
Each page on your website should have a unique title tag. Duplicate titles can hurt your SEO because search engines can become confused about that page’s intent.
4. Make It Relevant and Descriptive
Your title tag should accurately reflect the content on your page. A well-written title tag helps click-through rate (CTR) and can reduce bounce rate (the percentage of people who leave your site after viewing only one page).
5. Avoid Using Stop Words
When it comes to title tags, shorter is almost always better. Avoid using stop words like “a,” “an,” “the,” and “of” — these words don’t add any value from an SEO standpoint.
6. Don’t Forget About Branding
Make sure that your titles are branded by including the name of your company or website at the end of your title tags.
Here is an example of a branded title tag:
How to Perform an SEO Audit 2023 [Checklist] | Page One Power
Further Resource
Title Tag Optimization: A Complete How-to Guide
Meta Description Optimization
Meta descriptions are short summaries of a webpage that appear in search engine results (SERPs). They help users understand the subject of a webpage before they click on it.
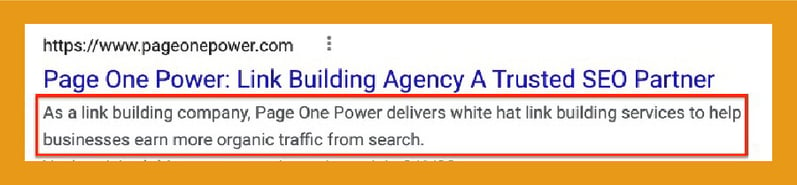
They aren’t an official ranking factor, but they still have a significant impact on click-through rates and should not be overlooked when it comes to on-page SEO.
Optimized meta descriptions are well-written, informative, and contain relevant keywords. If a user’s query is present in the meta description, it will appear in bold on the search engine results page. It is a great way to improve your website’s visibility.
Here is an example of a well-written meta description with relevant keywords:
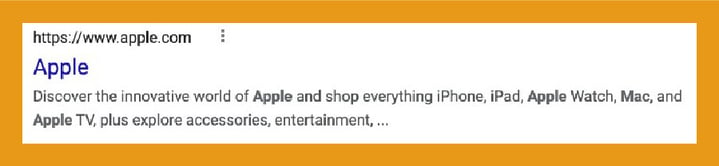
Meta description best practices include:
- Keeping your meta description concise with fewer than 150-160 characters.
- Highlighting the unique value proposition or key benefit of your website/product/service.
- Including relevant keywords (without being spammy).
- Including a call to action.
- Avoiding duplicate meta descriptions.
- Avoiding non-alphanumeric characters.
Further Resources
Control your snippets in search results
Image Alt Attributes Optimization
Image alt attributes, also known as “alt text” or “alt tags,” are HTML attributes associated with an image file that help search engines understand what’s in the image. They also provide a text alternative if the image is unable to load.
Here is an example of an image alt attribute in HTML source code:
<img src=“image.jpg” alt=“image description”>
Image alt text is also used by tools that make it possible for people with disabilities (such as visual impairments) to access the web. Screen readers are a perfect example; they convert elements such as images and buttons into speech, or braille for the user.
Consider the following best practices for image alt text:
- Be specific — try to keep it under 125 characters for screen readers.
- Use keywords (but don’t be spammy).
- Don’t add alt text to decorative images.
- Avoid obvious phrases “picture of” or “image of.”
Keep in mind that some images shouldn’t have an alt tag. For example, a background image is used for design purposes so it doesn’t provide any value to the content.
Further Resources
Google image SEO best practices
Accessibility: Image Alt text best practices
Header Tag Optimization
Header tags (also called H tags) (<h1>, <h2>, <h3>) are HTML elements that organize and structure content on a webpage. Header tags indicate the hierarchy of content on a page. This hierarchy helps users and search engines easily identify key topics on the page.
The most essential header tag is the H1 tag, which should accurately describe the topic of the page. Each of your <h2> is a subsection of the topic <h1>. An example might be if you are talking about different spaniel breeds, you would have the title wrapped in an <h1> then each of the <h2> would be a different breed.
Once you have the breeds listed, you may further talk about certain characteristics of each breed, such as temperament and diet. These would be headings for your <h3>.
Header tag best practices:
- The most important header tag is the h1 tag — your page title.
- Each webpage should only have one h1 tag.
- Use other tags such as h2, h3, h4, etc. as subheadings.
- Don’t skip subheadings. H3 should always come after h2.
- Use relevant keywords.
- Do not use header tags to make body text bigger or bolder.
- Make sure the content within your header tags is meaningful and relevant to the topic you are discussing.
- Avoid stuffing keywords into your headings as this can have a detrimental effect on SEO.
Don’t forget to use CSS instead of headers to style – this way you won’t compromise the effectiveness of those HTML elements.
Further Resources
Google-Headings and titles
How To Properly Optimize Headings to Improve SEO
Off-Page SEO Audit Checklist
The most important aspect of off-page SEO is backlinks. Whether you are trying to rank locally or nationally depends on the different types of links you are looking to build.
The different types of backlinks include:
- Editorial links
- Guest post links
- Resource page links
- Social media links
- Bio links
- Image links
- Industry-specific directories
- Local directories
Here are some tips on how to evaluate your links:
-
Check for relevance: Make sure that the link is relevant to your website’s content. If it’s not, search engines may see it as spammy.
-
Look at the authority of the linking site: A link from a high-authority site carries more weight than one from a low-authority site. Use tools like Moz’s Domain Authority or Ahrefs’ Domain Rating to check a site’s authority.
-
Check for quality: Links that appear natural and organic are more valuable than those that seem forced or manipulative. Avoid buying links or participating in link schemes.
-
Consider the anchor text: The words used in the hyperlink (anchor text) can also affect its value. Use descriptive, relevant anchor text rather than generic phrases like “click here.”
-
Get listed in local directories: Make sure your business is listed in all relevant local directories, such as Google My Business, Yelp, and Yellow Pages. These listings provide valuable information to potential customers and help build your website’s authority.
By evaluating your links using these criteria, you can prioritize which ones to pursue and improve your website’s SEO.
Further Resources
Beginners Guide to Link Building
Link Building ebook
Conducting an SEO audit takes time, patience, and some underlying technical knowledge — which is why many businesses employ an SEO company to help conduct the audit. Additionally, once you’ve implemented the elements in this guide, it’s important to review your site yearly, if not more. Search engine algorithms are constantly changing; making sure you’re in compliance will help keep your website at the top of the SERPs. Lastly, remember that some results take time. However, by taking the steps in this guide, you’ll be on your way to rising in the ranks.



