Reaching the top of the SERP requires hard work, time and effort, but it can become even harder if someone uses SEO against you. Bad actors can resort to dirty tricks to get your website penalized and throw you off the ranking ladder.
Let’s take a look at the most infamous negative SEO practices, how to react to each attack type, and which actions you can take to stay safe.
What is negative SEO?
Negative SEO means using black-hat SEO methods and practices against another site. These attacks can cause the victim site to lose positions in the search results, get penalized by search engines, or lose customers.
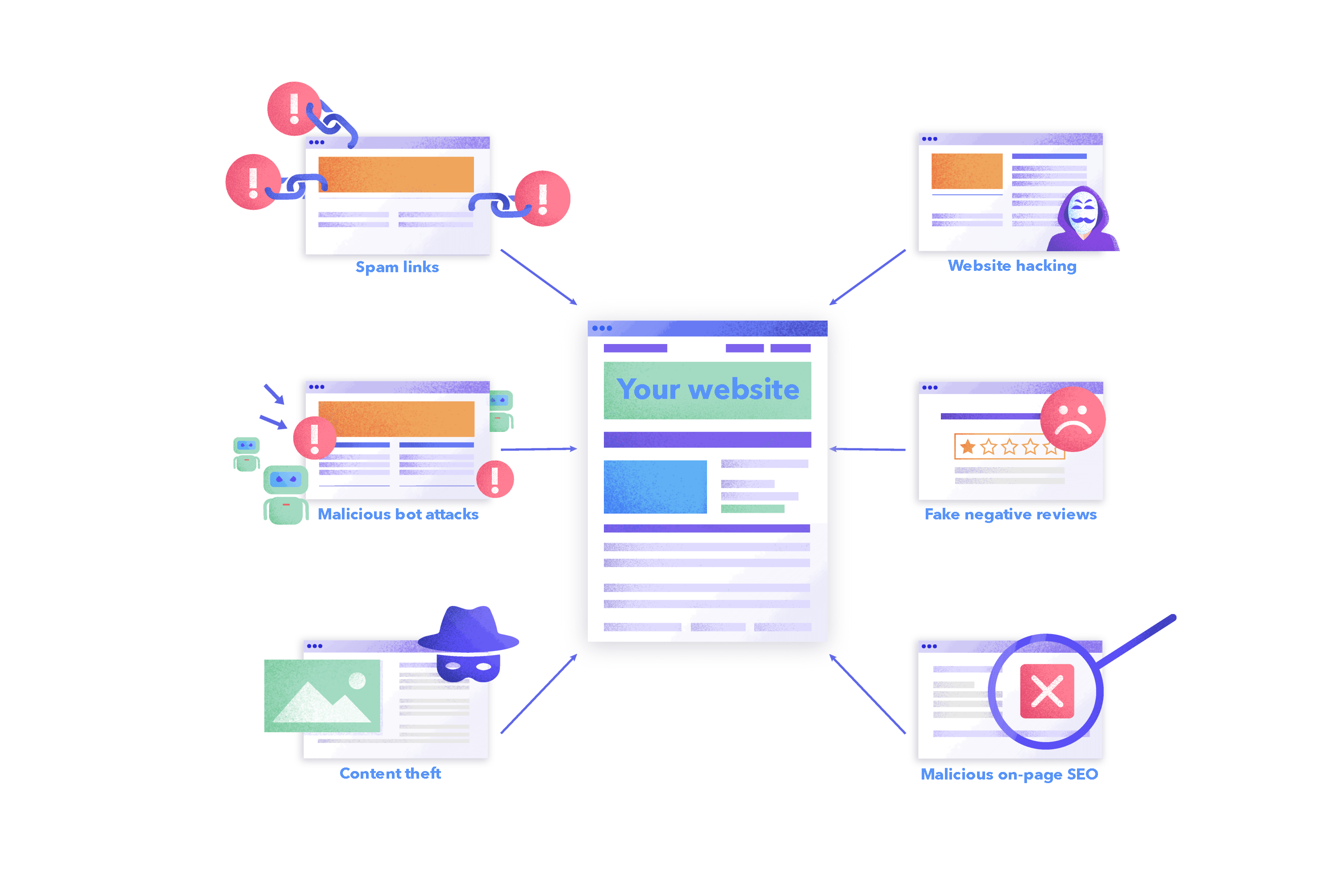
Unscrupulous players who use these malicious approaches can be found in any niche where there is a lot of competition. Small and medium-sized businesses and new sites suffer from negative SEO the most. Let’s take spam links as an example. Big and old sites with thousands of backlinks may not be as susceptible to, let’s say, a hundred new spam links, as a small or recently-created site that’s still trying to build its backlink profile.
Negative SEO techniques may be used by competitors who believe in the “all is fair in **** and war” rule. Your company’s current or former employees might even sabotage the performance of your website after being bribed or to take revenge.
There are also unintentional negative SEO cases. For example, an SEO specialist might use unethical tactics out of ignorance or lack of experience. But search engines don’t consider lack of SEO knowledge to be an excuse.
Types of negative SEO attacks
Like “positive” or traditional SEO, negative SEO can be approached in three different ways:
- Off-page
- On-page
- Non-website
See more details about each of them below.
Off-page attacks
These negative SEO attacks come from sources beyond your website. The attacker doesn’t have to have access to your site to commit these kinds of attacks.
The most common off-page attacks include:
Backlink manipulation
One of the most “popular” link-related tactics is attacking a website with spam backlinks. These links are often located on the so-called link farms or PBN (public blog networks) and lead to the victim’s site.
These attacks don’t just include two or three links, but hundreds and sometimes even thousands of them. It’s meant to be done on a massive scale.
Another component of a “successful” backlink manipulation attack is the anchor text. Malefactors usually follow two scenarios:
- They build numerous backlinks with identical anchor texts that contain the victim site’s target keywords (exact-match or keyword-rich anchor texts), usually from low-quality spammy domains. This sends a signal to search engines that the victim site is using manipulative link-building techniques. It also distorts the victim’s backlink profile by filling it with low-quality domains instead of reputable ones. This can lead to Google penalties and lower rankings.
- Attackers will also create backlinks with irrelevant anchor texts. Let’s say you run an online exotic plants store, but your competitors build thousands of backlinks pointing to your site with “fake bags” or “payday loans” anchors. They might also use keywords related to ***** content, *******, *****, etc. This is a common practice used in highly competitive niches, especially gray ones.
Some malefactors go even further. They may contact webmasters of the sites where you have high-quality backlinks and ask them to either remove your link or link out to another page—their own.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Monitor your backlink profile growth and look out for unusual spikes in backlinks.
- Check the quality of your backlink profile. The more quality links you have, the less damage attackers will do.
- Analyze the anchor texts used in your backlinks.
- Keep track of your most valuable links and be ready to react to any changes.
Here’s how to react to backlink manipulation:
- Reach out to the website owners whose pages include spam links to your website and ask them to remove them. This can be time-consuming if you are attacked by hundreds of spam links.
- Use the Google Disavow Tool to eliminate toxic backlinks pointing to your site. Make a list of toxic links that you can’t remove and submit it to Google.
- Contact website owners whose pages had important links of yours that were removed and ask them to put them back.
Content manipulation
Bad actors can copy the victim site’s texts and use them for their own purposes. They can either do it manually or use automated software (text parsing tools). This approach is called content scraping, allowing thieves to steal massive amounts of content.
If Google indexes pages with the stolen text first, the search engine will perceive them as original and rank them, while yours will be filtered out.
Another approach the attacker might use is to claim that the content on your site is stolen. Although this kind of attack is quite complex, risky and involves filing a DMCA complaint against you, the consequences can be pretty nasty if the attackers succeed.
Pages with falsely accused texts could be removed, or access to them could be disabled for some time. If this happens to an old blog post with little traffic, you might be able to live with the inconvenience, but if it happens to a critical promo page for a big campaign, you can lose precious traffic and potential customers.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Use plagiarism detection software like Copyscape or Plagiarism Detector, or the plagiarism feature in SE Ranking’s Content Editor.
- Set up your website code to disable RSS and restrict bot access to the XML sitemap (instead of putting the XML sitemap in a robot.txt file, you can send it directly to Google via Google Search Console).
- Use Google’s anti-scrape tool called reCAPTCHA Enterprise.
- Consider using Cloudflare Bot Management and Wordfence security plugins or Blackhole for Bad Bots if WordPress powers your website.
- Disable text selection using CSS styles.
- Set up Google Alerts for portions of your important content, and you’ll get notifications once it’s stolen.
If you’re sure your content is stolen, there are several things you can do:
- Reach out to the site owner and ask them to remove the stolen copy from their site.
- File a DMCA takedown notice to make Google remove the stolen content from the SERP.
Malicious bot manipulation
Malicious bots may not only scrape your content but cause click fraud and heavy crawling.
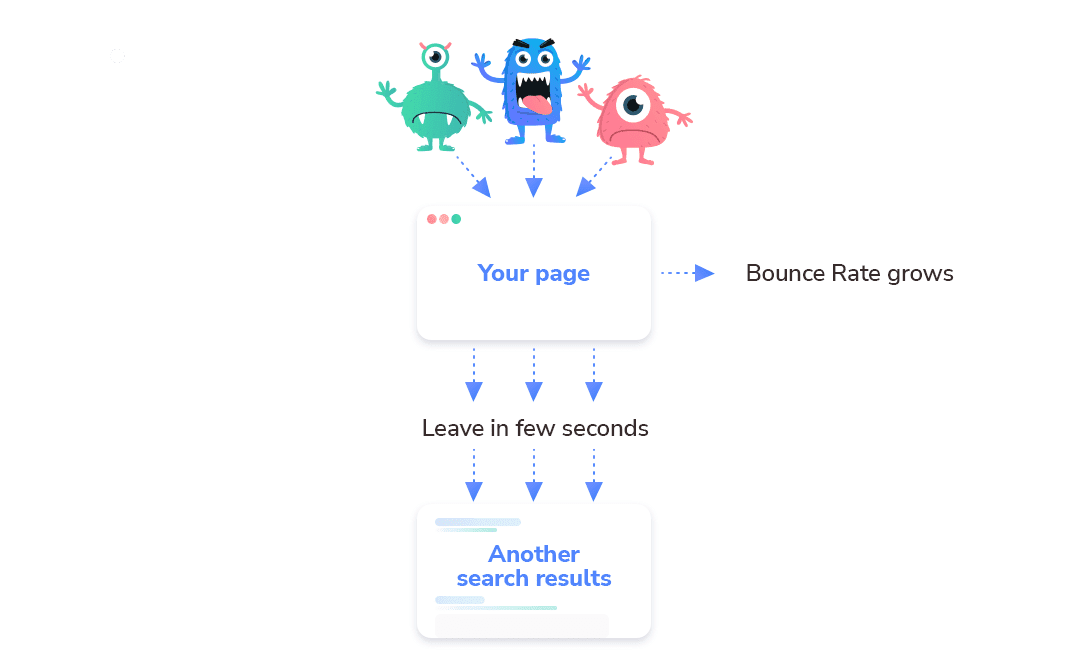
Click fraud means competitors are using bots to increase your bounce rate. This metric shows the percentage of site visitors who landed on a particular page of a website and left it without taking any action. These are not engaged sessions.
Malicious bots choose your page in the SERP and quickly leave it to check other search results. This prompts Google to think that users don’t find your page useful, causing you to lose rankings.
Heavy crawling is another negative SEO practice, where bad actors send numerous bots to crawl your website and increase your server load. This results in slower loading speeds and, in the worst-case scenario, leads to a website crash.
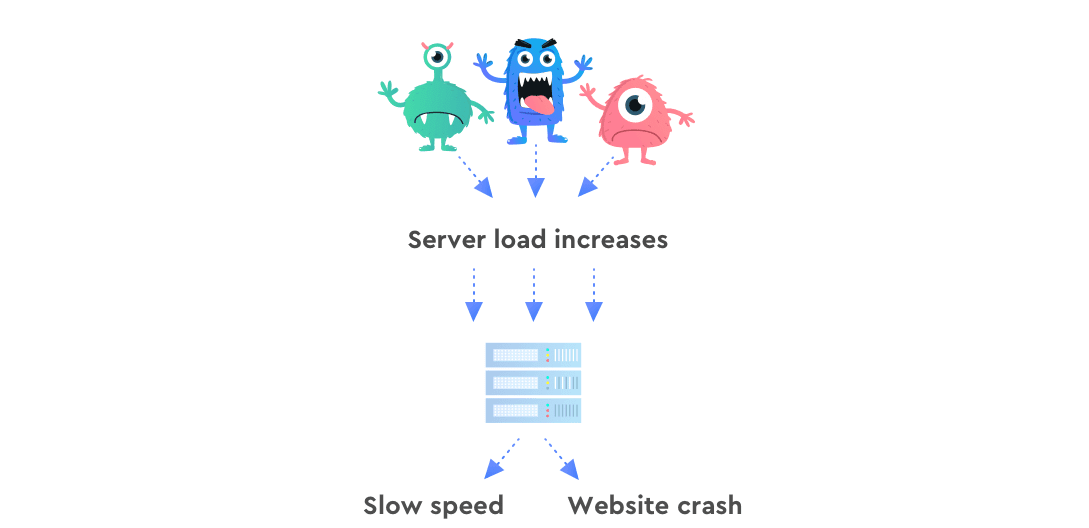
If your website crashes for a long time, Googlebot will eventually give up on trying to access and crawl it. The search engine will just kick your website out from the index so as not to waste its bot’s efforts.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Run your website pages through Google PageSpeed Insights to see its Speed Index.
- Use security plugins and protection like Cloudflare Bot Management, Wordfence, or Blackhole for Bad Bots, to protect your website from malicious bots.
- Check your site’s Engagement and Bounce rates in Google Analytics.
What to do if malicious bots attack your website and cause increases in loading speed and bounce rate:
- Try to block the malefactor’s activities with security software like paid WordPress plugins and Cloudflare protection.
- Remove resource-consuming plugins or add-ons.
On-page attacks
These negative SEO attacks usually involve site ******* and changing the SEO settings and parameters. This could be done by a hacker or a vengeful or outbought employee, current or former, who still has access to your site.
The most malicious threats in this category are:
Altering the robots.txt file
The robots.txt file contains recommendations on how to interact with your site. It specifies which pages you want the bot to crawl and index. An attacker can change your settings and make Google Bot ignore your important pages or even your entire website. Adding a Disallow: / rule to the robots.txt is all it takes.

Steps to protect yourself:
- Regularly check your rankings for sudden drops.
- Regularly check the Google Search Console Page Indexing report to see pages indexed and the reasons why some of them aren’t indexed.
If you know that some (or all) of your pages have been de-indexed due to this kind of attack (and it wasn’t some penalty from a search engine), immediately fix your robots.txt file and change your site’s credentials so that the attacker no longer has access to it.
Messing up tags
Search engines use tags to understand page content better and to determine where to include the page in search results. Some attackers will perform dirty tricks on the most critical SEO tags to decrease your site’s position in the SERP.
Malefactors can change the following tags of yours: <title>, <meta>, <img>, <header>, <h1> … <h6>, <footer>, <div>, etc. For instance, they may delete H1 tags or mess up titles and descriptions on your website’s pages. These elements usually contain the highest priority keywords, and deleting them can cause you to lose precious positions in search for a given keyword.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Run a website audit regularly to catch any tag issues.
- Check your most important tags to respond quickly to errors.
If you’re sure that your tags are out of order because of the attack, immediately change your site password and correct the errors identified during the audit.
Modifying redirects
Websites need redirects to send users and bots to relevant pages. For example, if the page has been deleted, changed its address, was closed for an update, or changed its protocol, you can use temporary and permanent redirects to transfer users to working pages.
If redirects are configured correctly, your site won’t have any problems. But if attackers have access to the site, they can redirect users to pages with irrelevant content or spammy websites, create redirect chains or loops, mix redirects and canonical tags, and much more.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Watch your rankings and traffic. They may suffer if your redirects are modified or disabled.
- Audit your website regularly to spot any problems with redirects.
- Check your website’s loading speed because redirect chains can lower it.
To prevent any negative on-page SEO attack, begin by setting a new and strong password. This will stop the attacker from accessing your site and will prevent them from making things worse or reversing your fixes. After that, double-check your redirect settings, adjust them so they work correctly, and then redirect visitors and bots to active and relevant pages.
Inserting outbound links
If your site was hacked, attackers can use it as a backlink source for the platforms they want to promote. What’s more, a hacked site can end up in what’s known as the hacked site database, causing it to become a spam link platform for thousands of other dishonest actors.
While outbound links aren’t a ranking factor, they still matter to your content’s EAT. By linking out to relevant sources, you’re confirming that the information you publish is reliable. This can make your content and website more authoritative.
Google’s John Mueller also explained that high-quality outbound links matter to your users.

John Mueller
Search Advocate at Google
Linking to other websites is a great way to provide value to your users. Oftentimes, links help users to find out more, to check out your sources, and to better understand how your content is relevant to the questions that they have.
Remember, what matters to users matters to Google.
But the key here is ‘high-quality outbound links’. Hacked websites don’t get these.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Audit your website to regularly monitor your outbound links because attackers can hide them carefully.
- Pay attention to the target domains of these links. It’s a bad sign if these domains aren’t related to your niche or business or aren’t even relevant to the content you publish.
If you notice questionable outbound links from your site, delete them. And, of course, change your website credentials immediately and make the new password as secure as possible to avoid potential hacks.
Non-website attacks
It’s not always necessary to attack your site from the outside or inside in order to lower your position in the SERPs. Attackers can use other channels to their advantage, like GBP.
If you want to rank in local search, your Google Business Profile should have accurate information and feature positive customer reviews. Fake negative reviews published by attackers can impact both your business’s reputation and its local rankings.
Steps to protect yourself:
- Secure your profile from potential hacks.
- Watch for massive negative reviews. You can’t please everyone, and there will always be negative reviews, but if you suddenly see a lot of them and they contain false information, your competitors are probably trying to ruin your business and its reputation.
Here’s your plan of action if your GBP profile is attacked:
- Flag fake reviews for Google once they’re spotted.
- Ask several people to report the fake review so it gets removed faster.
- Respond to these reviews to show your customers that all of the accusations are false.
Have a WordPress website? Be doubly careful.
W3Techs reports that 43% of all websites on the internet are powered by WordPress, making it the most popular CMS right now, but this doesn’t stop hackers. On the contrary, it pushes them to action. In 2021 alone, more than half a million WordPress sites were attacked.
Another two reasons why WordPress sites are often attacked are:
- The website uses an outdated version of WordPress. If you don’t update the CMS when a new version is released, you don’t get access to new features, including security improvement updates.
- Many WordPress plugins and themes have vulnerabilities, especially free ones. The WordPress repository is constantly growing, and not all plugins can be of high quality. Some of them have security loopholes, while others are outdated.
The top 5 malicious software infections that WordPress sites can suffer from are:
Backdoors
This negative SEO technique is when hackers access and damage your website through some entry point. Backdoor attacks usually occur due to outdated software or loopholes in your website’s security. Sometimes, they use default passwords. However, the solution is simple: close the backdoor that the hacker used to attack you. Limiting access to your site’s environment and making it hard to penetrate can help prevent future attacks like this.
Drive-by downloads
This is when attackers inject links into your site, causing visitors who click on them to download all kinds of viruses or software that pose a threat to their devices. Hackers have the highest chance of succeeding here if you have outdated software, weak or compromised credentials, and SQL injections.
Pharma hacks
Hackers insert links into your website that redirect visitors to various pharmaceutical company websites. They do this to get traffic, reach the top of the SERP and make a profit. These attacks can be hard to detect because malefactors can use conditional rules to control what the user sees.
Malicious redirects
This is another attack aimed at getting more traffic. The hacker redirects your site’s visitors to scam, spam, or other malicious sites containing the automatically downloaded payloads. Such attacks can also happen if the site is running an outdated version of WordPress or if access to the environment has fallen into the wrong hands.
SQL injections
An SQL injection attack attempts to gain unauthorized access to your site’s database, which stores all of your content, links, users and their information, etc. If they succeed, they can do whatever they want. For example, hackers can delete your database, insert malware into it, steal data, control user accounts, and much more.
How can SE Ranking help?
After everything you’ve read, maybe your first instinct is to panic. But don’t. These attacks can be easily detected and corrected with the right software.
SE Ranking has over 30 tools that make traditional SEO more effective, but you can also use them to spot negative SEO attacks and their consequences.
Keyword Rank Tracker
Our keyword tracker will help you discover sudden drops in rankings, as well as drops out of the index in any location, device, or language.
You’ll be able to work with a ranking table after creating a project. With it, you can then compare rankings and track how your site’s positions change across different search engines and time periods.

Ranking changes will be marked with a specific color and an arrow pointing in the respective direction.
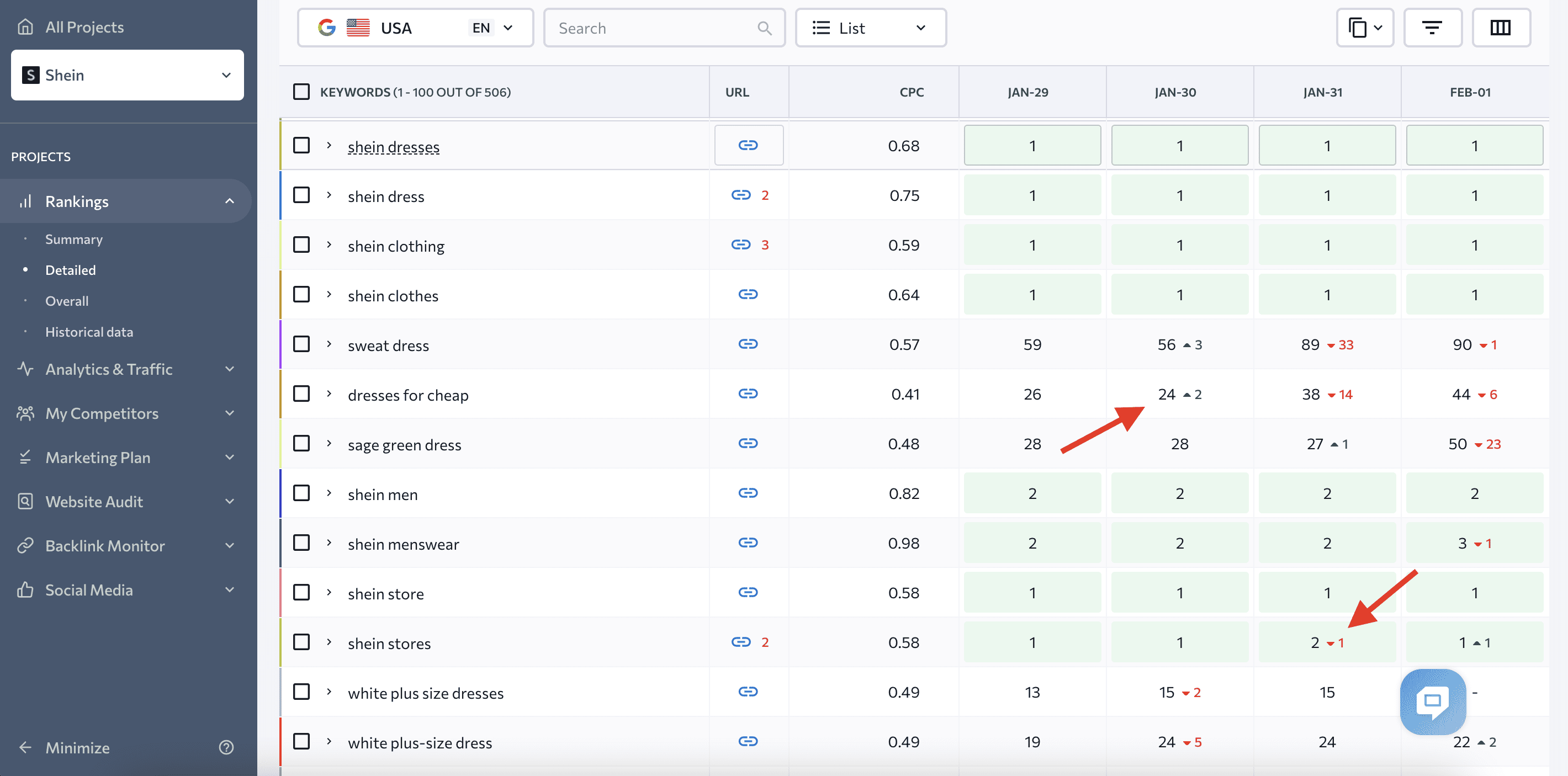
If you want to analyze ranking dynamics for a certain keyword, click on it. You’ll see the chart where you can choose different time periods.
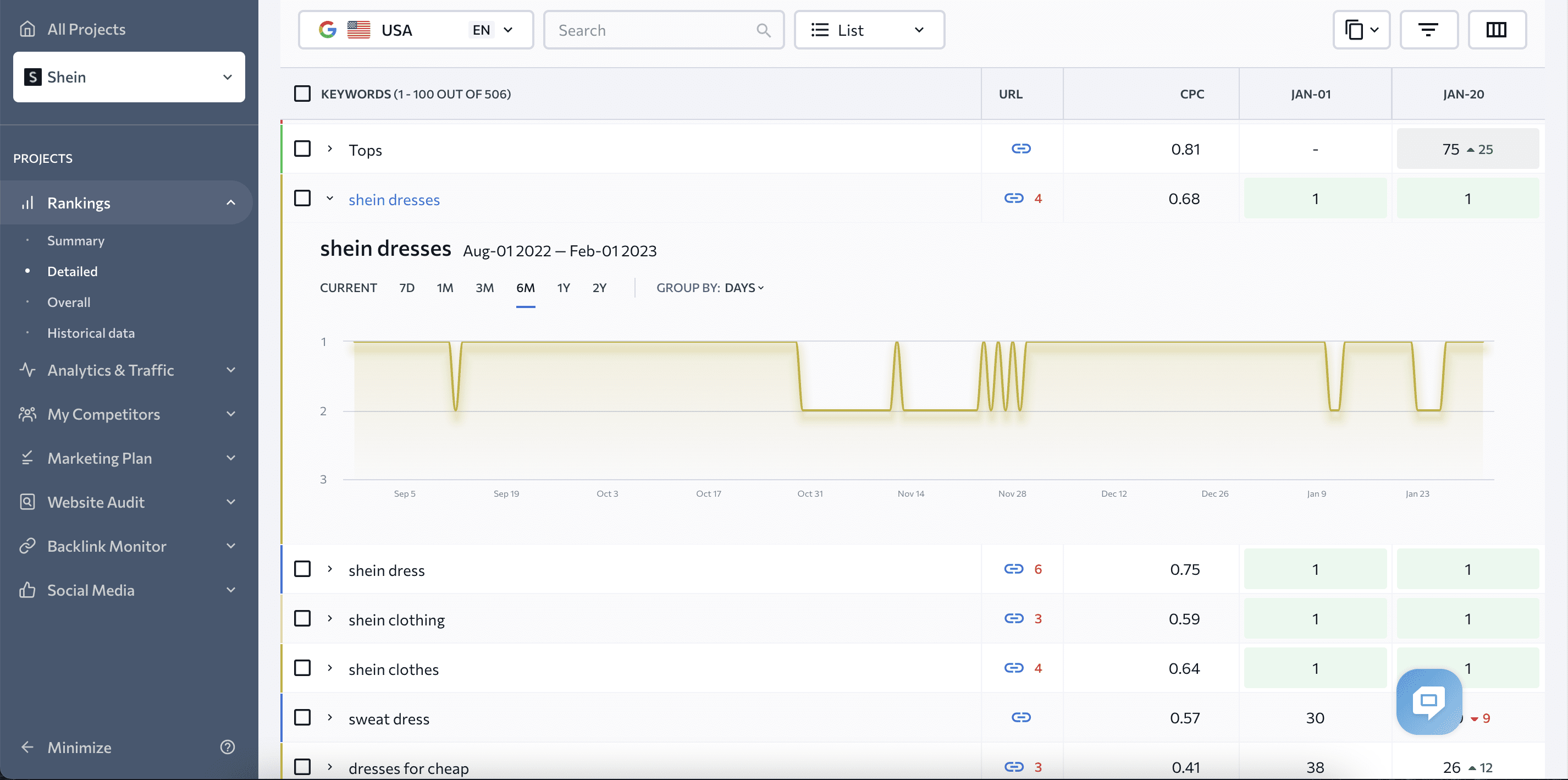
You can also set the target URL for a keyword that is important to you and monitor other pages that rank for it. This will help you identify content cannibalization issues or potential theft.
Backlink Checker
This tool finds each and every backlink pointing to your website and analyzes them. It looks at the referring domains they came from and the anchor texts used, according to multiple parameters. All of this aids in detecting backlink manipulation.
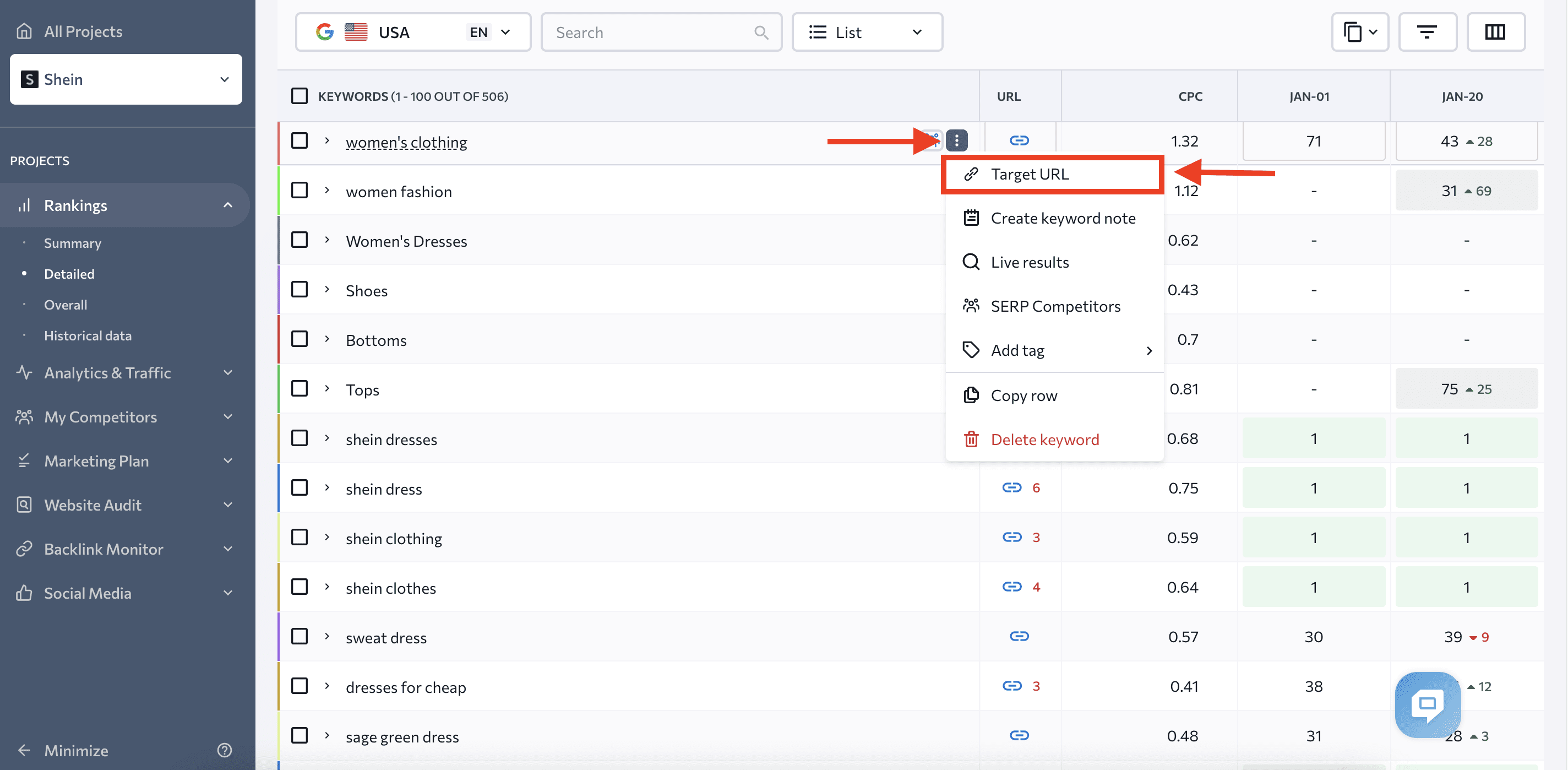
You can find Backlink Checker in the drop-down menu under the Backlinks section.
Once you scan for backlinks, you can look at them from various angles to identify possible manipulations.
First, you can check the quality of your website’s active backlinks. You’ll get a list of all links along with their:
- Backlink anchor text. See if the wording used is relevant or doesn’t precisely match your target keyword. Correlate your anchor texts with Domain Trust and other link metrics to see who is linking to your website and how they’re doing it. Pay attention to keyword-rich anchor texts from low-quality, spammy domains.
- Domain and Page Trust scores. See how authoritative the linking domain and page are.
- Address of the page. This is where the backlink is located. Check how relevant this page’s content is to yours.
- Backlink target page. This page is located on your website. Check it again to make sure it’s relevant and the linking is natural.
- Backlink type. Check to see if the link is dofollow or nofollow, or if it is featured in a text or an image.
- First and last seen dates. Check these to see when the link was last found and checked.
You can also monitor new and lost backlinks to respond quickly to an unusually large appearance or loss of backlinks. The following screenshots show the kind of spikes in backlink gains and losses to look out for.
To check the quality of domains linking to your website, go to the Referring Domains tab. Here, you’ll see the:
- Summary of all referring domains (1)
- List of all domains linking to your website (2)
- Domain Trust score (3)
- List of all backlinks coming from that domain (4)
- **** of discovery of the referring domain(5)
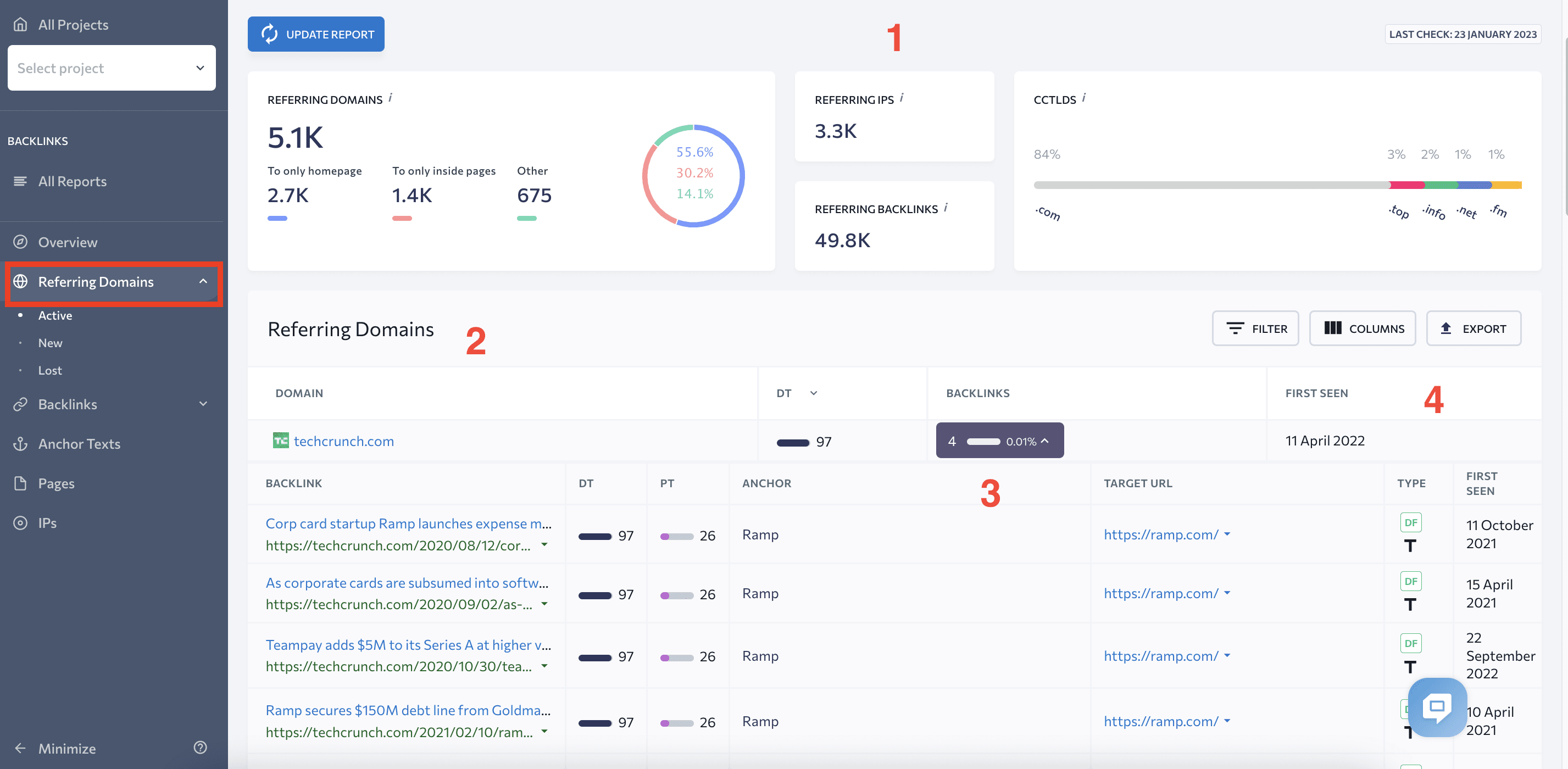
This tab also provides data on new and lost referring domains, as well as the dates when they started or stopped sending backlinks to your site.
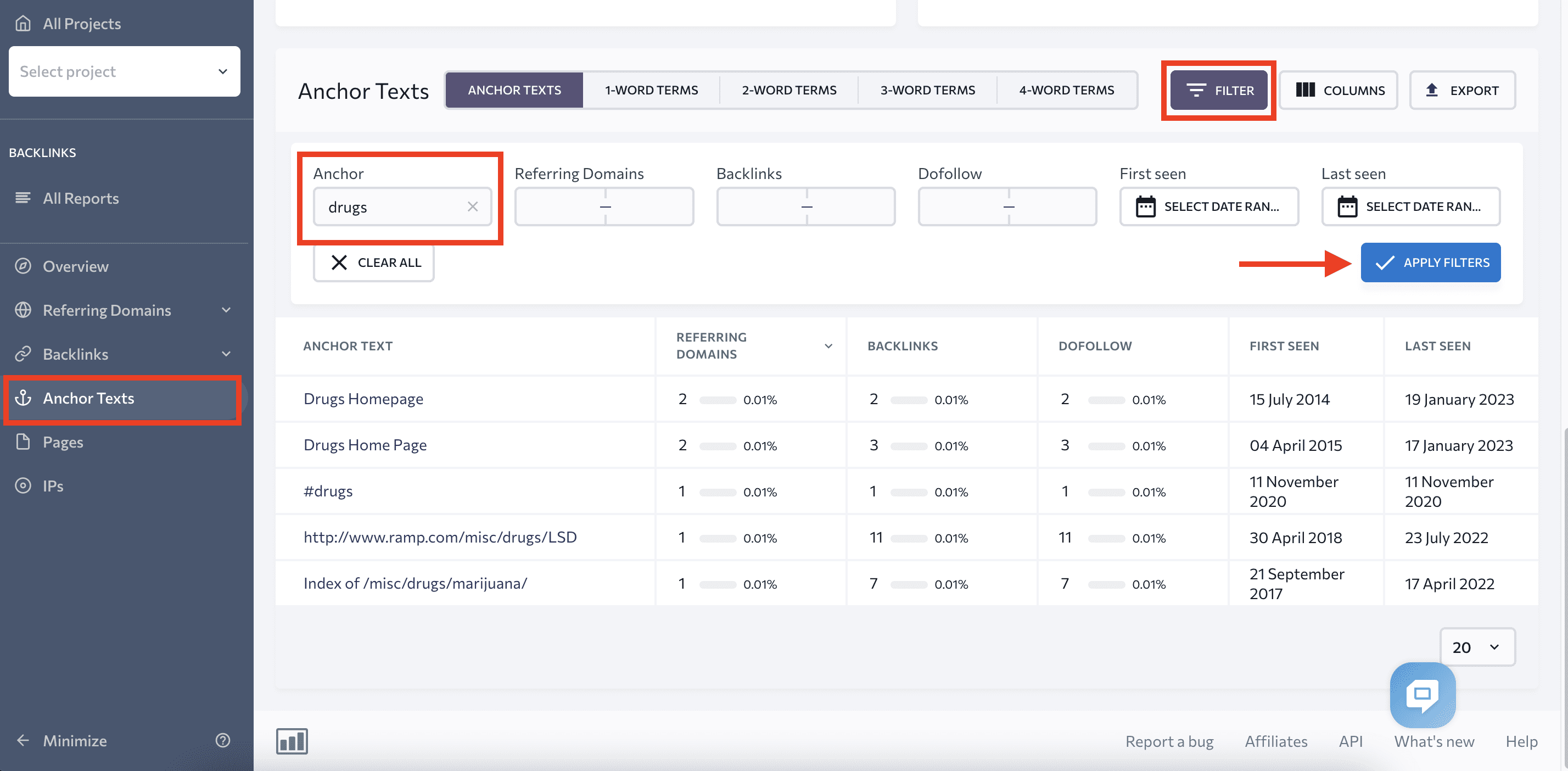
If you have concerns about anchor texts, we recommend checking them with the Anchor Texts tab. You can use filters to find keyword-rich or spam anchor texts and determine whether they are or aren’t the result of a negative SEO attack.
To do this, type in the word in the filters, as shown in the screenshot below. You’ll get a list of all anchor texts containing that word and the backlinks using them.
On-Page SEO Checker
If you have suspicions about content theft, On-Page SEO Checker will help you identify the thief.
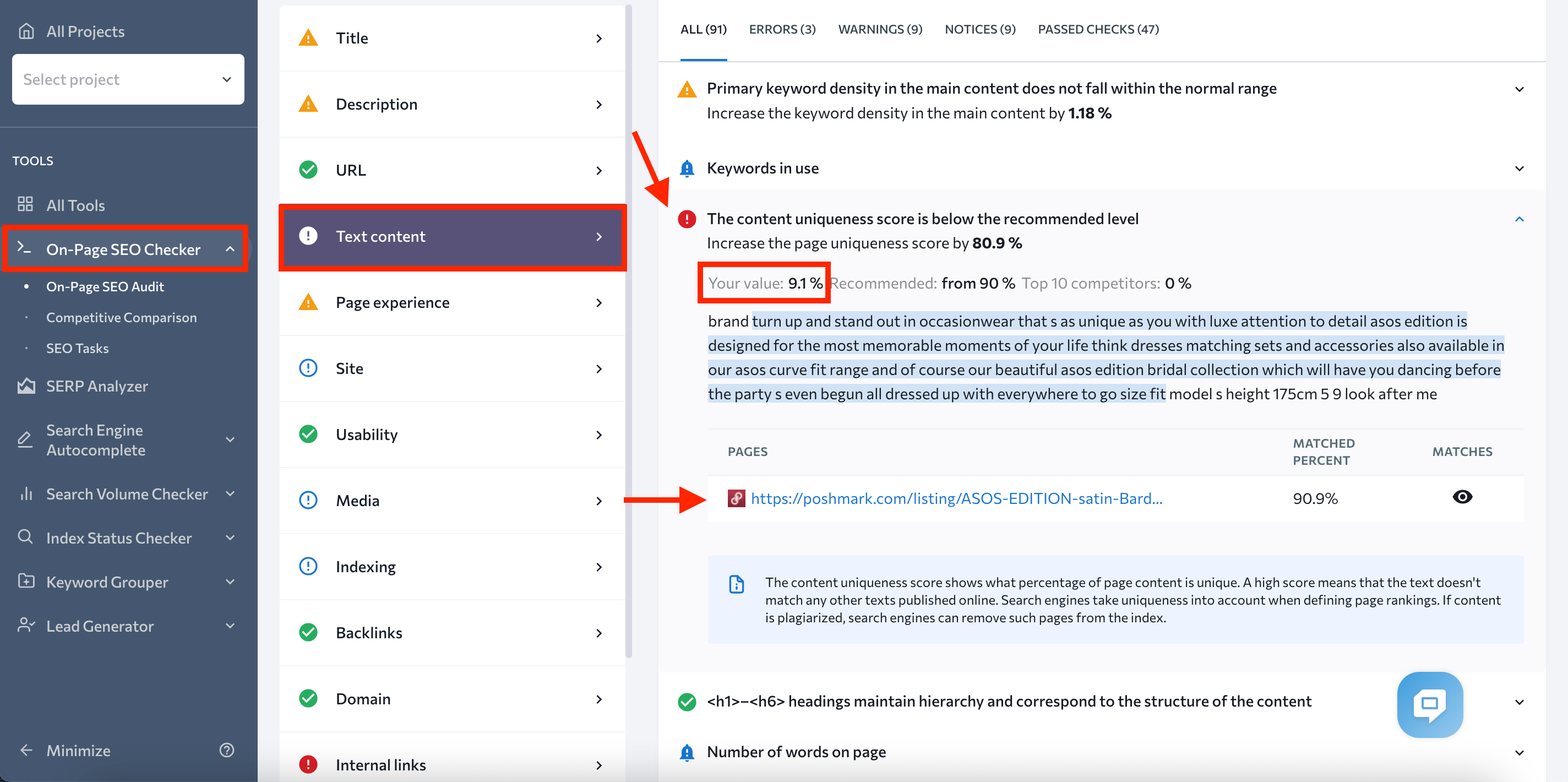
Let’s say you’ve noticed that some of your pages have dropped in rankings. One of the reasons could be stolen content. Insert the URL into the On-Page SEO Checker and run an audit to put your theory to the test. In a matter of seconds, you’ll receive a full report, including a uniqueness analysis.
Check the content uniqueness score by choosing Text Content in the Issue report, which is located lower on the Overview page. You’ll see your text’s uniqueness value and highlighted parts that match other pages.
If your score is lower than 70-80%, look at the pages matching your content. You may find a site that scraped your content and posted it as theirs.
Website Audit
This tool will evaluate your website based on 120+ criteria and notify you of any SEO/content issues. It will help you detect problems that can result from negative SEO attacks on your website’s:
- Security
- Crawling and indexing
- Speed
- Redirects
- Internal and External links
- Tags
- Content
To detect errors in time, you can customize the audit schedule and set up email notifications. Just click on the gear icon in the top right corner of the Website Audit module to access settings.
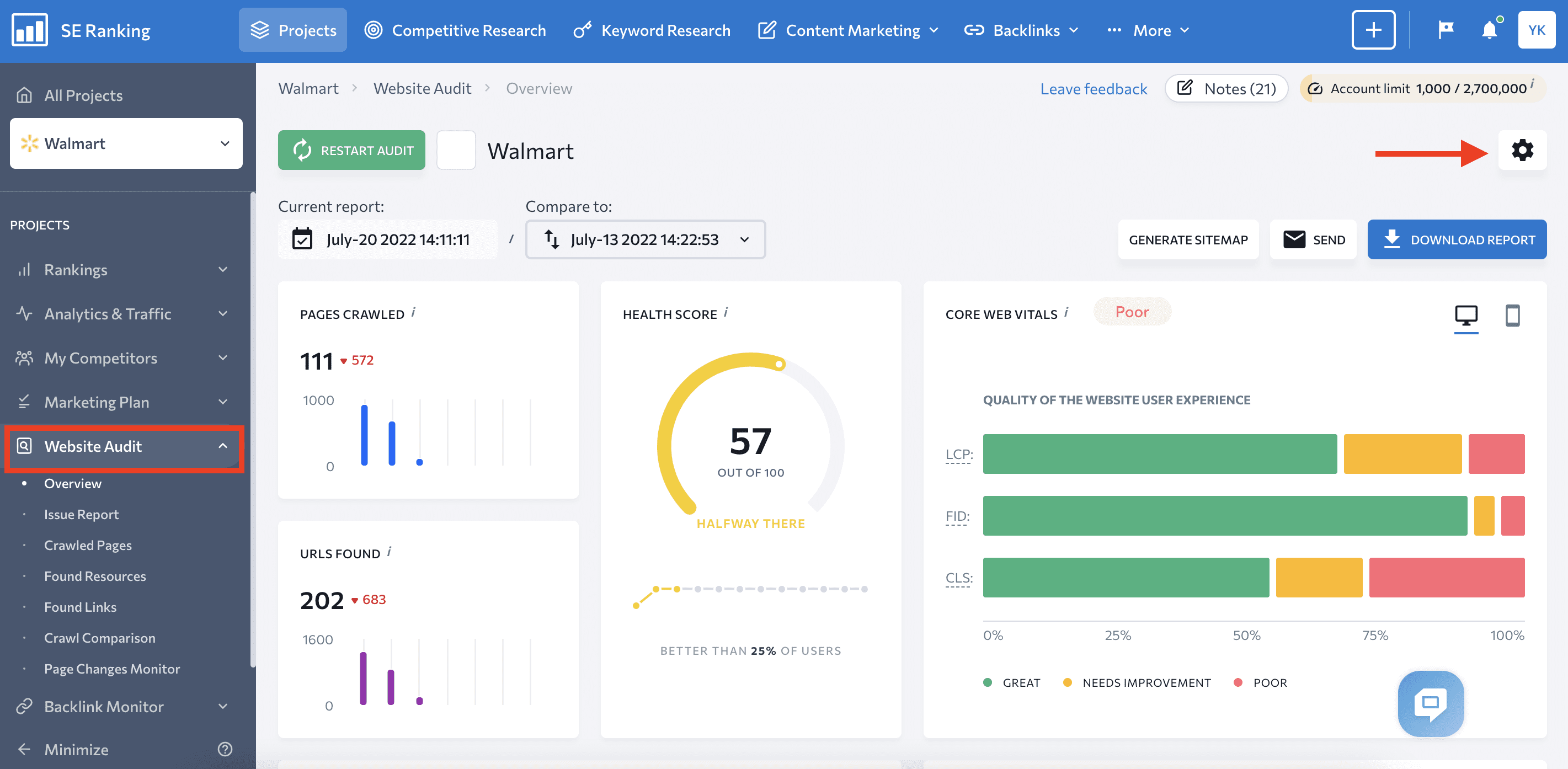
Choose the Schedule tab, decide how often you want your site to be audited (monthly or weekly), and select email to get notifications.
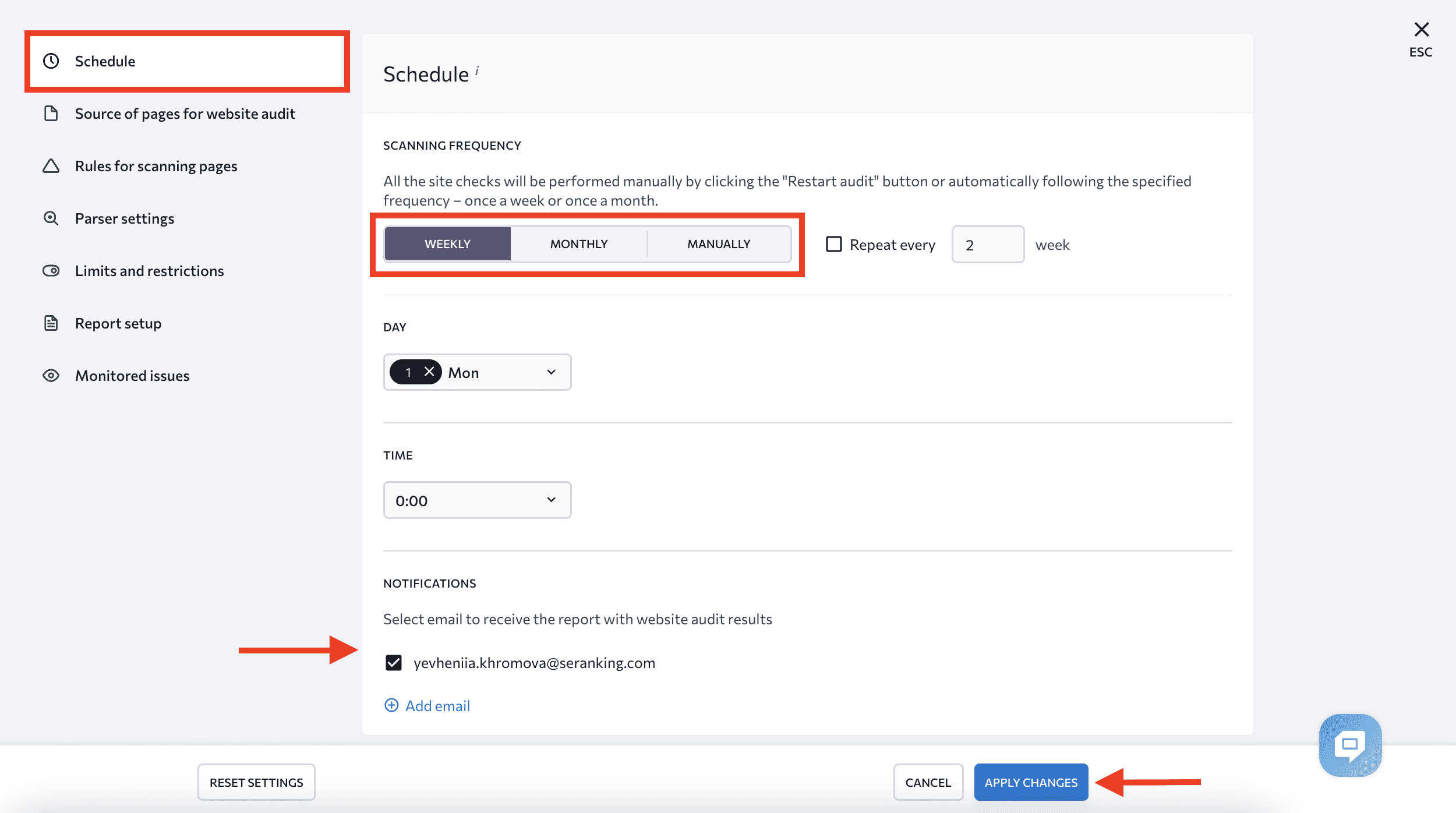
You can also choose which checks you want to run. Possible negative SEO attacks were already identified, so you can customize the audit accordingly. Choose Monitored Issues and enable or disable them using the toggles near each category and check marks near each issue.
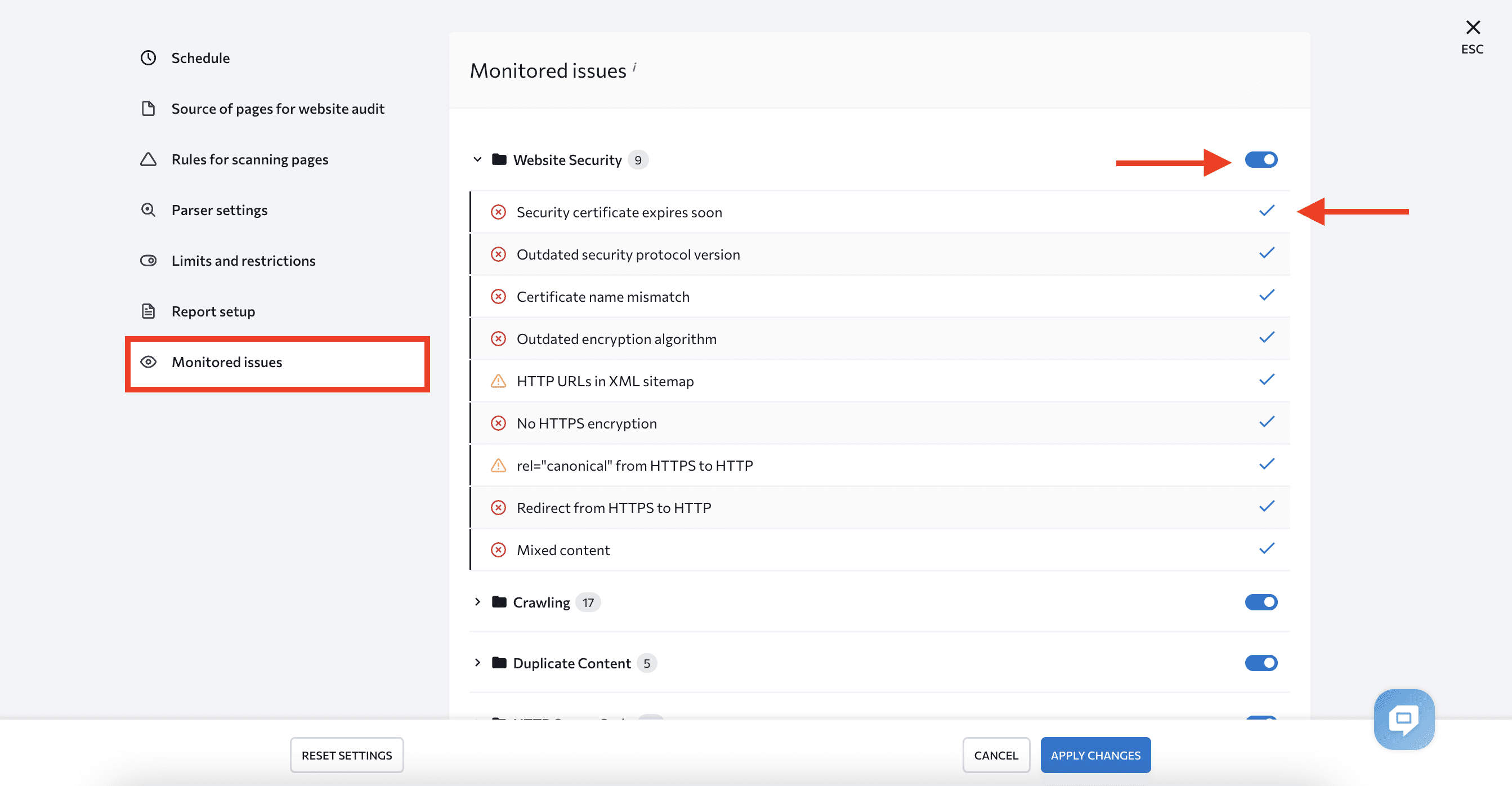
The Issue Report shows all the problems detected. Each error has a special mark indicating its severity, as well as an issue description and tips for fixing it.
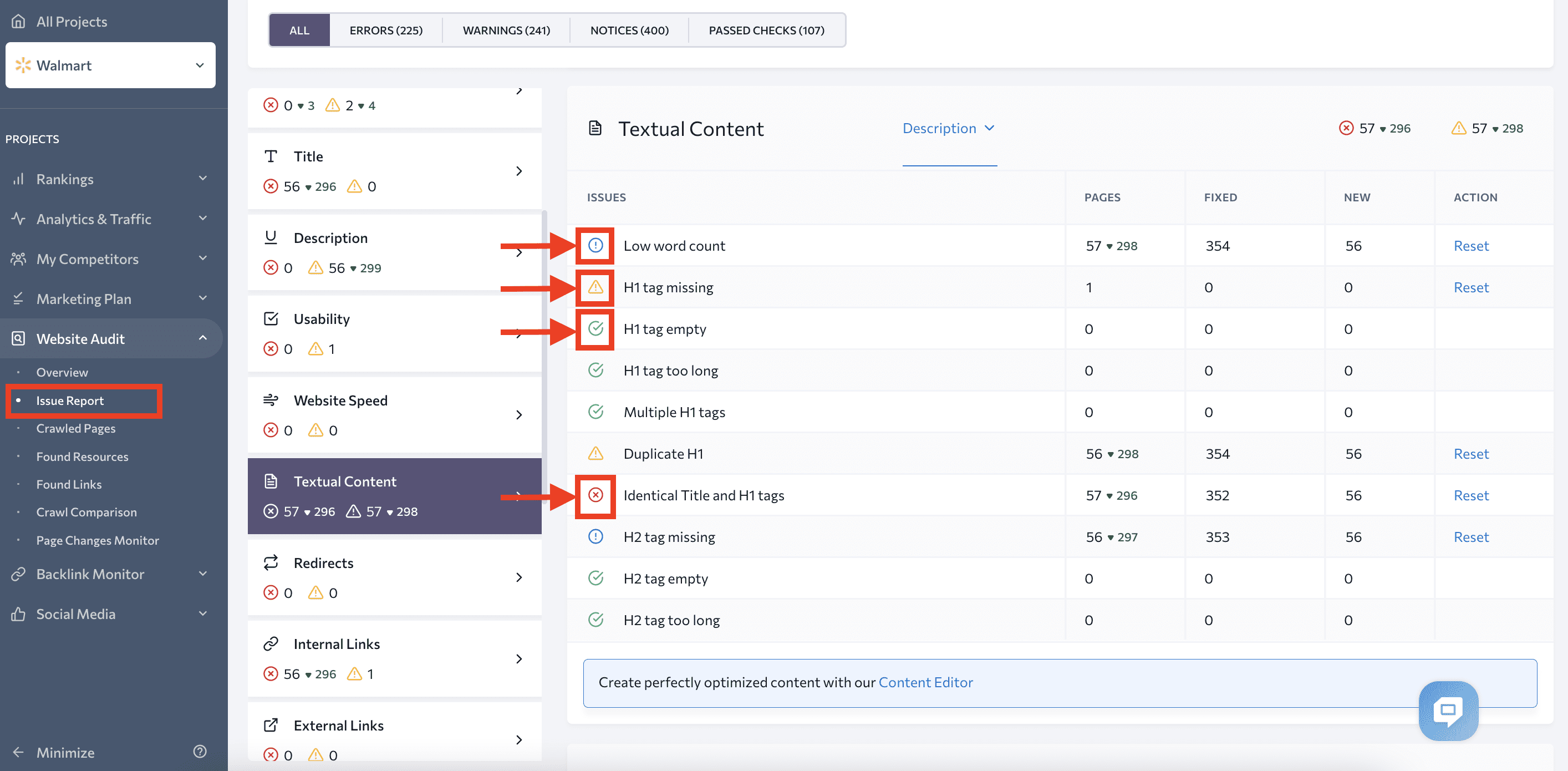
If you have concerns about harmful internal and external links, check the Found Links section to see every link’s status code, type, source URL, and its anchor text.
Page Changes Monitor
This feature (located within the Website Audit tab) deserves special attention. It allows you to monitor any changes made to your most important pages. When a change occurs, you’ll get an instant notification and will be able to respond immediately. This is super helpful if you suspect your website has been hacked and that someone has tampered with its content and SEO settings.
You can find the Page Changes Monitor in the left-hand vertical navigation bar.
Add any pages that you want to monitor, specify frequency, and mark changes to track, such as:
- HTTP code
- Title and description
- Keywords
- Canonical URLs
- Content
- Robots.txt
- Internal and external links
- Etc.
How to protect your website from negative SEO
We’ve already advised you on how to protect yourself from different attacks, but the following tips are the master key for avoiding negative SEO.
Perform checks regularly
Remember that no matter how well you protect your site, regular checks are still one of the most reliable ways to catch negative SEO attacks and protect your website. It’s best to perform a website audit to detect security, optimization, and content issues. Keep track of your backlinks and any sudden increases or decreases in their number.
If you are aware of your weak areas, check them more often. If you have already been the victim of a negative SEO attack, make the subject of the attack a priority in your subsequent checks to prevent history from repeating itself.
Keep your CMS and plugins updated
Outdated CMS and plugins give attackers a loophole from which to **** your site. Once they have access, they can do whatever they want, so you must update your environment regularly.
You can set up automatic updates or do it manually by following the notifications. This is a quick procedure and can save your site from significant problems in the future.
Set up a strong password
A strong password contains:
- Uppercase and lowercase letters
- Numbers
- Special symbols
Some systems, among other things, specify a minimum and maximum password length. If you don’t follow them, you can’t save the password. But even if there are no system restrictions and recommendations, you shouldn’t take creating a password lightly. If it’s too easy to crack, attackers can **** it and gain access to the site.
Other tips for creating a strong password:
- Don’t use personal information in the password.
- Don’t use passwords you’ve already used before.
- Don’t share your passwords.
- Don’t use sequential letters or numbers.
We also recommend using two-factor authentication if available. The hacker will have to jump through another obstacle even if they manage to steal or crack your password.
Set up GSC email alerts
Google Search Console can send you email notifications after detecting issues with your website. Some of the issues it detects include malware attacks, indexing issues, connectivity problems, or Google manual penalties. If you set up email alerts, you can respond quickly to any problem.
Begin by opening GSC and clicking on User Settings. Choose Email Preferences. Next, turn on email notifications and choose to receive alerts for all types of issues.
Are negative SEO techniques ever worth the trouble?
It depends.
Succeeding at negative SEO is a matter of time, money, and other resources. Even if the attacker has an unlimited supply, the outcome may only be significant on rare occasions.
- Google is smart enough to recognize such scams. It is especially good at distinguishing high-quality backlinks you create from low-quality ones that come from nowhere. For this reason alone, it may not be worthwhile for malefactors.
- The success of the attack depends on the optimization level and quality of the victim site. It takes a lot of effort to cripple a large site with high-quality content, a strong backlink profile, and professional optimization. Sites like these evolve and improve every day, and attackers may find it difficult to do enough damage to outweigh the site’s current quality.
Not to mention that if the attacker is identified, they may face serious legal consequences.
Google can detect negative manipulations, but this won’t always stop them from having an impact. This holds especially true if it is a new type of attack that Google has never encountered before. It won’t yet know how to catch it.
Sabotage can also work if the site hasn’t developed a reputation yet and lacks sufficient content or backlinks. An attacker can easily stir the pot after identifying a weak point.
In any case, informed means armed.
You can fall victim to a negative SEO attack no matter:
- What niche you work in
- How old or young your site is
- How often you post content
- How many backlinks you have
If the attackers have a goal, they’ll achieve it by any means, and search engines cannot always protect you. However, now that you know of the various negative SEO methods and how to respond to them, attackers can no longer take you by surprise.
Closing thoughts
While negative SEO is time-consuming and doesn’t always bring malefactors their desired results, it can still damage your website and rankings. Attackers can bombard you with spammy links or negative reviews, but it’s even worse when they **** into your site and mess with your SEO settings. Sadly, there will always be people out for a quick buck who will try to drag you down by using unethical means.
The good news is that Google is constantly improving its algorithms to make sites more resistant to all kinds of manipulations. You also know now what you can do to avoid being harmed by dishonest competitors.
Please know that we also have your back. SE Ranking is always here to help you.
We suggest always starting with a site audit. If you’re using our platform to run checks on your website, we’d like to know if you’ve ever been a victim of negative SEO. Tell us in the comments below what kind of attack it was and how you dealt with it.



