Posted by
Darrell Mordecai

People Also Ask boxes have been around forever.
What’s more, they are everywhere.
I mean, they appear on around 70% of desktop search results.
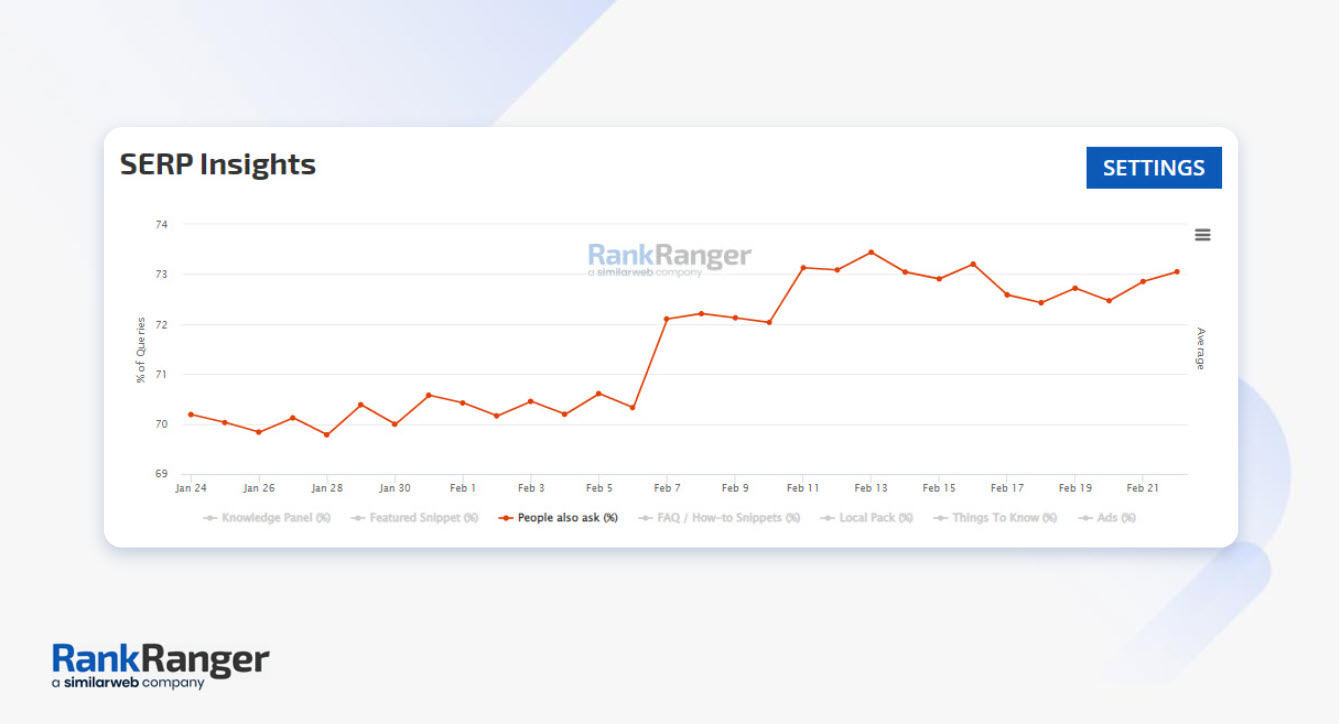
So the question is…
How can you use People Also Ask boxes to boost your SEO? Can you use them to bring targeted traffic to your site?
In this blog post, I’ll get into how to rank in Google’s People Also Ask boxes. I’ll first cover how the feature works and then get into the strategy and tactics for ranking in PAA boxes.
What is Google’s People Also Ask?
Google’s “People Also Ask” (PAA) feature presents a list of questions that are related to the original query and may be of interest to the user. These questions are usually presented in a drop-down format, allowing users to expand the list to view additional questions and answers.
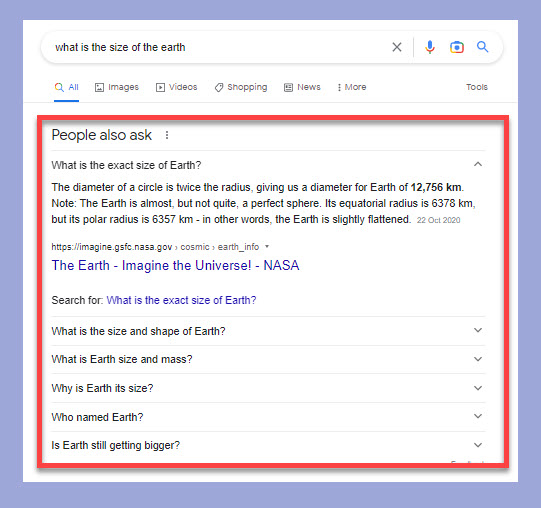
The PAA feature uses machine learning algorithms to analyze search queries and identify common related user questions. The questions generated are topically related to the user query and rank based on relevance and popularity.
The feature updates in real-time providing the most relevant and up-to-**** information to users.
How Do PAA Boxes Serve the User?
Google is constantly looking for ways to improve its user experience.
One way is to help refine the questions you type into Google because the better you can word your query, the better the search results will be.
In other words, the People Also Ask feature is not trying to serve better answers. It’s helping you ask a better question.
Because, in order for Google to bring a relevant answer, Google’s Natural Language Processing algorithms analyze your query. But Google doesn’t always get this right.
The reason is, there might be slight semantic differences in how you ask your query. Slight semantic differences might result in dramatically different search results.
To help you out, Google presents the People Also Ask box, which lists queries related to the general topic of the search.
A Google patent speaks this out:
‘Providing related questions to users can help users who use un-common keywords or terminology in their search query to identify keywords or terms that are more commonly used to describe their intent.’
In simple English…
If you search for something using unusual language you might not find the results you need. To solve this, Google suggests a list of common queries that users have made in the past.
Now to truly understand this, let’s take a deep dive into how Google understands a search query.
How does Google process a Search Query?
Allow me to illustrate.
Shortly after the Queen died, I searched Google for Prince Charles. At the time I noticed that Google had updated the title of the Knowledge Panel to ‘King Charles’.
What’s interesting is, Google understood that the query was actually about the entity Charles III (and not about Prince Charles).
This is the hallmark of a semantic search engine. It attempts to understand the entities in the query and not just the series of characters that make up the query string.
Since Google understood that my query was about Charles III (the monarch), Google was able to bring me new updated information.
This must mean that Google analyzed the search query before trying to match the query with any content.
Let’s explore the topic.

When you search Google, it tries to understand the meaning behind the query.
This means:
- Identifying known entities
- Looking for synonyms
- Analyzing the context within the query
- Understanding the general topic of the query
In our case, the known entity is Charles III.
Perhaps my query ‘Prince Charles’ is a synonym?
Since the query only included the words ‘prince charles’ there is no context that could change the meaning of the query.
Just to be clear…
Context refers to how the words are put together, because…
When words are put together, their meaning often changes.
To illustrate the point with 2 different queries…
🚚 gm trucks
🌽 gm corn
What does ‘gm’ mean?
In the first query, it refers to General Motors.
In the second query, it refers to Genetically Modified.
Google uses context to figure this out.
And, since my query consists of two words (prince charles), there really is no extra context.
Now that Google has a basic ‘understanding’ of the query, it attempts to understand the topic the query is about.
This step is crucial in creating People Also Ask boxes.
Here’s why…
Google has a database of previously submitted queries. The database is arranged into topics and the user’s query is matched with one of these databases. This is done by matching the topic in the query with the topic in the database.
Google identifies the topic you are asking about. If users over time have written common questions about that same topic, Google will have a database of questions for your query.
Once your query is matched with the relevant database, Google then has to decide what queries to show in the PAA box.
Queries are ranked in two ways:
- How frequently the queries have been asked by users
- How often users select a search result after submitting one of these queries
And that is how People Also Ask boxes appear in search results.
We now understand how Google understands queries and also how Google matches search queries with a database of ranked queries.
Now let’s get into how to optimize for Google’s People Also Ask boxes.
People Also Ask SEO: How to Rank Your Content
Now before I get into the tactics and data you need to rank in the People Also Ask boxes, let’s discuss the general strategy. Because, when it comes to SEO, there are a near-infinite number of tactics you can use.
To save yourself from burning out, build a strategy that brings your business the biggest gains in the shortest period of time.
Once you’ve done that, you can move on to other opportunities.
People Also Ask boxes can potentially give your site targeted quick wins that take minimal effort to implement.
In a recent interview with Jason Barnard, Jason explained how he used the PAA box to help one of his clients expand their brand reach.
This strategy works if there are PAA questions about your brand. (Later I’ll cover what to do if there are no questions about your brand.)
The strategy is simple.
Type your brand name into Google and take a look at the PAA box.
Are any of the People Also Ask questions about your brand? If there are, it’s crucial that your brand features the answer to all of those questions.
If it doesn’t, that means a different brand features on your branded keyword and could potentially win clicks away from your site.
And your best prospects are the ones that are typing your brand name into Google. Don’t give them a chance to visit your competitors.
This means you should feature an FAQ section on your site that answers all of the questions that are showing up about your brand. (I’ll explain exactly how to do that later on in the post.)
Once you’ve answered all of those questions, check your brand keywords periodically. If any new questions are showing up, answer those questions also.
If you want to see what other questions Google is suggesting about your site, try Googling all the questions that appear on the PAA box on your brand SERP. You might find more questions either about your brand or related to your industry.
Make sure to answer all of those questions on your FAQ on your site.
Once you’ve answered any and all questions about your actual brand, or if there are no PAA questions about your brand then focus on answering all questions related to your niche.
This is an ongoing process that can result in quick wins.
Especially on branded queries.
Now that we’ve covered the high-level strategy, let’s get into specifics.
Find PAA SEO Opportunities
As I mentioned above, the first queries you should rank for are branded queries.
Once you’ve collected a list of branded keywords, move on to niche-related questions.
To do this, look in your rank tracking tool for keywords where your URL is ranking on the SERP but only your competitors are featured in the PAA boxes.
As you can see from the screenshot below, the Rank Ranger Rank Insight report for allrecipes.com shows a list of SERPs where only competitors are showing up in the People Also Ask boxes.
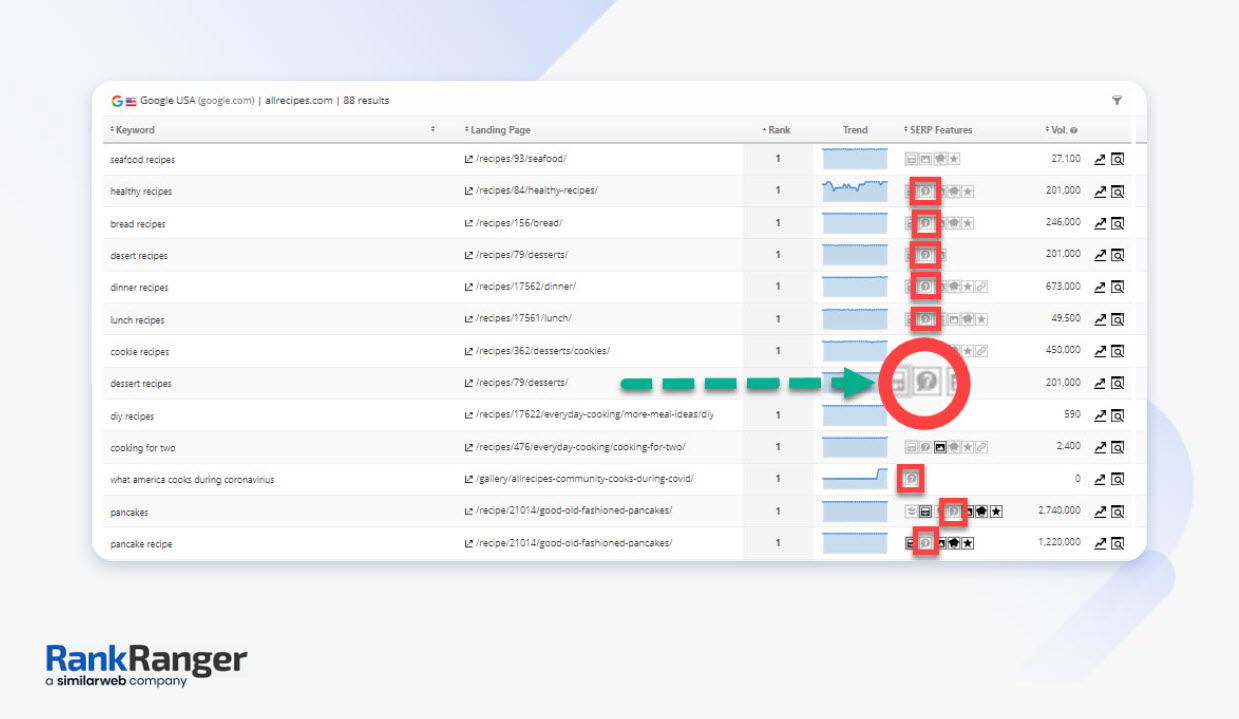
But, allrecipes.com is ranking at the top of the SERP. It’s just not featured in the People Also Ask box.
This indicates that Google already considers the content to be relevant for the target keyword. And since PAA questions are topically related to the target keyword, they don’t have a long way to being relevant for those questions too.
Now before starting, make sure to focus on your highest-ranking content.
Start with content that’s ranking above the fold. Once you’ve exhausted those keywords, move on to pages ranking on page one below the fold.
Thinking about it this way helps you prioritize what to work on first.
Now that we’ve discussed how to find opportunities, let’s get into how you can analyze the current PAA boxes so that you can have your content featured there.
SERP Analysis
The first thing to do is a little SERP analysis. This is free and easy to do.
Simply type the query into Google and look at the questions in the PAA box. But don’t just look at the top questions. Click the results to see more results. The more results you click, the more results will appear.
Now if you keep doing this, eventually Google will show you questions that are not entirely relevant to your target keyword.
This will show you the outer limits of Google’s topical ‘understanding’ of the query.
For instance, if you google ‘how to fly a kite’ and keep clicking on the questions in the People Also Ask box, eventually, Google presents questions about kite surfing.
Kite surfing is clearly a different search intent and therefore marks the outer limit of Google’s query database.
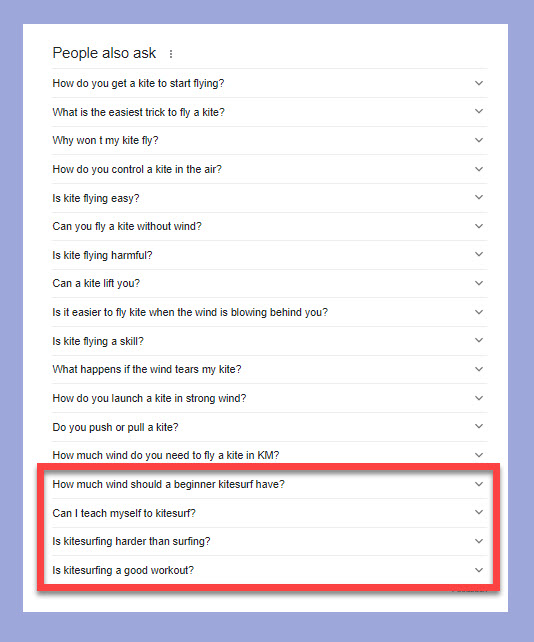
Once you’ve reached that point, you can see all the questions that Google sees as topically relevant to the original search query.
This means you can easily create a cluster of relevant content based on all of these queries.
You can also click any of the questions to see how Google presents the answers. This will help you create your own content designed to rank for those questions. More on this later.
SERP Feature Analysis
Now that you’ve performed a little SERP analysis, it’s time to look at some data.
So let’s have a look at the Rank Ranger SERP Feature Monitor for the term ‘appetizer ideas’.
As you can see from the screenshot below, there are four questions showing up and there is some volatility. This means there are some questions that might show up consistently while others come and go.
Focus on the ones that are more consistent.
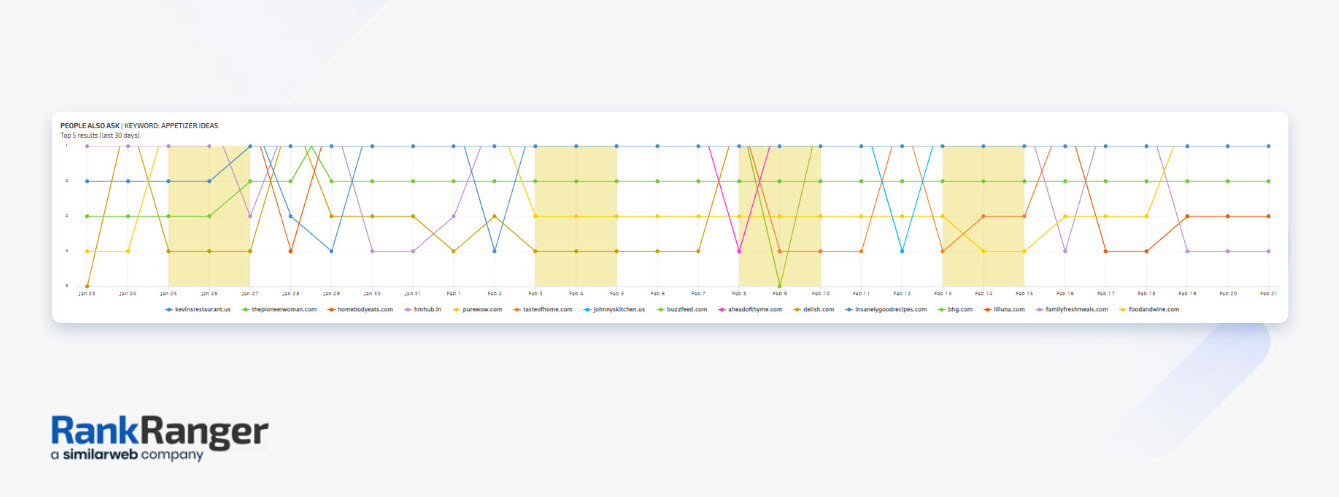
If you scroll down in the report, you’ll see how the individual URLs are performing in the SERP feature.
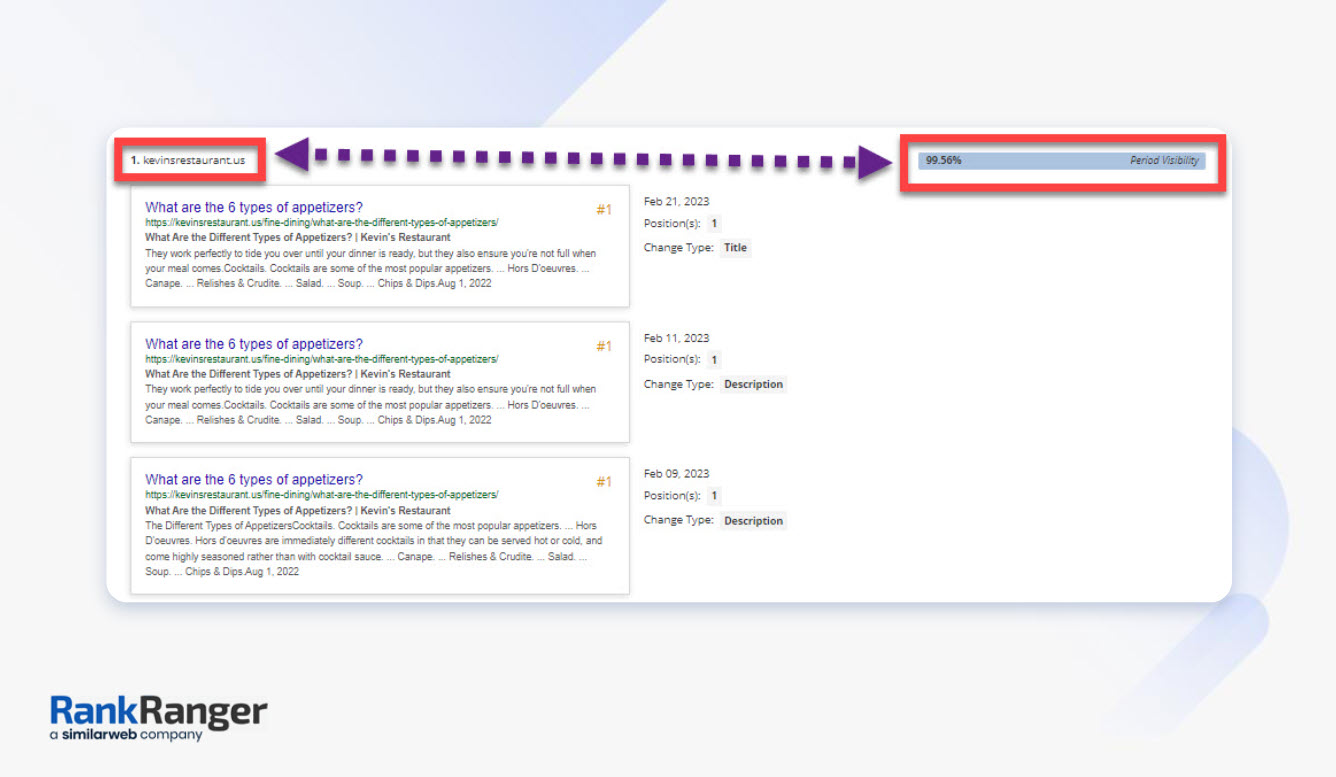
As you can see in the screenshot above, the domain kevinrestaurants.us has a Period Visibility of 99.33%. Over the tracked 30-day period, it was almost always visible.
This means Google considers this query as highly relevant and presents it constantly. It also means that Google considers the answer that it gets from kevinrestaurants.us as a good answer to the question.
If you could have your URL featured there, your brand would feature consistently. But you’ll have to create a better answer than kevinrestaurants.us.
To do that, you can see all the changes that Google has made to its snippet.
As you can see from the screenshot below, we track every change that Google made to the snippet over time. Google is constantly editing the results, including:
- The title
- The descriptions
- The rankings

Use these changes to see what Google considers a relevant answer. If Google is constantly editing, it might be a sign that it hasn’t found the best answer. Yet.
Validate Your Opportunities
In order to rank in a PAA box, your content must include the most relevant answer for your target query.
This means if you Google your target query, your content should show at the top of search results.
If you are not yet ranking at the top for your target query you’ll have to create new content to rank on that SERP.
If, on the other hand, you already rank in the top ten, you have a good opportunity to rank in the PAA box with just a little effort.
So for instance, in the screenshot below you can see allrecipes.com ranking in position six for the keyword ‘appetizer ideas’.
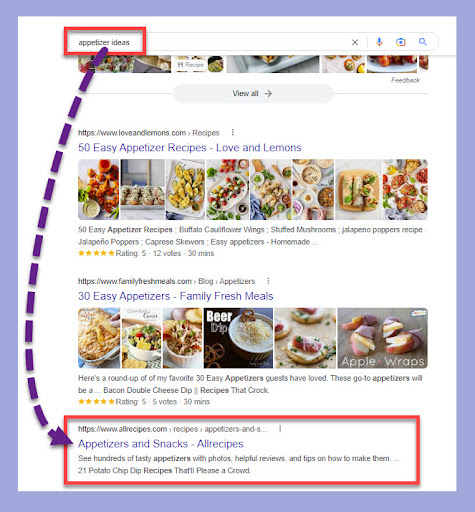
But allrecipes.com is not featured in any of the People Also Ask results.
Here’s why.
When I Google any of the questions in the PAA box (for instance, ‘What are the 6 types of appetizers?’), allrecipes.com is nowhere to be found.
This means allrecipes.com would have to create new content to rank on these queries.
If they are able to do this effectively, they’ll be able to rank in the PAA boxes for multiple queries.
Create Your People Also Ask Content
Okay, so you’ve found some People Also Ask queries that you want your content to feature in.
Here are some steps to take.
Include the query in your content
It’s a best practice to actually write out the query in your content. It doesn’t have to be an exact match query as I demonstrated above in the section ‘How does Google Process a Search Query’, Google’s NLP algorithms analyze the query based on synonyms and broader context to understand the query.
You don’t have to use the exact wording you found in a People Also Ask box. Google ‘understands’ what you mean. But, it’s important to write simply and clearly as Google often makes mistakes.
Also, when writing out the question, make sure to write it out as a question and use a question mark. In other words, don’t imply the question.
For instance…
An implied question would be: training benefits
Instead, you should write out the question: What are the benefits of training?
Include the Answer Immediately After the Question
It’s true, Google is pretty good at editing. Google will often find the answer to a question in the body copy of a piece of content.
But, you should always stack the **** in your favor.
That means, to increase your chances of having your content chosen for a PAA answer, include your answer directly after the question.
Also, make sure to use language that demonstrates that you are answering the question. For instance, if your question is ‘What are the benefits of training’, start answering by writing ‘The benefits of training are…’.
Optimize Your Content Format
Before actually creating your content, take a look at how Google answers the question.
Look at the format.
Ask yourself, is it a:
- Text answer?
- Ordered list?
- Video?
When creating your content, use the same format.
So for instance, in the screenshot below you can see that Google is presenting a bulleted list.
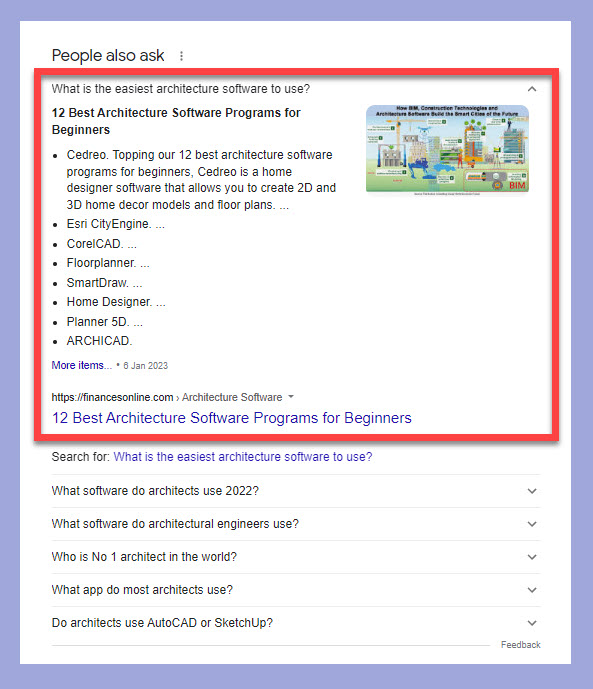
Now you can easily see how Google created that snippet. Just click the link at the bottom of the snippet. In the case above, the link is ‘12 Best Architecture Software Programs for Beginners.’
Once you get there, right-click and select ‘view page source’.
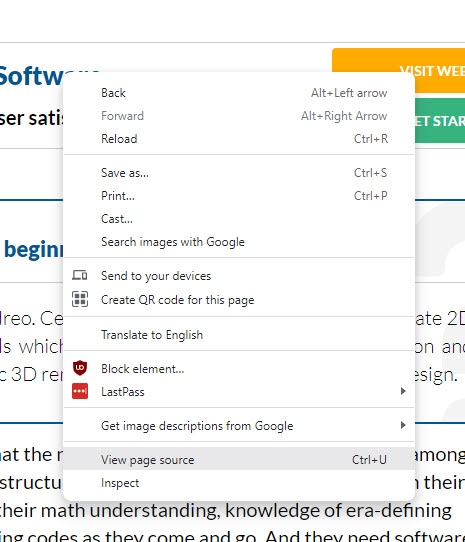
Then search for the items in the bulleted list.
From experience, you’ll either find a bulleted list or you’ll find all the items in the list in the headers. Most commonly H2s or H3s.

Once you’ve figured out how Google created the snippet, create something similar. If Google is drawing a bulleted list from a list, create one on your page.
Add FAQ Markup
Schema markup is your way of letting search engines know what your content is about.
Schema is a way to present your content in a structured machine-readable form.
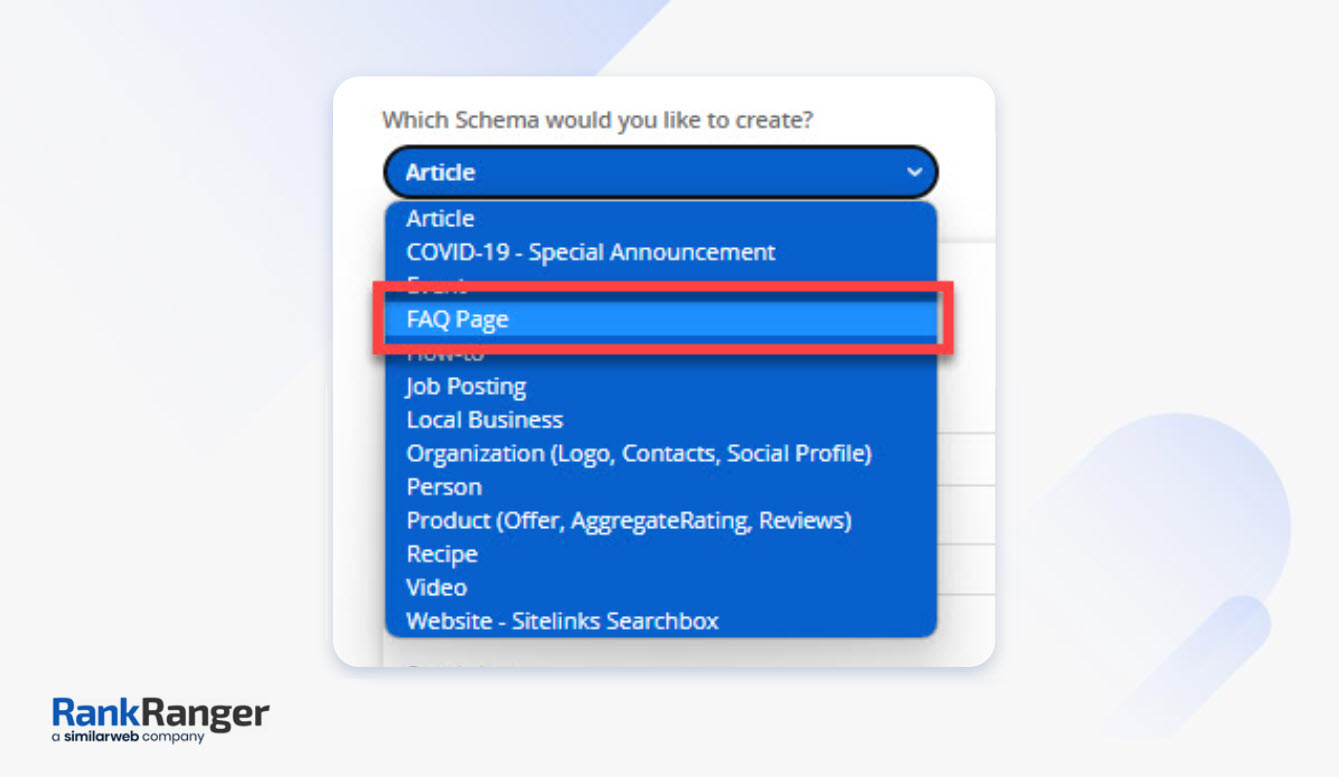
Now, creating FAQ schema is pretty easy to do.
Just go to the Rank Ranger schema markup generator and our free tool will write the code for you.
Just make sure to select FAQ markup and simply fill in the fields.
PAA SEO: The Big Picture

You should now understand how Google creates People Also Ask boxes, starting with how the semantic search engine analyzes search queries and creates query databases and how queries are ranked according to popularity and relevance.
You should also understand how to use People Also Ask boxes as part of your SEO traffic strategy to bring targeted traffic to your site.
It’s now up to you to test this strategy and see how it works for your business.
FAQs
How do you track People Also Ask?
The easiest way to track Google’s People Also Ask feature is to use the Rank Ranger SERP Feature Monitor. The tool shows you a visual graph of all the URLs ranking over time. You’ll see how volatile the various queries are. You can also use it to see any and all changes Google is making to the title, description, and ranking of the various URLs. This will help you create the best answer for your People Also Ask content.
What does People Also Ask mean on Google?
The “People Also Ask” feature is a SERP feature that displays questions topically related to the user’s search query.
This provides users with additional context related to their original query. By clicking on any of the related questions, users can expand the box to reveal a short answer or summary.
The “People Also Ask” feature is intended to help users discover new and relevant information and broaden their understanding of the topic they are researching. It can also help users refine their search queries and get more specific information.
How do you use people also ask?
To use the “People Also Ask” feature on Google, follow these steps:
- Enter your search query in the search bar
- Scroll down the search results page, to see the “People Also Ask” box
- Click on the drop-down arrow next to any of the questions to reveal a brief answer or summary related to that question
- If the answer is helpful, click on the link to read more about the topic, or click on “Back to Questions” to see more related questions
- Click on any of the related questions in the “People Also Ask” box to expand the box and see more questions related to your search query
By using the “People Also Ask” feature, you can discover new information related to your search query and explore related topics that may be of interest to you. It’s a helpful way to expand your knowledge on a particular subject and get more information on the topics that matter to you.




