![How to Do a Backlink Audit: A Beginner’s Guide [5 Easy Steps] » Rank Math How to Do a Backlink Audit: A Beginner’s Guide [5 Easy Steps] » Rank Math](https://rankmath.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Backlink-Audit.png)
Backlinks remain an important factor in determining your website’s authority and ranking. However, not all backlinks are created equal.
While high-quality backlinks can significantly boost your site’s visibility, poor backlinks can harm your SEO efforts and potentially lead to search engine penalties. This is where a backlink audit comes into play.
A backlink audit is a comprehensive process that evaluates all the links pointing to your website to ensure they contribute positively to your SEO health.
By conducting regular backlink audits, you can maintain a robust link profile, reduce risks associated with spammy or irrelevant links, and ultimately enhance your search engine rankings.
In this post, we’ll discuss the step-by-step process of conducting an effective backlink audit. We will cover essential tools and techniques, explain how to analyze the quality and relevance of your backlinks and provide strategies for dealing with harmful links.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started.
1 What is a Backlink Audit?
A backlink audit is a thorough examination of the links from external sources that point to your website. These external links, commonly known as backlinks, play a significant role in search engine optimization (SEO) by influencing your site’s authority and search engine rankings.
The purpose of a backlink audit is to assess the quality and relevance of backlinks to ensure they are contributing positively to your SEO efforts.
During a backlink audit, several key aspects are analyzed:
- Quality of Backlinks: Not all backlinks are beneficial. High-quality backlinks typically come from reputable, authoritative websites relevant to your industry. These links can improve your site’s credibility and search engine ranking. Conversely, links from low-quality or spammy sites can harm your SEO and may even lead to penalties from search engines.
- Relevance: The relevance of the linking site to your content is essential. Backlinks from sites related to your niche are more valuable than those from unrelated sources.
- Anchor Text: The clickable text in a hyperlink, known as anchor text, should be natural and varied. Over-optimized anchor texts with exact-match keywords can look manipulative and may be penalized by search engines.
- Follow vs. Nofollow Links: A balanced ratio between follow and nofollow links is important. Follow links pass SEO value to your site, while nofollow links do not. An unnatural imbalance can raise red flags with search engines.
- Toxic Links: Identifying and addressing toxic links is essential to the audit. These links can harm your site’s SEO, often from spammy, irrelevant, or low-authority sites.
2 How to Perform a Backlink Audit
Let us now discuss how to perform a backlink audit.
2.1 Gather Backlink Data
The first step is to gather backlink data.
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free and powerful tool provided by Google that allows you to monitor and maintain your site’s presence in Google search results. It offers detailed information about your site’s backlinks, making it an excellent starting point for a backlink audit.
First, log in to your Google Search Console account. Select the property (website) for which you want to perform the backlink audit.
In the left-hand menu, click on Links. This will open the Links report, which provides comprehensive data about the links to your site.
In the Links report, you’ll find sections for External links, Top linked pages, Top linking sites, and Top linking text.
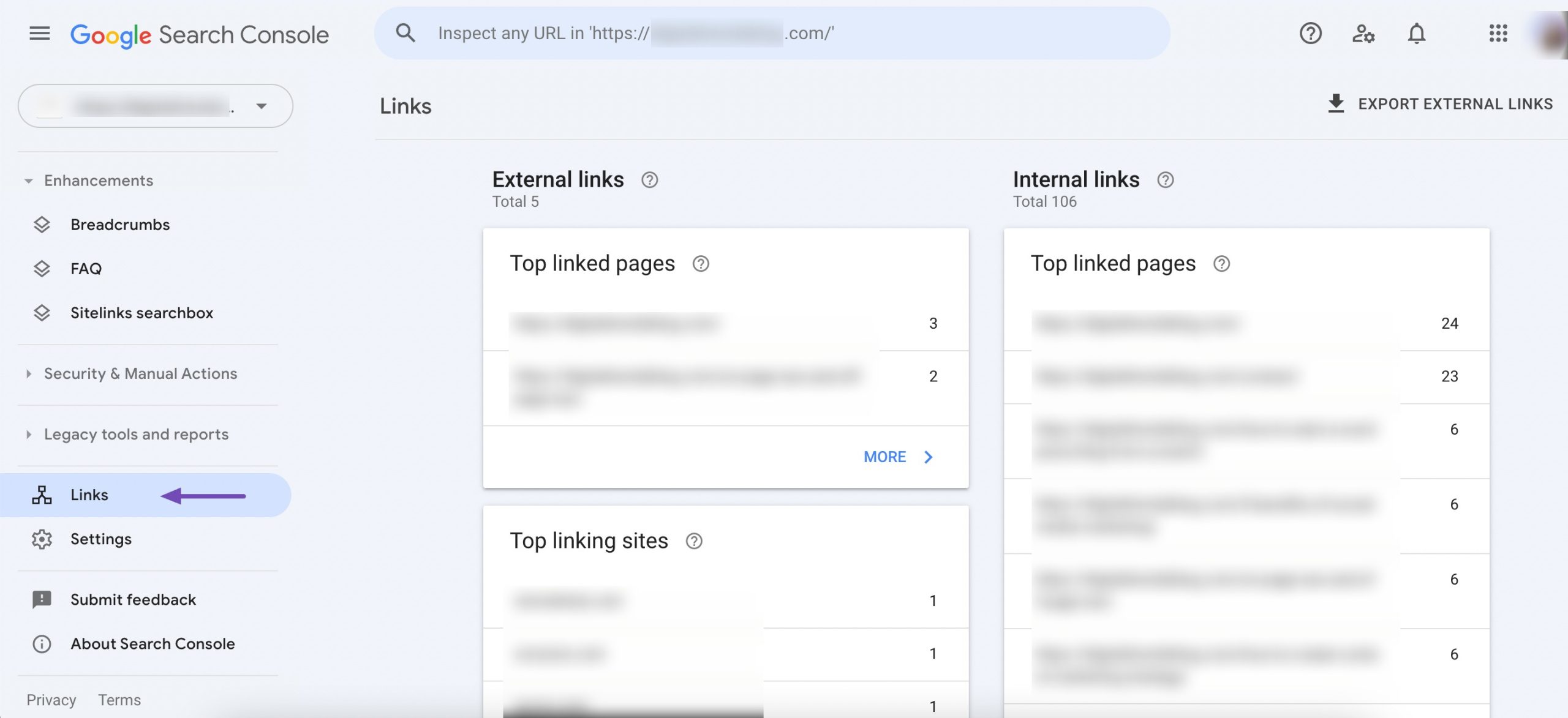
Review the Top linking sites and Top linking text sections in Google Search Console to understand the types of content and anchor texts that attract the most links. This analysis can help you develop your content creation and outreach strategies to align with what has proven successful in the past.
For a detailed audit, you can export data from these sections. To do so, click the MORE button in each section to see a complete list of links or domains.
Once the complete list is displayed, click on the EXPORT button located in the upper-right corner of the page.
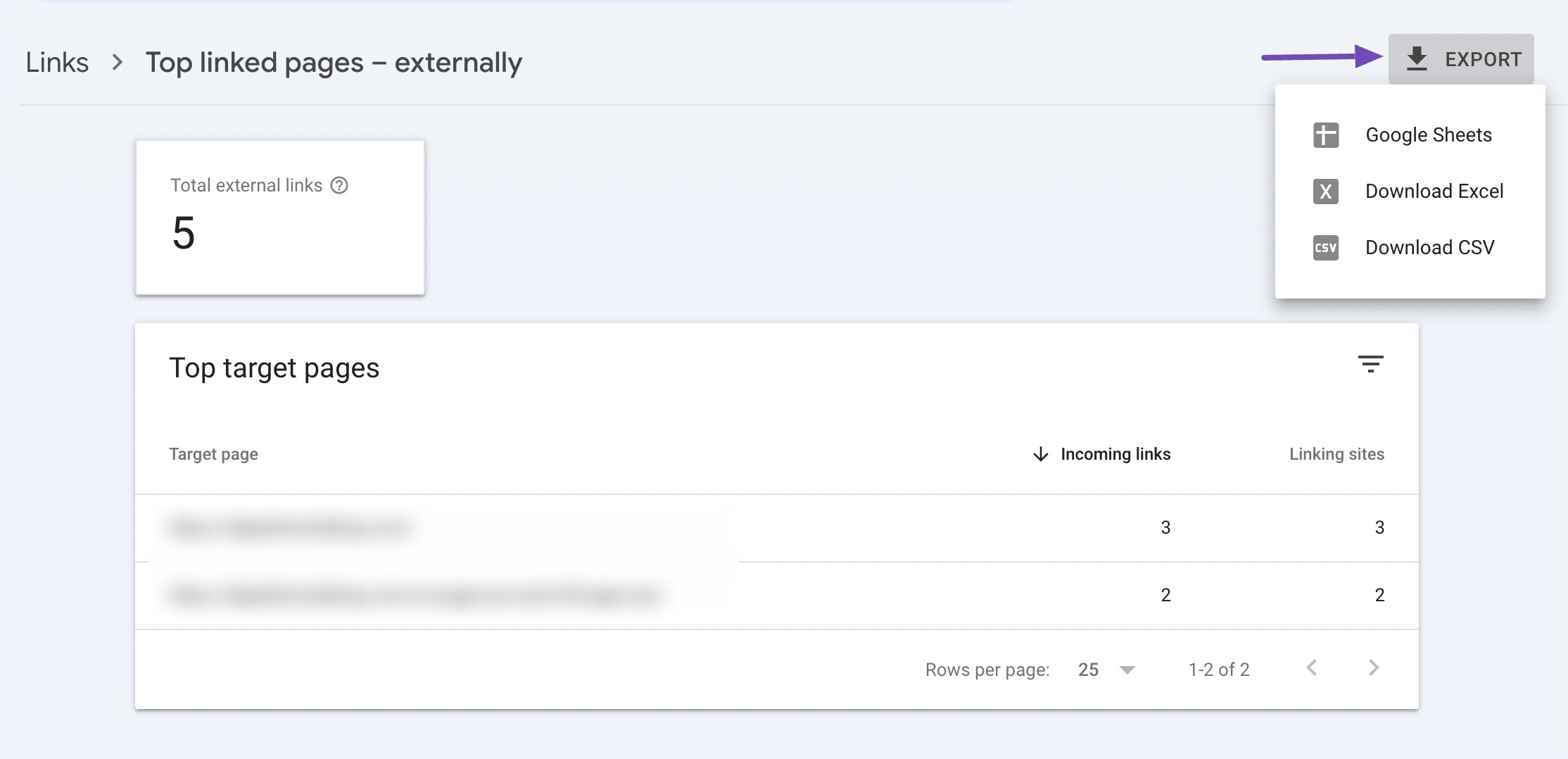
Choose your preferred file format, CSV or Google Sheets, to download the data.
Once you have exported the backlink data from Google Search Console, organize the data into columns for easy analysis.
2.2 Analyze Backlink Quality
Once you’ve gathered the backlink data, analyze the quality of your backlinks. This involves assessing various aspects of each backlink to ensure they positively contribute to your site’s SEO.
Identify and Flag Links from Low-Authority Sites
Review the sorted list and identify links from sites with low domain and page authority scores.
Flag these low-authority links for further review. While not all low-domain authority sites are harmful, many might not add significant value to your SEO efforts.
Relevance
Evaluate whether the linking sites are relevant to your niche or industry. Relevant backlinks are more likely to impact your SEO positively.
For instance, if you run a tech blog, backlinks from other tech-related sites or blogs are more valuable than those from unrelated industries like fashion or food.
Identify and flag links from sites unrelated to your niche or industry.
These irrelevant links might not provide significant SEO benefits and can be reviewed further for potential removal.
Anchor Text Analysis
Categorize Anchor texts based on the following:
- Branded: Anchor texts that include your brand name.
- Keyword-rich: Anchor texts that contain specific keywords related to your content.
- Generic: Common phrases like click here or read more.
- ***** URLs: The URL itself is used as the anchor text.
Look for over-optimization patterns, such as excessive use of exact-match keyword anchor texts. Flag these over-optimized anchor texts for further review and potential action.
Follow vs. Nofollow Links
Follow links pass SEO value (or link juice) to your site, positively impacting your rankings.
Nofollow links do not pass SEO value. They are often used for sponsored content or in situations where the linking site doesn’t want to vouch for the linked site.
Assess the ratio of follow to nofollow links in your backlink profile. A healthy backlink profile typically includes a natural mix of both types.

If you notice an unnatural imbalance (e.g., a high proportion of follow links), check this for further review, as it might indicate manipulative linking practices.
2.3 Identify Harmful Links
Identifying harmful backlinks is an integral part of a backlink audit, as these links can negatively impact your site’s SEO and even lead to search engine penalties.
Use SEO tools to check the source of your backlinks. These tools often provide indicators of a site’s reputation and history.
Spammy Sites
Search engines often penalize known spammy sites for violating SEO guidelines, such as engaging in link schemes or producing low-quality content.
Irrelevant content, especially low-quality or unrelated to your niche, is a red flag. Backlinks from such sites can be harmful as they might be seen as manipulative.
Link Farms and Networks
Link farms and Private Blog Networks (PBNs) are networks of websites created solely to manipulate search engine rankings through excessive linking.
Look for patterns like multiple links from a small group of interconnected sites with similar IP addresses or ownership.
If you identify links from suspected link farms or Private Blog Networks (PBNs), flag them for further review.
Toxic Links
Many SEO tools offer features specifically for identifying toxic links. These tools use a combination of metrics such as link quality, relevance, and spam score to flag potentially harmful backlinks.
Metrics may include low domain authority, high spam score, irrelevant anchor text, or many outbound links on the referring page.
2.4 Find and Fix 404 Errors
Identifying and addressing 404 errors helps maintain a healthy website and can significantly benefit your SEO efforts.
Google Search Console (GSC) is an invaluable tool for this purpose. To find the 404 errors, log in to your navigate to the Pages section. Here, you’ll find a list of errors that Google has encountered while crawling your site, including 404 errors.
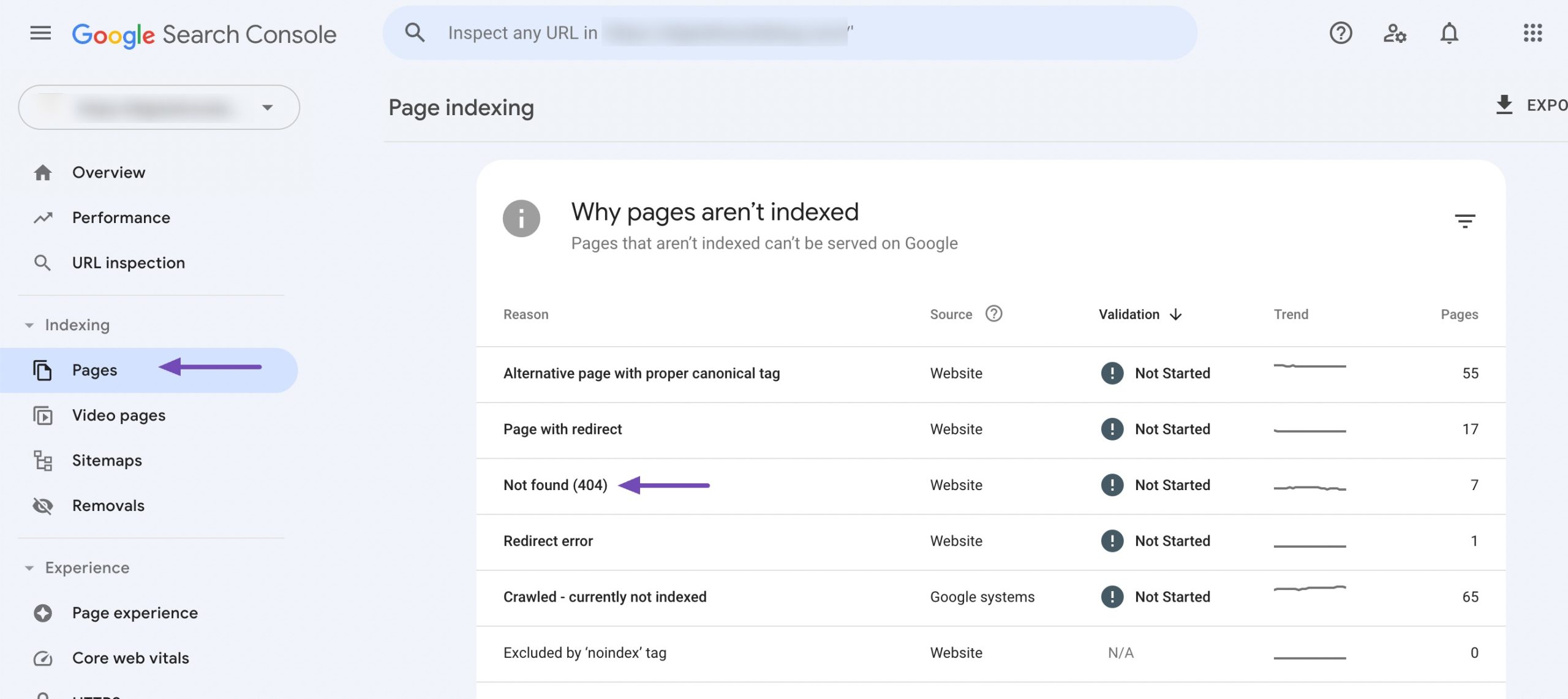
Review the list of 404 errors to identify pages that are not found. Pay close attention to URLs that previously had significant traffic or backlinks. Export this list for further analysis.
For valuable backlinks, you can fix the 404 errors by redirecting these URLs to relevant, existing pages on your site using a 301 redirect. This ensures that the link equity is preserved and passed on to the new destination, rather than being lost.
After setting up the redirects, monitor the changes in the Google Search Console to ensure that the redirects are functioning correctly and that Google has recrawled the redirected URLs.
2.4 Find New Opportunities to Build Backlinks
Google Search Console (GSC) is not just a tool for monitoring your site’s health; it also serves as a valuable resource for uncovering new backlink opportunities.
One effective way to do this is by analyzing the Performance report in Google Search Console. This report provides insights into which keywords and pages are driving traffic to your site.
By identifying high-performing pages and keywords, you can pinpoint content that is already resonating with your audience and is likely to attract backlinks.
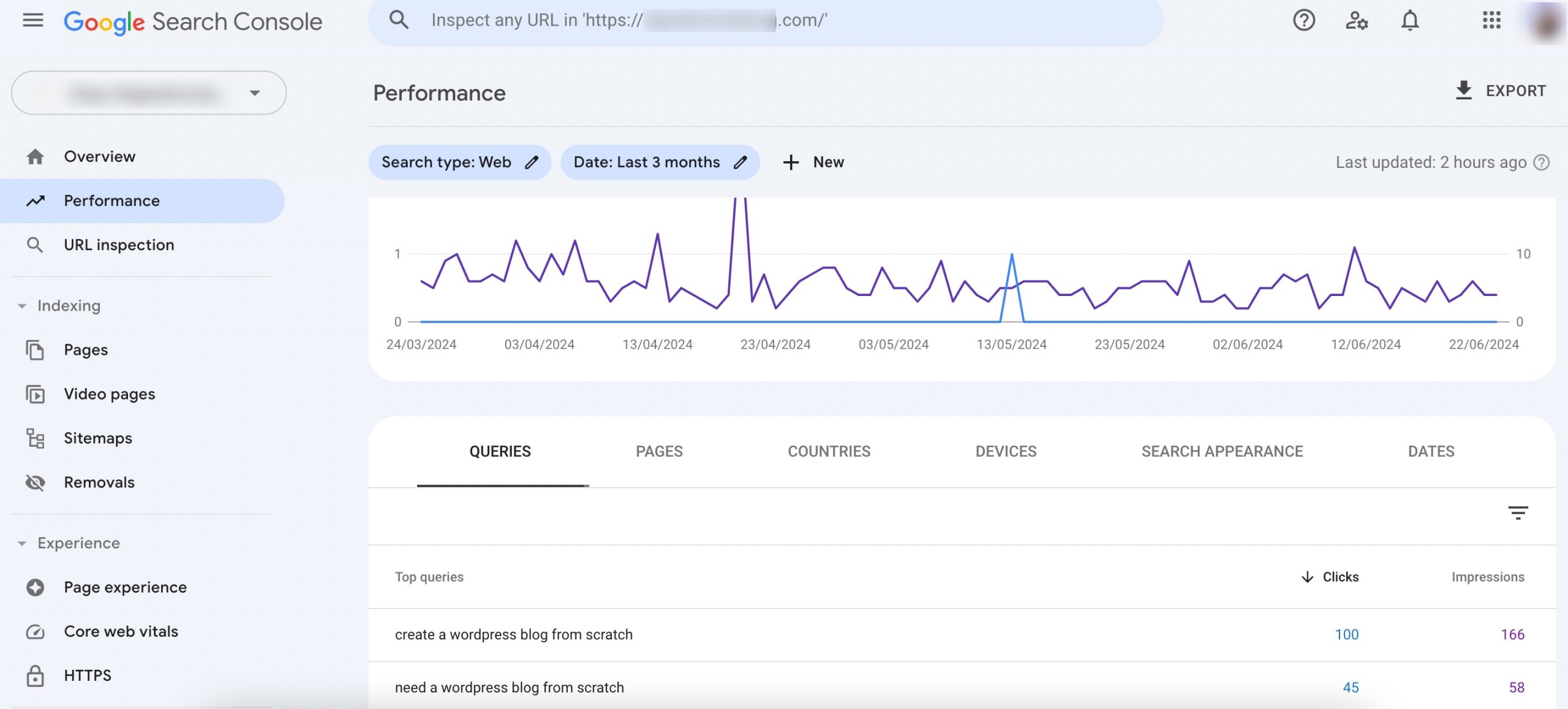
Here, you can see data on clicks, impressions, click-through rates (CTR), and average position for various search queries.
Focus on pages with high impressions but relatively low CTRs or pages that rank well for specific keywords but don’t have as many backlinks.
Once you’ve identified these high-potential pages, create a list of relevant websites and influencers in your niche that might be interested in linking to your content. Look for sites that have previously linked to similar content or have a history of sharing valuable resources.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on link-building to naturally earn links for your website.
2.5 Check Your Competitor’s Backlinks
The next step is to perform similar checks on your competitors’ websites.
This comparison will allow you to evaluate how your backlink profile stacks up against those of your competitors.
By analyzing this information, you can identify areas for improvement and gather valuable data to inform your next link-building strategy.
Refer to our dedicated tutorial on finding your competitor’s backlinks to understand where your competitors’ backlinks are coming from.
3 Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I perform a backlink audit?
You should perform a backlink audit at least once a year. However, for sites with frequent changes in their backlink profile or those operating in highly competitive industries, quarterly audits are recommended.
What should I do if I find toxic backlinks?
If you find toxic backlinks, you can contact the webowners to request link removal.
How can I improve my backlink profile?
Improve your backlink profile by acquiring high-quality links from reputable sites, ensuring links are relevant, maintaining a natural anchor text distribution, and regularly auditing and removing harmful links.
4 Conclusion
Conducting a thorough backlink audit is essential for maintaining a healthy and effective SEO strategy.
A backlink audit not only helps in safeguarding your site from potential penalties but also opens up new avenues for acquiring high-quality links.
Regular backlink audits ensure that your link-building efforts are aligned with current best practices and industry standards, helping you stay competitive in search engine rankings.
Implementing the insights gained from these backlink audits will lead to improved visibility, higher organic traffic, and a stronger overall online presence.
If you like this post, let us know by Tweeting @rankmathseo.