
Reading Time: 15 minutes
Meta titles, descriptions, alt text, anchor text, images, videos, HTML…the list of things to tweak and include on your website seems never-ending, doesn’t it?
When it comes to ecommerce, no matter how good your product is, how positive the reviews are, and how much you invest in marketing, there’s a catch.
If you don’t follow some fundamental ecommerce SEO practices, your website will not reach the top search results. Or worse, when users visit your website, they may exit almost immediately. This could be because of red flags like repetitive content, random images, confusing links, haphazard categories, etc.
Ecommerce SEO tactics come to the rescue at this stage.
You can make your ecommerce website rank-ready by building a strong SEO foundation. As you get started with ecommerce SEO, you will find that even minor tweaks can boost organic traffic and rankings, and help with website maintenance.
If your ecommerce SEO is a Jenga tower, the following are the blocks that form the foundation:
Choosing the Right CMS for Ecommerce SEO Success
You probably know that your content management system (CMS) will do a lot of heavy lifting for you as you build your ecommerce website’s online presence. Here are six considerations you must take care of when choosing a CMS. These apply regardless of whether you are redesigning your website or moving to a new CMS.
The goal is to automate dreary processes and let the CMS take over some optimizations for you.
Ask yourself the following questions: Does the CMS…
1. Generate Clean and Semantic HTML Markup?
When organizing content on a web page, you want to prioritize structure. Headings, sub-headings, lists, tables – your CMS should be able to identify the structure of all these and assign semantic HTML tags (labels) for them. This means the title and heading tags (among others) must describe precisely what element they are there for.
An example of this would be that the title of this section is an <h3>, or the title of this blog is an <h1>. Your CMS should be able to generate the proper headers, footers, and images. Here’s an example of what the HTML markup might look like for an ecommerce website, such as a candle shop:
<body>
<header>
<h1> 5 Candles You Need For Christmas </h1>
</header>
<section>
<main>
<article>
These are some candles you can buy this December.
<p>
<h2>Winter Wonderland Soy Candle </h2>.
<p>
<p>
</article>
</main>
<aside> Comment Section </aside>
</section>
</body>
This will show up as:
These are some candles you can buy this December.
[…para 1…]
Winter Wonderland Soy Candle
[…para 2…]
[…para 3…]
[place for comment section]
If you look at the HTML markup of popular websites like Sephora and Zappos , you may find that they do not use such tags. But they have established websites. They do not need to care as much about SEO to rank.
A CMS should be able to generate this clean and semantic HTML markup. Some ways to identify a CMS that creates semantic HTML is to check:
- Whether it differentiates between a main topic and sub-topics
- If it has larger-sized text marked as heading tags just because they are the same font size as heading tags
The page templates also need to avoid using too many nested DIVs and HTML that makes the DOM unnecessarily large, as that can increase page load time by increasing payload size and processing time.
2. Control the URL Structure of Your Website?
Each website page needs to have a URL structure consistent with the URLs of the rest of the pages.
Most websites follow a naming scheme such as:
domain.com/category{category-name}
domain.com/product/{product-name}
Placing specific page types in their own subfolders makes it easier for reporting and having developers create internal links. Try to avoid having category and product pages reside in the root folder of your site as it can complicate reporting and troubleshooting problems.
Let’s go back to the candle shop example.
Here are some URL structures from two pages of candle shop websites:
- Product page for the New Home Candle: https://homesick.com/products/new-home-candle – it is simple and covers the website name, the category (products), and the name of the product (New Home Candle)
- Blog page titled ‘Top 3-Wick Scented Candles to Light Up Your Home’ – https://www.candledelirium.com/blog/3-wick-candles/ – it includes keywords, mimics the title of the blog to an extent, and is short and specific. Can we improve this? Yes, by adding the keyword ‘scented.’
According to a study by Backlinko, URLs that contain terms similar to a keyword have a 45% higher clickthrough rate compared to URLs that don’t have a keyword.
Be careful about how your site navigation and filters uses parameters. While parameters are not generally a problem, if the CMS doesn’t carefully control the parameters, they can potentially cause duplication and an almost unlimited number of additional URLs on the site, which can cause problems with crawling and indexing.
3. Use Meta Tags and Descriptions?
Meta-tags are snippets of text that describe your website’s content. You need unique meta tags and descriptions for all your pages because they are vital for indexation and SEO.
While most CMS’s have an approach to generating meta tags, you also need the ability to override them in some cases, for example, if a page needs to be removed from the search results, one way to do this is to use a meta robots noindex tag. The CMS dashboard should allow you to control this either by product group or for individual products.
You may feel that you can stick to having the same meta description tag for all your product pages, but since this is displayed in the snippet of the search results, it’s much better to have unique descriptions for each product, and the ability to override them individually.
Let’s look at some examples of meta-tags on product pages of candle shops online. This image is from the ‘Langston Luxury Candle’ product page of Harlem Candle Co. the meta description tag is:
“The Langston Luxury Candle is a 12 oz. soy candle scented with nutmeg, clove, leather, jasmine, cade, vanilla, sandalwood, and amber. Harlem Candle Company creates luxury candles, travel candles, and votives inspired by the Harlem Renaissance.”
This clearly describes the size, scent profile, and main ingredient of the candle. Adding relevant, unique copy such as the names of the spices used in the scent and other categories of candles together create an informative snippet that will help describe the product to users in the search results and help improve the click-through-rate to your site.
Now let’s look at the meta description tag of the ‘Speakeasy Luxury Candle’ from the same brand and category to compare:
”The Speakeasy Luxury Candle is a 12 oz. soy candle scented with palo santo, patchouli, vanilla, and dark chocolate. Harlem Candle Company creates luxury candles, travel candles, and votives inspired by the Harlem Renaissance.”
As you can see, the meta description tag follows the same format, but contains unique copy for that product.
Another tip is to keep the meta-tag short since Google may feature it in the SERPs. 150-160 characters can fit in the search results without getting truncated.
4. Create Sitemaps?
XML sitemaps (a list of all the pages of your website) help search engines find your web pages and index them. You may feel tempted to skip this step if you have a good internal website structure, but even with an excellent internal structure, you need a sitemap.
Choose a CMS that can generate XML sitemaps for your website; the more products you have on your site and the more frequently they change, the more important this feature becomes.
5. Optimize Images?
A good CMS will also take the product images you upload and optimize them to be the right size and compress them to improve download times and improve page speed. Every photo also needs alt text for accessibility purposes. The alt text also comes in handy if the image doesn’t load as it may be displayed in place of the image until the image can be downloaded and displayed by the browser. The alt text is also read and used by search engines for relevance which is used in image search. Avoid using generic file names or stuffing keywords in the alt text instead of describing the image.
6. Integrate With SEO Plugins?
While most CMS platforms today have some SEO capabilities built in, there may be additional SEO features that need to be added. Many CMS platforms allow for customization installing plugins or apps. This can be a quick and inexpensive way to gain additional functionality without needing additional custom development.
Why Is IA/Taxonomy Important for Ecommerce SEO?
Your website’s taxonomy (classification systems) and information architecture(IA) are crucial for SEO because they help relevance, internal linking, and make user navigation easy.
The taxonomy of your website refers to the classification and naming convention of your content. Information Architecture (IA) refers to the organization of content and products on your website, the category names and their hierarchy. If a user cannot instinctively find what they need on your website, the bounce rate will be high, and you will lose a customer.
How do you develop great information architecture and taxonomy?
Identify what issues the current taxonomy is causing. Since the structure and taxonomy of the website has a direct link to navigation and user experience, customers will face navigation issues if it’s unclear or confusing. These degrade the user experience and increase the number of clicks customers need to find your products. Clean up messy classifications through a complete audit. Maintain a spreadsheet of the type of content and relevant category headings. Remove the redundant categories and add new ones based on patterns and content relationships.
Here’s an example. Say a customer is back to the candle shop website. They can see a jumble of candles of different sizes, colors, aromas, and occasions. This is confusing. Instead, they need a categorized view, such as:
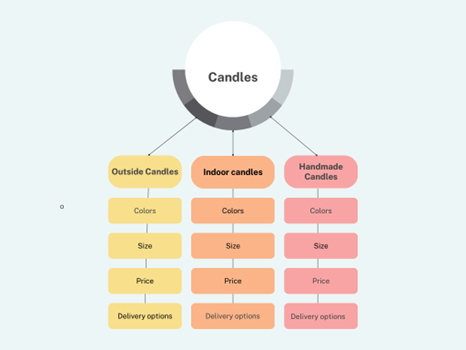
Here is a live example of clear taxonomy by Candle-Lite:
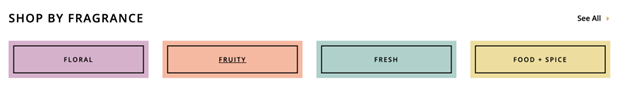
The website has three distinct categories:

Well-designed architecture and logical taxonomy improve:
Crawlability
The search engine can use the structure to discover and find all of your products. The more products you have on your site, the more important this becomes.
Ranking
As search engines scour through your systematically categorized and semantically relevant content, the taxonomy is what passes on relevance between categories, subcategories and to the products. This passing of relevance creates topic clusters and helps improve the ranking of those pages in the search results.
User Experience
Site visitors will find it easier to navigate your website and find products if navigation menus, labels, and categories are clear and resonate with them. If users struggle to know where to click and how to navigate your site they will leave out of frustration and go to your competitors.
Internal Linking Strategy for Ecommerce SEO
Including internal links within your product content or blog content has multiple benefits:
- Search engine crawlers go through internal links and connect the pages if they find the linking relevant. Based on this, they create a database of related pages (which helps with the information architecture we discussed earlier) and can index your products faster.
- Links to related and complementary products can help retain visitors. This can help increase discovery of other products, which can increase basket size and revenue.
- Contextual linking will establish you as a source of authentic and trustworthy information in the eyes of the customer.
Here are some best practices for internal linking:
Link to Your Most Important Pages
Which are the most important pages?
Your homepages, category pages, and best-selling product pages, i.e., pages you want your customers to find first. Why? Because they bring in maximum traffic and/or revenue.
When you link to these pages from other pages on your website, you redirect your user’s attention to the most profitable pages. This increases the chances of conversion.
For example, 90.7% of traffic for Grammarly comes from only 11.2% of its pages!
Insert Relevant Anchor Text
Anchor text (the clickable text in a link) needs to be descriptive and relevant as search engines read this to help them understand how the linked page connects to the source page. Being specific is vital to help the search engine make the connection, so avoid using generic words like “click here” or “read more”.
Use Internal Linking Throughout Your Website
Don’t limit your internal links to just the critical pages or blogs. Create a systematic map of relevant internal links for each webpage.
The length of the content on the page will determine how many internal links you should ideally have, so accordingly, plug in internal links on every webpage. There is no rule as such, so try experimenting.
Would you read a short 300-word piece crowded with hyperlinks? Understanding the consumption habits of your visitors will determine how you structure your blogs.
This, in turn, will contribute to your website’s information architecture, making it easier for the search engine to understand the relationship between pages and the overall IA of the website.
Avoid relying on the ecommerce platforms to generate links. It is a good idea to add internal links to category and product pages. This improves your website’s overall information architecture and helps search engines understand the relationship between pages.
Consider manually adding links to resources like buying guides, related product pages, links to accessories, and popular items from the same brand.
By providing relevant and useful internal links, you can improve the user experience and help guide customers towards making a purchase.
Check out this case study on Zapier that attributed its 1.6M organic visits partly to the interconnectedness of the website’s content due to links inside blog posts to other content features and links to the homepage.
Incorporate Internal Links in Your Blog Posts
Use a step-by-step system that follows the do’s and don’t of internal linking. First, identify the main categories that your site covers. These could be the various product categories and list them. Next, create a list of all the blog posts on your website and add these to a Google spreadsheet.
Now go through these blog posts and product categories to see which blogs they relate to. Form clusters based on the topic. Insert internal links to blogs that are relevant within each cluster.
So, for example, a blog on skincare routines for summer could link to sunscreen product pages, blogs about how to layer skincare in the summer, best practices for exfoliating after a swim, etc.
Each of these blogs could link to each other, thus creating a chain of related content.
Doing this will take your user from one blog to another for associated topics. It will also indicate to the search engine that there’s a valid connection between the blog post and other pages on your website.
Include Internal Links for Related, Complementary, and Often Bought Together Products
We don’t have to tell you the benefits of cross-selling and upselling. You are nudging the customer to add more to their cart by including internal links for related or complementary products.

Sometimes, spotting a complementary product (in the example below, this is what showed up when we searched for a candle product) within or around the product description of the first item will be enough for the customer to buy both. They won’t even need to go through the product page of the other recommendations.
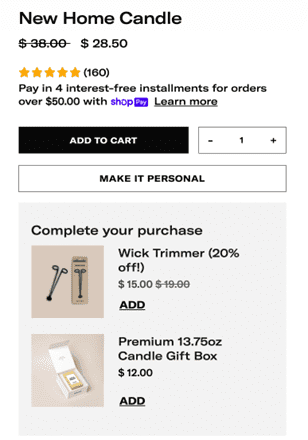
Add internal links to other related products you offer within your product descriptions. The search engine will make connections among the products and better understand how your products and content relate to each other.
Provide Recommendations for Other Products From the Same Brand or Similar Products From Other Brands
When a visitor is browsing through a category of products, you can also suggest similar products from the same (or different) brand. You show that you care about their needs and want them to buy something that ticks all their boxes. Recommending other relevant products is a way to establish trust with your customers. This helps build brand loyalty.
Recommending other brand products if the e-commerce website hosts different brands can tap into other needs of the consumers. This is an excellent example by Crate & Barrel. The product page for the candle features other products from different brands that match the vibe of the candle:

Handling Similar SKUs/Duplicate Content for Ecommerce SEO
We all know the monotony that can set in when describing similar products in different ways. But sticking the same content in each product description is not helpful to the visitor. They won’t know how to differentiate between multiple products.
Search engines will flag duplicate content and penalize you, leading to fallen rankings.
More importantly, search engines can identify duplicate content and may filter it out of their search results. This can lead to missed opportunities for organic traffic and lower rankings for your website.
Penalties for duplicate content may not be levied. But avoiding using the same content for multiple product descriptions will maximize your chances of ranking well in search results.
So how do you avoid confusing your visitors and prevent the penalty?
Use Unique Product Descriptions for Each Product
Do not insert the same product description for every product. You need to use descriptive language that is unique to each product and accurately describes the product.
Here are unique product descriptions of candles that we have pulled from a candle shop website. They include the physical attributes and aroma details while creating an appealing vibe for the customer to picture as they contemplate buying the product:

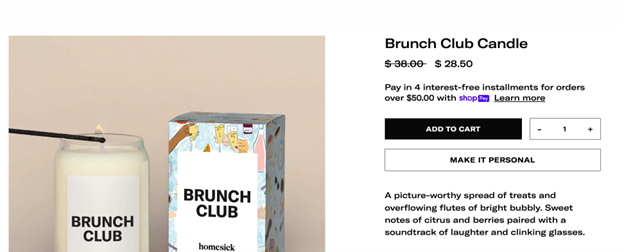
Employ the services of experienced product description writers to ensure they are unique and well-written. Here is an example of a product description that can confuse the reader, because on first glance, it doesn’t indicate anything related to the candle product:
Include Relevant Keywords in Your Product Description
Your product descriptions are an excellent place to plug in relevant keywords that can help you rank. Imagine (or use tools like answerthepublic) what terms the buyer must be using while searching for the product in question. Incorporate those words and phrases in your product descriptions.
Let’s move away from the candle example and explore electronics. In the following example, you can spot keywords like “noise-canceling”, “virtual surround sound”, and “high-quality audio.”

Add Synonyms and Variations of Keywords
Consider following a keyword analysis plan to come up with relevant synonyms and variations of keywords. The headphones example in the previous section includes synonyms like “solid”, “durable”, and “built to last.”
Using the exact keywords repeatedly can lead to drab descriptions and unnatural phrasing. Avoid keyword stuffing by using synonyms and other variations of keywords. Have one primary keyword that you pepper across the content, and use secondary keywords and synonyms in other places to make the description unique and interesting.
Insert Images and Videos
The media you include on your ecommerce website is as vital as the content. A year ago, Google updated its Video Indexing Report to show the parameters for video indexing.
You can do the following to insert optimized images and videos:
- Choose relevant images (if not original images, follow best practices for stock photos)
- Include other media (gifs, memes, etc.) that can boost your topical relevance and authority
- Shoot original and informative videos that follow video SEO rules, such as dividing your video into sections and labeling them, as seen below:
Users don’t want to see walls of text. Relevant media interspersed with the information leads to more impactful content.
For any form of media, you must follow SEO content best practices related to meta descriptions, keywords, titles, and heading tags.
For any form of media (and in general), you must follow SEO content best practices related to meta descriptions, keywords, titles, and heading tags.
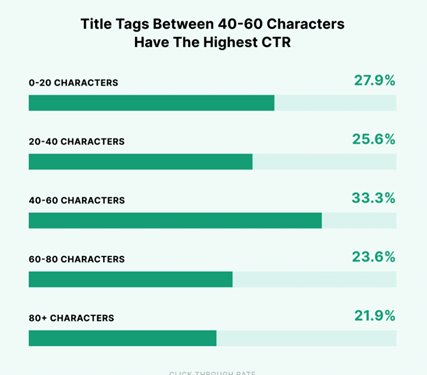
Write for Humans, Not Robots
With generative AI tools like ChatGPT and other virtual writing assistants, you may feel tempted to use the output they give. You can use these tools to generate ideas and outlines, but make sure that a human reviews and edits before publishing the final version.
Sure, your content needs to be optimized for search engines, but not at the cost of it being difficult or awkward for humans to read. This means using simple and specific language, following UX principles for effective user experience, and catering to user intent rather than algorithms.
How to Deal With Inventory Management and Pricing Issues
Although not directly tied to SEO, no matter how much you optimize your ecommerce website, it won’t help if your inventory management systems are faulty. Here’s what you need to do:
Respond to Customer Feedback
Focusing on customer feedback from those who have completed a purchase is insufficient.
You need to track and respond to customer comments at different stages of the buying journey. Those who do not buy because of inventory management or pricing issues will likely discuss their experience in social media comments or emails.
Maintain a systematic record of these to stay on top of problems preventing potential customers from buying.
Set Competitive Prices and Offer Free Shipping or Discounts
Nowadays, customers are spoilt for choice for most products. What can set you apart is identifying the sweet spot for pricing, flexible shipping, and other benefits.
Competitor study and understanding customer psychology will be your most significant strengths. These will ensure you give your customers suitable discounts and shipping options without incurring losses. Experiment with gamified offers, percentage discounts versus free items, giveaways, and other such pricing practices.
Keep Your Inventory Up-to-****
Search engines don’t crawl and index your page just once. They do it frequently to update the search results and rankings. So if a product is out of stock, your customer should not be able to purchase it, and it should ideally not show up in the search result. You need to disable the purchasing funnel and point them to similar products on your website instead.
If you have discontinued the product, create a 301 redirect to another product. You can create a 302 redirect for the product page URL if the product will return soon.
In the following example, the e-commerce website could improve the chances of a purchase if they had included a link to related products under the message:
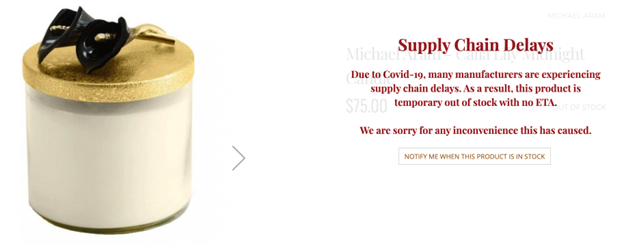
Ready to Ace Your Ecommerce SEO Game?
Here’s an easy reference checklist to build a robust ecommerce SEO foundation to help meet core web vitals:
| Choosing the right CMS by checking if it… | Internal Linking best practices | Handling duplicate content |
|---|---|---|
| Generates clean and semantic HTML markup | Link to the most important pages | Use unique product descriptions for each product |
| Controls the URL structure of your website | Insert relevant anchor text | Include relevant keywords in your product description |
| Uses meta tags and descriptions | Vary your anchor text | Add synonyms and variations of keywords |
| Creates sitemaps | Use internal linking throughout your website | Write for humans, not robots |
| Optimizes images | Incorporate internal links in your blog posts | Insert images and videos |
| Integrates with SEO plugins | Include internal links for related, complementary, and often bought together products | |
| Provide recommendations for other products from the same brand or similar products from other brands |
At Vizion Interactive, we have the expertise, experience, and enthusiasm to get results and keep clients happy! If you run an ecommerce site and are due for a redesign or have just launched a redesign, our SEO Audit Services identify problems with your site and lay out a plan of action. Then our experts will be right by your side with our ongoing ecommerce SEO Services to grow organic traffic and take your site to the next level. Get in touch with us to discuss more, we’re looking forward to hearing your story.



