
Updated: March 3, 2023.
Learn how to audit headings on a page and the entire website like a real SEO auditing pro.
The structure of headings on a website is one of the most important on-page elements that every SEO audit should check.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the steps for auditing the structure of headings on a website.
You’ll learn:
- the basics of the use of headings,
- common heading issues,
- how to manually audit headings,
- how to audit headings in bulk,
- how to check if JavaScript changes headings and whether Google has issues indexing their content.
I’ll also provide you with actionable tips and tools that you can use to analyze the structure of headings on your own website or your clients’ websites.
Let’s dive in!

Step 1: The basics of page headings
If you are a beginner SEO auditor, here is everything you should know about headings:
- Headings are an essential element of a well-structured website. They are the text elements that are used to divide content into sections or subsections, allowing users to quickly and easily navigate the website’s content. Headings are also important for accessibility reasons since people using screen readers rely on them to navigate the content.
- There are six different types of headings, ranging from H1 to H6, with H1 being the most important and H6 the least important. Each heading has its own purpose and represents a different level of importance in the content hierarchy.
- It’s important to use headings consistently and logically throughout the website. For instance, the H1 heading should be reserved for the main title or headline of the page, while H2 headings should be used for subheadings. H3 and H4 headings can be used to further divide the content into sub-sections. When headings are used consistently, they provide structure and clarity to the content, making it easier for users to navigate and comprehend.
Here is the information and best practices for headings from Google Search Central documentation.

Step 2: How to manually audit page headings
You should always include detailed information about the heading structure in your SEO audit.
To manually check the headings on a website, you need to go through each page and identify the different headings and subheadings.
This will help you identify any issues with heading structure and hierarchy that may be specific to certain types of pages.
Here is how to do it:
1) You can do this by using the “Inspect Element” feature in your web browser or by viewing the page source code.
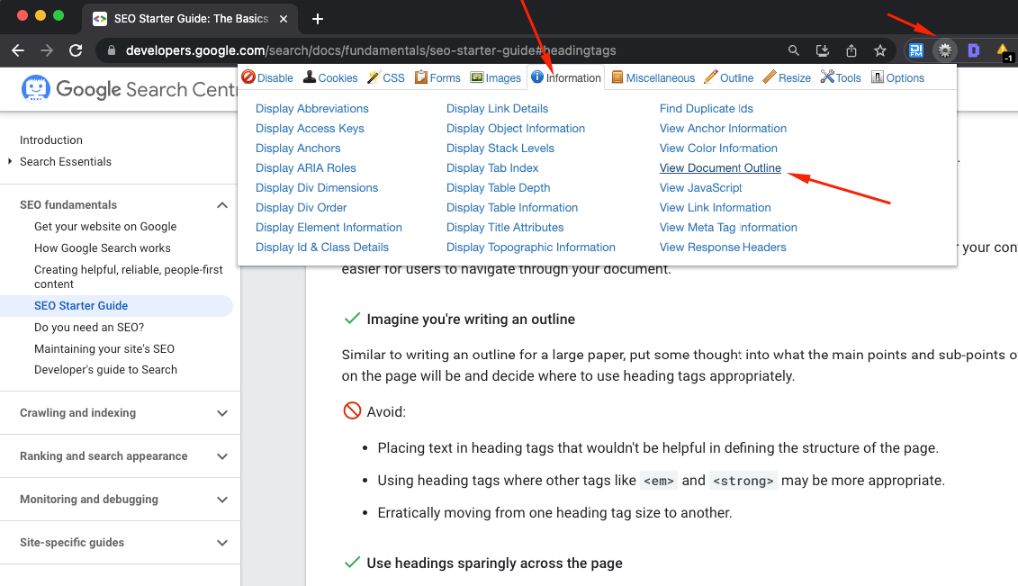
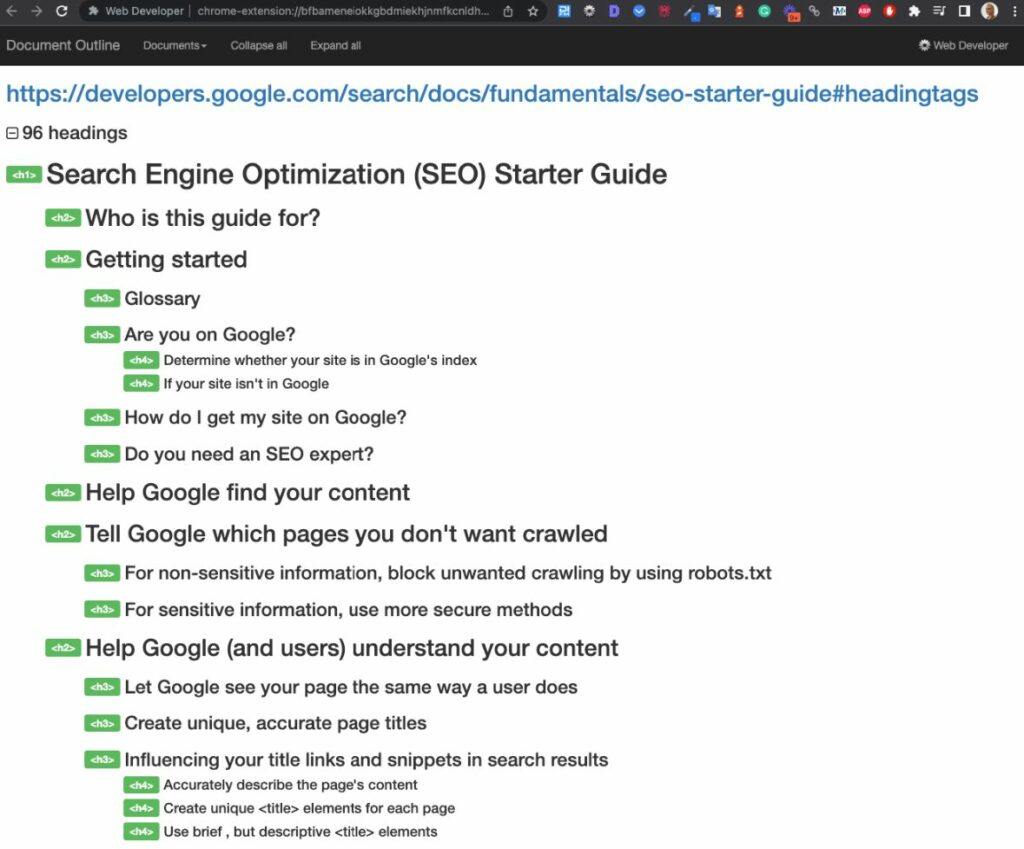
2) Use the Web Developer Chrome extension. Simply click on the extension, go to “Information”, and “View Document Outline”.
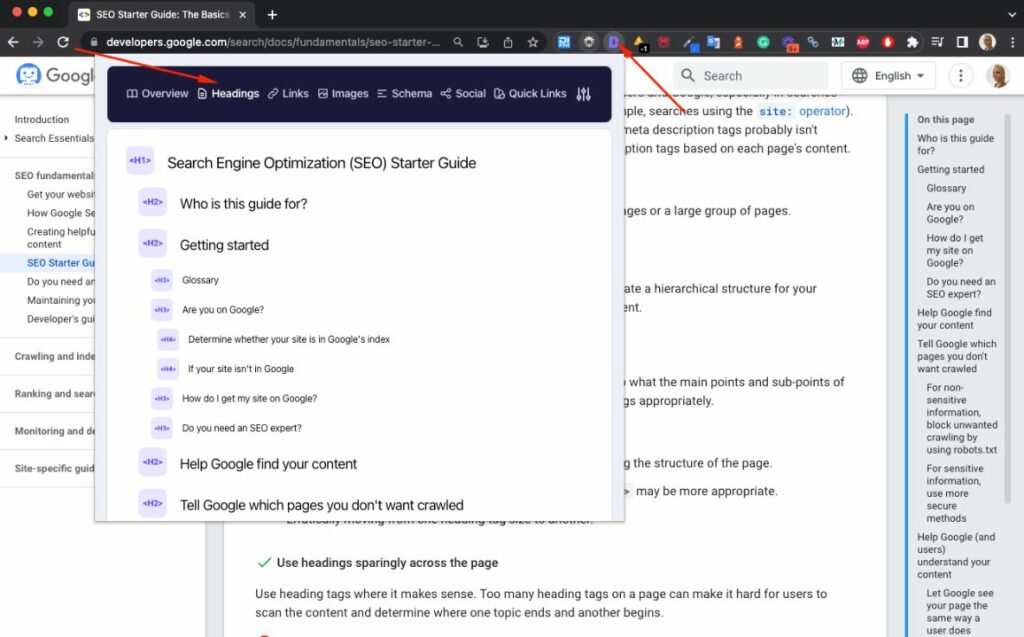
3) Use the Detailed SEO Extension. Simply click on the extension and select “Headings”.
Common heading issues to look for
- Consistency: Make sure that the headings are consistent throughout the website, using the same formatting and hierarchy on each page.
- Hierarchy: Check that the headings are used in the correct order, starting with an H1 tag and moving down to H2, H3, and so on. The hierarchy of headings should reflect the organization of the content on the page.
- Placement: Ensure that the headings are placed in the correct location, i.e. they should come before the content they are introducing.
- Duplication: Check that each heading is unique and not used more than once on the same page.
- Keyword usage: Use the headings to improve the keyword focus of the page by incorporating relevant keywords.
- Accessibility: Make sure that the headings are also descriptive and concise. People using screen readers rely on headings, so it’s important that the headings accurately describe the content they precede.
Once you have identified any issues with the heading structure, you can take steps to correct them. Here are some common mistakes and how to correct them:
- Missing or duplicated H1 tags: Make sure that each page has a unique H1 tag and that it accurately reflects the main topic of the page.
- Incorrect hierarchy: If the headings are not in the correct order, you can simply restructure them to reflect the hierarchy of the content.
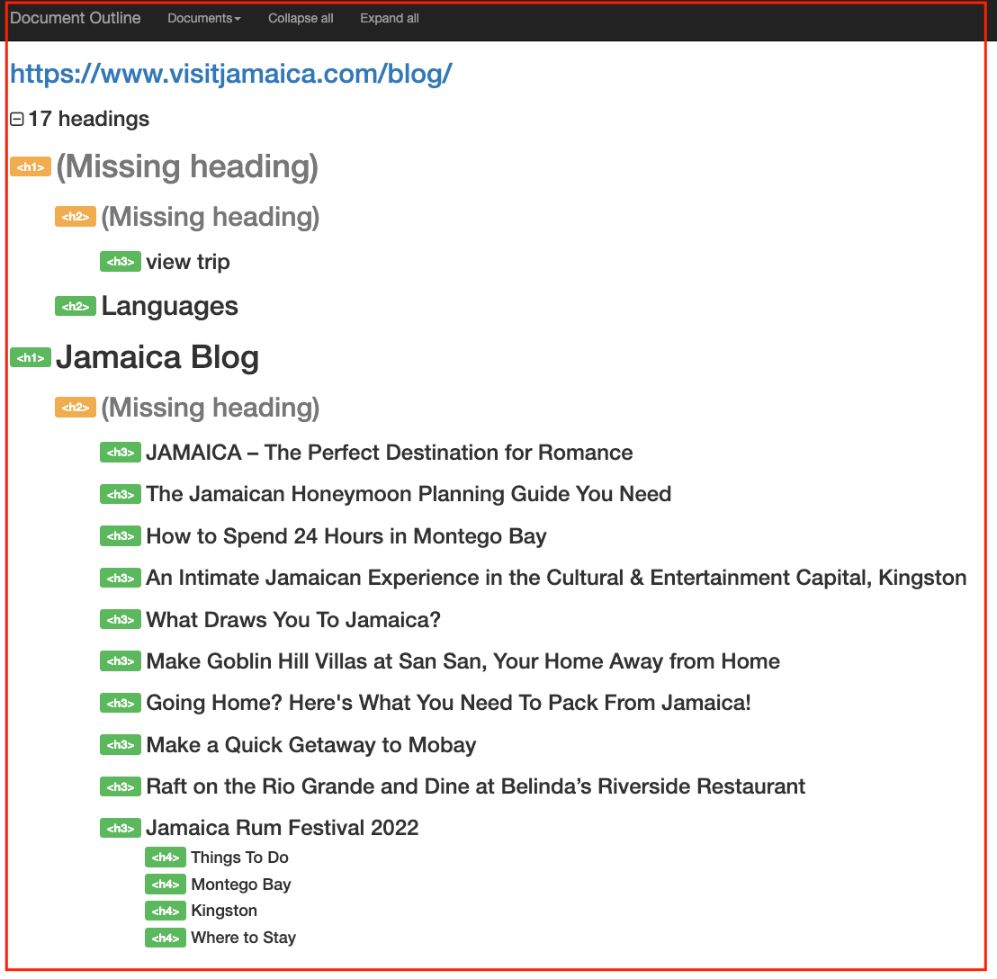
- Missing or inconsistent formatting: Ensure that the headings are formatted consistently throughout the website and use the same font size, color, and style.
- Too many or too few headings: Check that the number of headings on each page is appropriate for the amount of content. There should be enough headings to break up the content into readable chunks, but not so many that they become overwhelming
- Using headings for styling purposes instead of to convey meaning (importance). This is a big one! I often see it on lawyer websites.

In your SEO audit, you should discuss the structure of headings on every page type and present an example correct structure of headings for each page template.
It is not enough to say “The structure of headings is incorrect. Fix the structure.” 🤣
Step 3: Tools to automate headings auditing
Practically any popular website crawler can help automate the headings auditing process. Some popular options include:
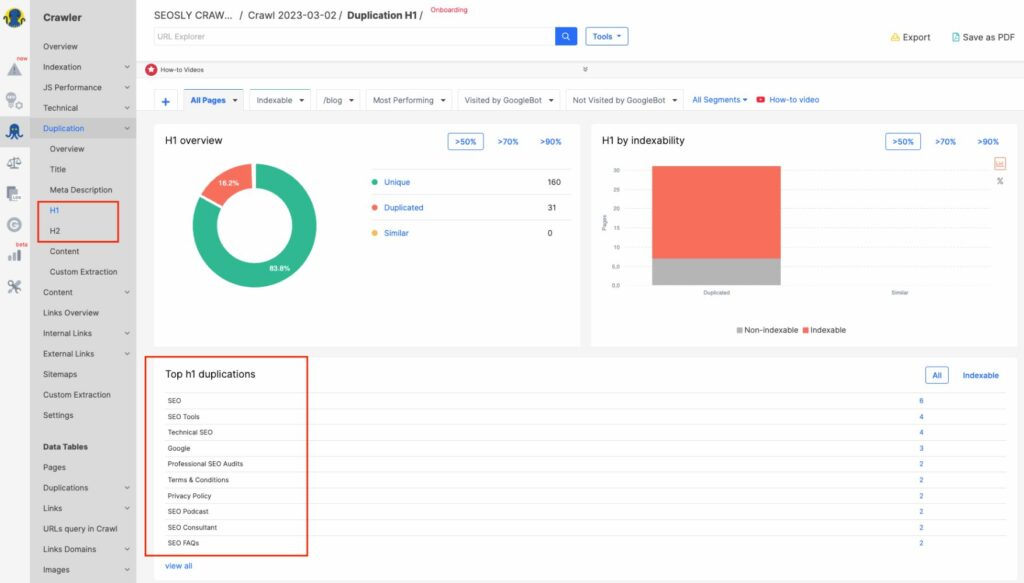
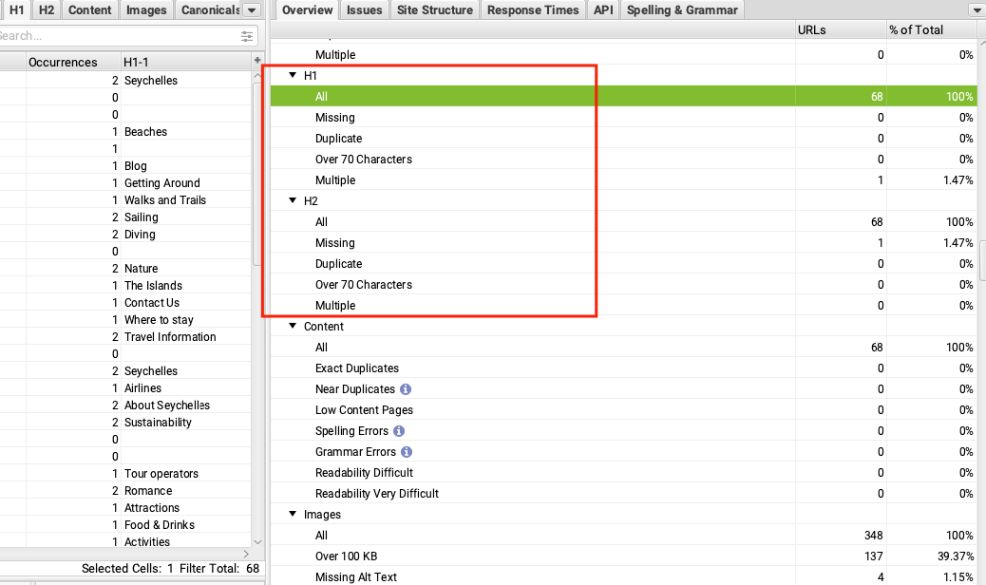
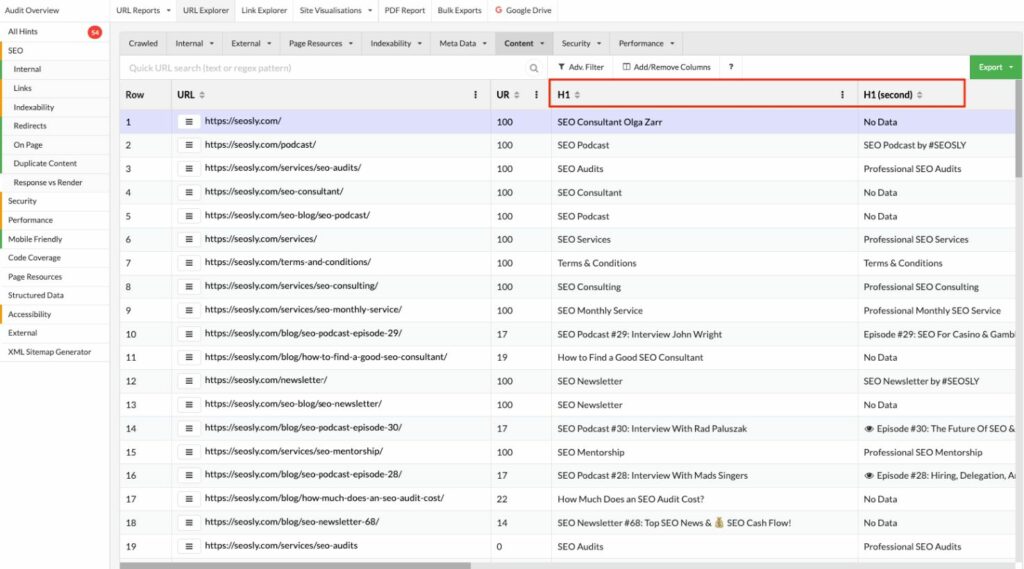
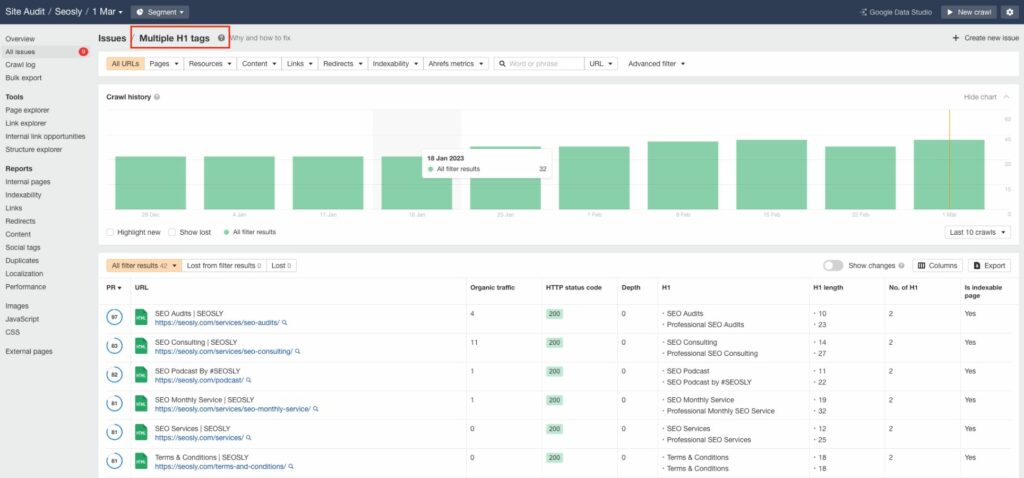
Using tools for headings auditing can be beneficial as they can help to quickly identify issues across a large number of pages. You won’t be manually checking thousands of pages, will you? 😂
However, these tools will not catch all heading-related issues, and manual auditing is always a must.
- These tools usually do not analyze the entire heading structure of every page. Generally, these crawlers only check for H1 and H2 tags, and whether they are duplicated, whether there are multiple H1 headers on a page, or if headers are too long or too short.
- Additionally, crawling tools may not be able to provide recommendations for how to fix heading-related issues, so you need to have a solid understanding of heading best practices to suggest necessary changes.
A note about headings and JavaScript
Keep in mind that the structure of headings on a website may change after JavaScript has been executed.
The above-mentioned crawling tools are awesome for checking whether the structure of headings changes after JavaScript has been executed and whether Google can correctly see the headings added with JavaScript.
Here is the JavaScript report in Screaming Frog.
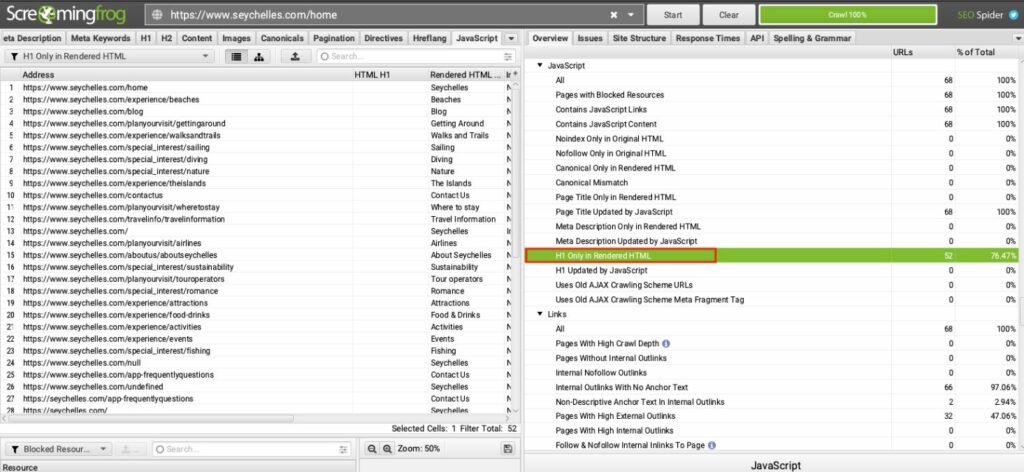
As you can see, in the case of this website, H1 tags are visible only in the rendered HTML.
This is not a problem in itself but you need to make sure that Google indeed sees and indexes that content.
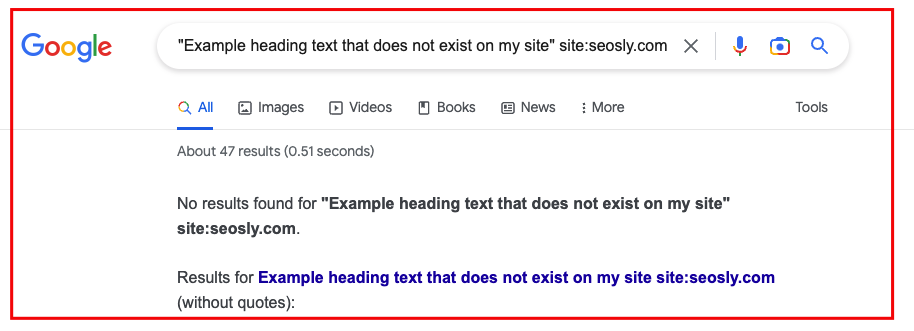
To check whether the content of the heading is indexed simply do a Google search for the content of the heading in quotation marks with the site: operator like this:
"The exact content of the header added with JavaScript" site:domain.com
If you can find the exact sentence in search results, it means Google has no problems indexing the content. If you see something like below, then you need to dive deeper into JavaScript and indexability issues.
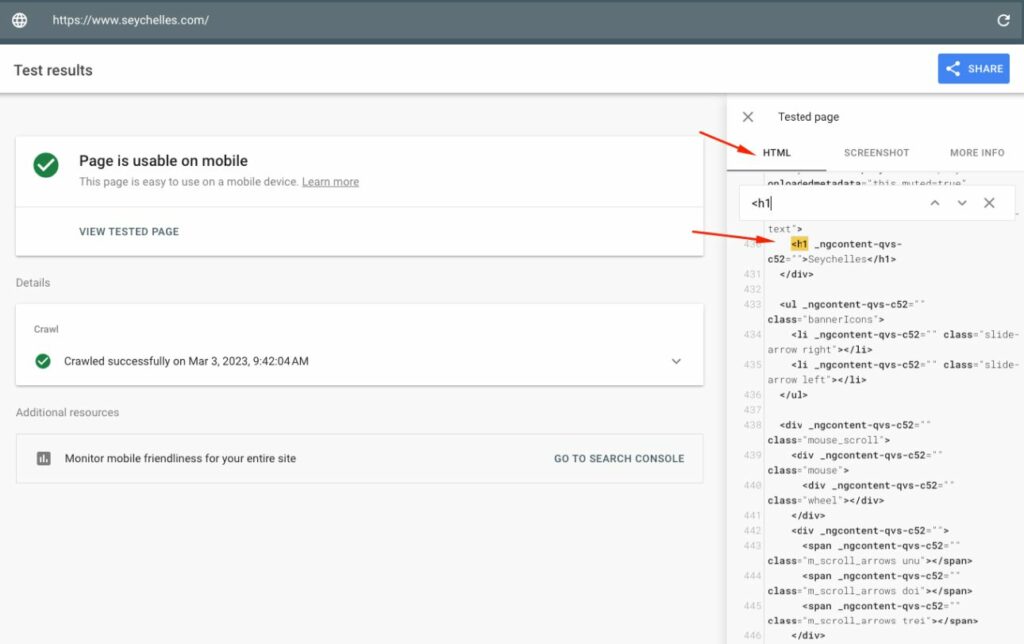
Alternatively, you can run the Mobile-Friendly Test and look for the heading in the rendered code.
Final words of wisdom about auditing headings
Heading structure is a critical component of a website’s SEO, accessibility, and user experience. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can audit and improve the heading structure of any website, making it easier for both users and search engines to navigate and understand the content. Remember to check each page type, use tools to automate the process, and manually check for common mistakes.
And if you want to learn more about SEO auditing, check out my other articles on SEOSLY:



