Google Sues Rank And Rent Marketer

Google is suing an online marketer for violating it’s terms of service and to prevent the defendant from causing additional harm to Google as well as to business owners and consumers.
The person being sued was a member of a public Facebook group called, Rank and Rent – GMB Strategy & Domination.
The lawsuit claims that the company has been misleading users, engaging in activities that violate both federal and state laws, and violating their contract with Google as laid out in their terms of service.
There are three main schemes the defendants are accused of:
“(1) fraudulent verification of nonexistent Business Profiles,
(2) posting fake reviews on Business Profiles, and
(3) selling real businesses leads from unsuspecting customers who seek services from the businesses listed on Defendants’ fake Business Profiles. “
The two entities being sued are GMBEye and Rafadigital, which Google links together as one company.
Rank and Rent
Rank and rent is a practice where someone will create a business website and an associated business profile for the purpose of selling leads from it, renting it to a business for a set price or selling the business profile and website.
This practice gained prominence around 2019.
Remarkably, demonstrating the level of naivete (lack of wisdom, experience or judgement) of those involved in rank and rent, the practioners operate a public Facebook page out in the open discussing strategies and advertising sale of their websites and business profiles.
Google’s lawsuit includes a screenshot of that public Facebook group, with a description of the defendant claiming to “renting out GMBs” and “selling GMBs”
The defendant was in a rank and rent Facebook group stating that he rents Google Business Profiles and sells them, which is a part of what Rank and Rent is.
Screenshot of Rank and Rent Facebook Group Published in Google Lawsuit
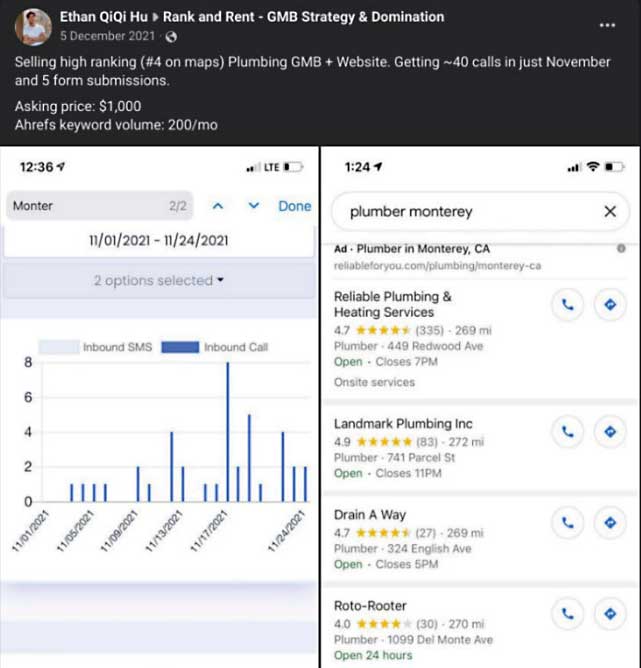
The lawsuit describes the business practice:
“Once Defendants successfully verify these dummy Business Profiles, they proceed to either sell the listing or modify the fake business’s information to make the Business Profile more desirable to potential buyers.
At times, Defendants transfer control of fraudulently-verified Business Profiles, updated to include an unverified real-world business’s business information, to their buyers.”
Google Business Profile Verification Service
One of the services that the company provided was Google Business Profile verification services, as well as promising top listings.
According to Google:
“GMBEye is replete with express and implied assurances that Defendants are able to bypass the verification procedures that Google requires of most merchants, and also to ensure a particular business listing is ‘at the top’ of Google Search results—a misleading and false statement, for no business or entity can guarantee such placement by Google’s Search algorithm.
Much of Defendants’ messaging suggests that GMBEye has preferential access to Google or is otherwise uniquely positioned with respect to Google, allowing it to secure the ‘Premium Business Listing Verification’ that is unavailable to those who verify their businesses through Google’s free processes.
…GMBEye’s customers and prospective customers likely include both legitimate merchants seeking a shortcut through Google’s procedures, as well as other scammers or bad actors who abuse fake business listings; while the latter may quickly recognize GMBEye as a fellow scammer, the former may not.”
The lawsuit makes statements about the website messaging that suggests that they have “a proprietary process” for establishing trust with Google, which allows them to “fast track” the process.
There are also descriptions of extraordinary claims made by the defendant.
According to the lawsuit:
“Further explanation on the GMBEye website boasts that Defendants can even verify businesses ‘with [s]pammy names,’ suggesting the service avoids Google’s measures to maintain accurate and high-quality Business Profiles.
Defendants similarly claim that “[m]ost verification methods cant [sic] handle that because Google will suspend your listing but with our method you can sustainability rank your GMBs with Spammy names helping you rank on Google in no time!”
GMB Profiles and Fake Reviews
The lawsuit claims that the defendant offers to improve Google Maps and “GMB” profile listings and “encouraging reviews.”
It also states that the business claims to be able to rank customers #1, which is generally known in the search marketing industry as a red flag because nobody is able to guarantee such a thing.
Lead Generation
The defendants, according to the lawsuit, advertised themselves as specializing in lead generation, which means driving sales calls and contacts, sales leads, to businesses, which is a part of the practice known as Rank and Rent.
The lawsuit states:
“Rafadigital claims that it can “[g]et high converting leads direct to your phone” “for all industries[.]””
Google Describes Rank and Rent Scheme
The lawsuit offers a description of how the defendants operated their scheme.
They write:
“…Defendants first create a Business Profile for a fake business, generally accompanied by a fake website based on a simple template.
Defendants typically associate these fake businesses with Voice over Internet Protocol (“VoIP”) phone numbers whose area codes correspond to the fake businesses’ supposed locations.
Upon information and belief, Defendants have been associated with over 350 fake Business Profiles listings since mid-2021.”
How Defendants Tricked the Google Verification System
Google’s verification system was shockingly easy to circumvent.
The defendant appears to have made little effort to create photos and videos for proving they are a real business, sometimes using the same toolbench, photographed from different angles, to prove they were a business.
A video screenshot included in the lawsuit shows the image of the individual who Google says is “purported to be associated with a nonexistent chiropractor, Wilmington Chiro Health.”
This was used as a part of the verification process for the non-existent chiropractor.
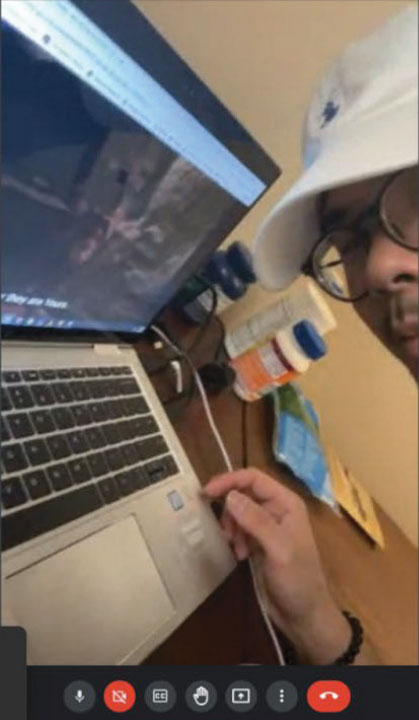

The lawsuit also posts images provided by the defendant during the course of verifying a company called, “Western Los Angeles Garage Door Repair.”
This is the image provided by the defendant to “mislead” Google into believing that it was an image of the work area.
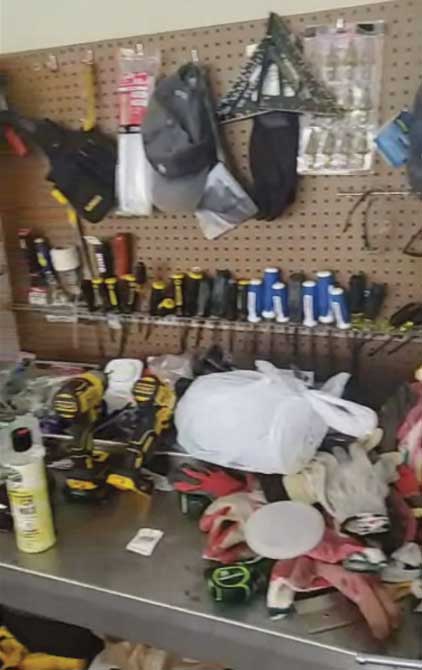

The following is the image provided to Google to verify a Houston, Texas “Pro Tree Service” that shows the exact same tool bench:
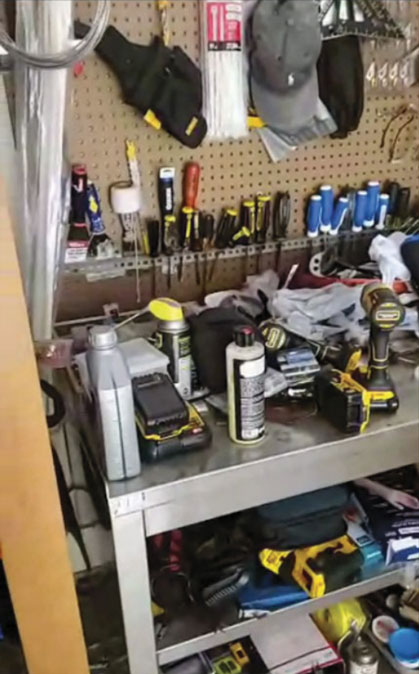

Google’s lawsuit provides another image the defendants used to verify “AS Budget Plumbers, purportedly based in Davis, California, when Defendants contacted Google to verify that fake listing on March 29, 2022:”

Rank and Rent – GMB Strategy & Domination Facebook Group
Google’s lawsuit names a Facebook group named, Rank and Rent – GMB Strategy & Domination as a place that the defendant used to sell business listings.
The lawsuit describes the process:
“For example, Mr. Hu posted the below offer to sell a Business Listing in a Facebook group called “Rank and Rent – GMB Strategy & Domination,” claiming that his listing for a “Plumbing GMB + Website” in Monterey, California, had received “~40 calls and 5 form submissions” in the prior month—presumably from residents of the Monterey area who were seeking assistance with a plumbing issue.”
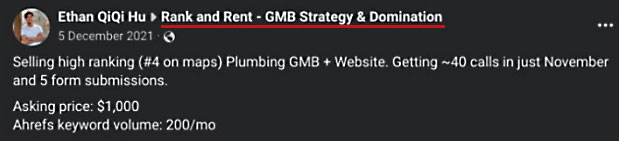
According to the lawsuit:
“Mr. Hu—who admits in his biography on GMBEye.com to “renting out GMBs” and “selling GMBs”—sought $1,000 for this nonexistent business’s Business Profile.”
Fake Google Profile Reviews
The defendant is also accused of selling fake reviews that Google claims were outsourced to fake review providers in Bangladesh and Vietnam.
According to the lawsuit
“To further bolster their fake listings’ illusions of legitimacy and credibility, and as an added service to their buyers, Defendants cause fake reviews to be posted to their fraudulent Business Profiles and those transferred to their clients.
…Upon information and belief, Defendants are connected to a network of over 350 fraudulent Business Profiles that involve at least 14,000 fake reviews.
Nearly all of the reviews awarded five out of a potential five stars.
And a majority of these reviews—including the at least 14,000 reviews noted above—were posted by two actors located in Bangladesh and Vietnam, an ocean away from the many purported U.S. businesses for which these accounts posted reviews.”
Damages Sought By Google
Google is suing the defendants engaged in the rank and rent scheme for triple the amount of actual damages, attorneys fees and prejudgment interest.
A Cornell University Law School webpage describes the meaning of prejudgment interest:
“The interest that a creditor, usually a plaintiff in the case, is entitled to collect, derived from the amount of a judgment, which compensates the creditor for an injury which occurred before the judgment.
… Another example is Short v. U.S., where the Federal Circuit awarded the Yurok Indians prejudgment interest on their damages to recover revenue generated from timber harvesting from which they were wrongly excluded.”
Google’s Terms of Service
Some people are flippant about violating Google’s terms of service, naively believing that Google is not the law.
Some marketers naively treat Google’s Terms of Service without the seriousness it deserves.
Google is suing the defendant for breach of contract for violating those terms of service related to Google Maps and Google Business Profiles.
What this lawsuit makes clear is that violating Google’s terms of service should not be taken lightly.
As can be seen with this lawsuit, Google has the right to enforce their terms of service in a court of law.
Source link : Searchenginejournal.com



