Posted by
Rank Ranger
What is the Google Panda Algorithm Update?

To avoid being penalized by Panda, make sure that your site contains unique content with strong relevance to your industry, product or topic. If your page contains links, make sure they’re relevant to the content and don’t overload the page with links. Take advantage of our On-Page Keyword Optimization Tool to analyze your pages for factors that can trigger search engine penalties.
History of the Google Panda Algorithm Updates:
- February 23, 2011: Panda 1
- April 11, 2011: Panda 2 (Ref. 2.0)
- May 9, 2011: Panda 3 (Ref. 2.1)
- June 21, 2011: Panda 4 (Ref. 2.2)
- July 23, 2011: Panda 5 (Ref. 2.3)
- August 12, 2011: Panda 6 (Ref 2.4)
- September 28, 2011: Panda 7 (Ref 2.5)
- October 5, 2011: Panda 8 – Flux
- November 18, 2011: Panda 9 (Ref. 3.1)
- January 18, 2012: Panda 10 (Ref. 3.2)
- February 27, 2012: Panda 11 (Ref. 3.3)
- March 23, 2012: Panda 12 (Ref. 3.4)
- April 19, 2012: Panda 13 (Ref. 3.5)
- April 27, 2012: Panda 14 (Ref. 3.6)
- June 8, 2012: Panda 15 (Ref. 3.7)
- June 25, 2012: Panda 16 (Ref. 3.8)
- July 24, 2012: Panda 17 (Ref. 3.9)
- August 20, 2012: Panda 18 (Ref. 3.9.1)
- September 18, 2012: Panda 19 (Ref. 3.9.2)
- September 27, 2012: Panda Update 20
- November 5, 2012: Panda 21
- November 21, 2012: Panda 22
- December 21, 2012: Panda 23
- January 22, 2013: Panda 24
- March 14, 2013: Panda 25
- June 28, 2013: Panda 26
- May 20, 2014: Panda 4.0
- September 23, 2014: Panda 4.1
- July 18, 2015: Panda 4.2
Tips to Recover from Google Panda Algorithm penalties
- Google has stated that “low-quality content on some parts of a website can impact the whole site’s rankings.” Therefore, it is important to remove low quality pages, merge or improve the content of individual shallow pages into useful pages, or move low quality pages to a different domain. All of these actions can positively affect your rankings.
- If you find negative-impact backlinks, or have been notified by Google of unnatural links pointing to your site (e.g., from link farms), you should send a request to the offending site owner to immediately remove the link. If the link is not removed, then use Google’s disavow links tool.
- Ask yourself about the quality of the page and if you would recommend this page to others, using questions such as “Does the site have duplicate, overlapping, or redundant articles on the same or similar topics with slightly different keyword variations?” or others that Google suggests.
- Remove any unnecessary duplicate content from your site, whether it appears elsewhere on your domain, or on another site. Google Panda “will provide better rankings for high-quality sites—sites with original content and information such as research, in-depth reports, thoughtful analysis and so on.” In some cases, this content is important to your site, when that happens use Canonical tags to tell Google not to index specific pages or directories that do contain duplicate content that is necessary.
If your site was penalized and you have made the necessary corrections, you can ask Google for reconsideration and they might recheck your site before the next Panda refresh.
How to monitor future Panda Updates
We monitor the Google Algorithm for you in our Rank Risk Index, which records SERP fluctuations as they occur. You can access that tool on a regular basis or use the embed code to add it to a page on your site.
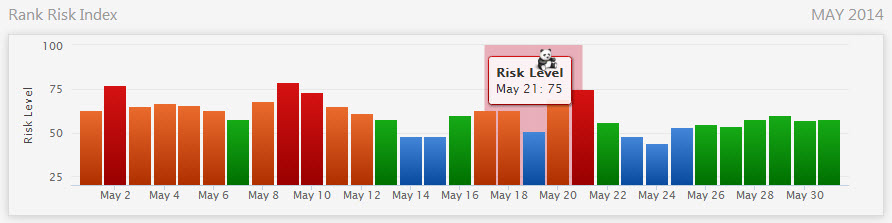
Panda is only one of many Google algorithms tasked with improving the quality of web search, so we have compiled a comprehensive history of Google Algorithm updates, along with SERP fluctuations recorded by our Rank Risk Index, announcements, insights and WWW reaction to each update for your convenience.




