Updated: April 15, 2023.
Here is the full guide to 404 errors and whether (and when) they hurt SEO.
404 errors might seem a bit daunting at first, but in my experience, they’re not always a cause for concern when it comes to your website’s SEO.
While they can negatively impact your search engine rankings in certain cases, there are times when you can safely ignore them without any repercussions.
In this guide, I’ll shed light on the topic of 404 errors and their effect on SEO.
I’ll tackle crucial questions, such as: What are 404 errors? What are soft 404 errors? When do 404 errors harm your site’s SEO? When is it okay to disregard them? And most importantly, what steps should you take when faced with a multitude of 404 errors on your site?
Ready? Let’s get started.

TL;DR: Do 404 errors hurt SEO?
404 errors can hurt SEO if they impact important pages with traffic or backlinks, or if they result from poor website management. However, search engines expect a certain number of 404 errors as part of the normal web ecosystem, and these do not necessarily harm your site’s ranking. Addressing unintended 404 errors and implementing custom 404 pages can help minimize their impact on your site’s SEO.
What are 404 errors?
To better grasp the concept of 404 errors, let’s explore their definition, how search engines and users encounter them, and some common causes and examples.
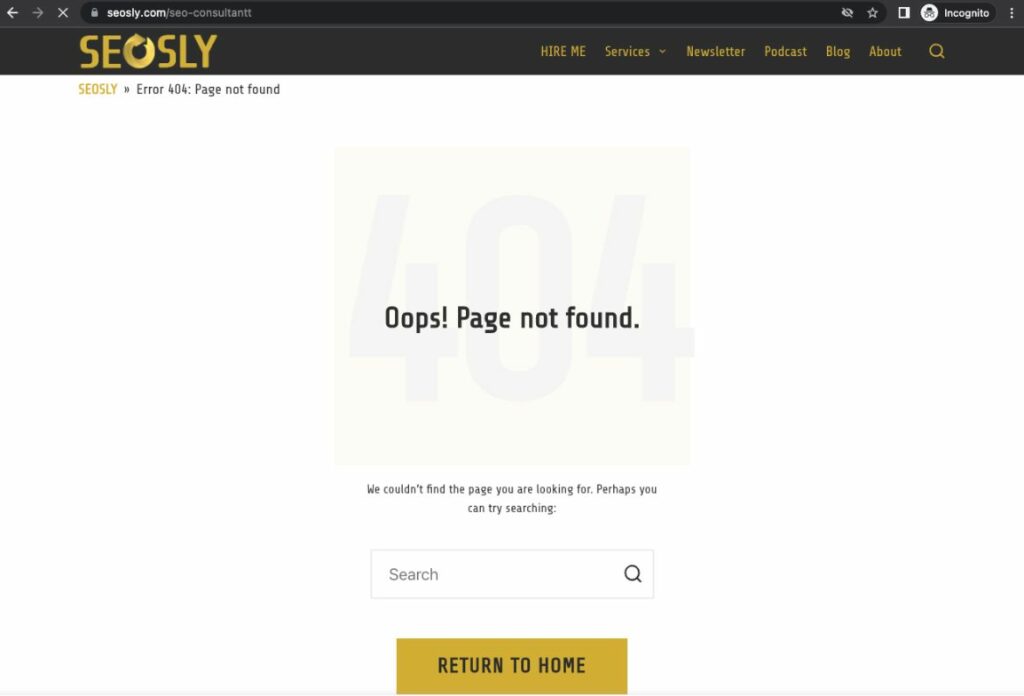
Here’s the basic information about 404 errors:
- A 404 error, or “Not Found” error, occurs when a user or search engine tries to access a URL that doesn’t exist on the server.
- The server returns an HTTP status code 404, indicating that the requested resource is unavailable.
- 404 errors are a standard part of the web, as content is continuously added, updated, or removed.
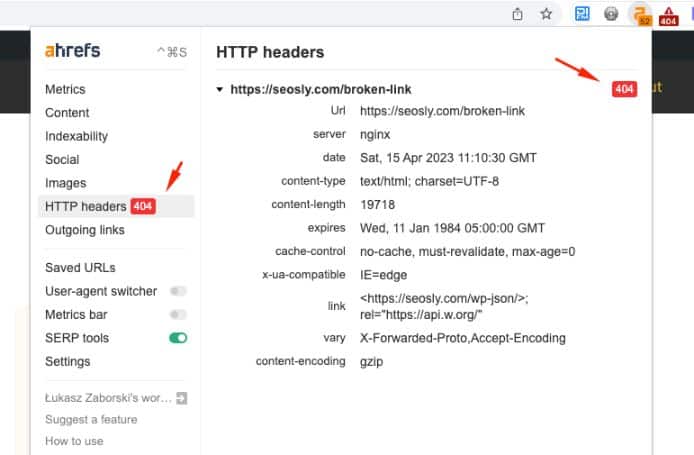
You can quickly check the status code of any page using the Ahrefs SEO Toolbar (HTTP headers section).
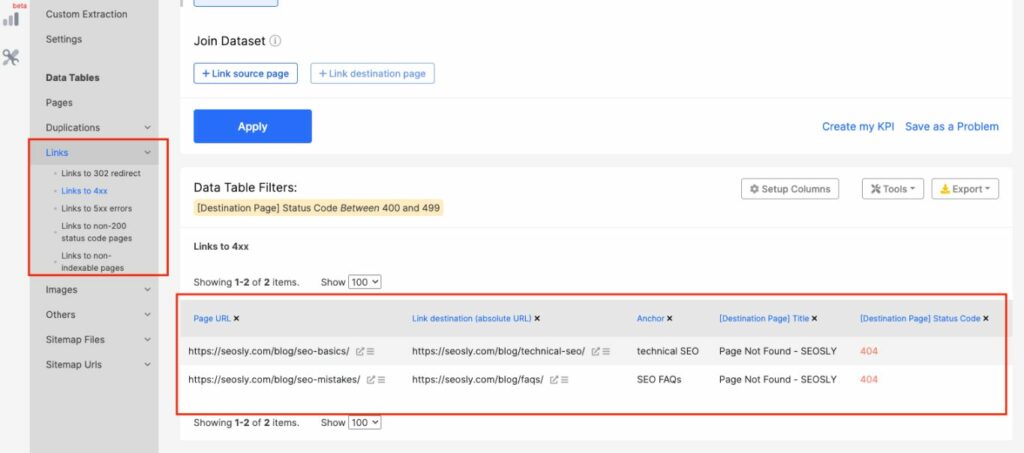
To check the status codes of many pages in bulk, you have to crawl the website with a crawler like JetOctopus.
How do search engines and users encounter 404 errors?
Here’s how search engines and users come across 404 errors:
- Users may encounter 404 errors when they click on a broken link or enter an incorrect URL in the browser.
- Search engines, like Google, can come across 404 errors when they crawl a website (or a sitemap) and find broken internal or external links.
Common causes of 404
Here are some common causes and examples of 404 errors:
- A page has been deleted or moved without updating or redirecting the old URL.
- Typos or mistakes in internal or external links will lead to non-existent URLs.
- A user or search engine tries to access a URL that was never created on the website by following an incorrect link (in the XML sitemap, a misspelled link on another website, etc.).
- A site restructuring or redesign where old URLs have not been properly redirected to new ones.
- Technical issues or misconfigurations in the website’s content management system (CMS) can cause 404 errors as well.
Do 404 errors affect SEO?
404 errors are a common part of the online landscape. As content is created and removed, it’s natural for websites to have some broken or outdated links that result in 404 errors.
When a search engine crawler encounters a 404 error, it simply acknowledges that the content is no longer available and eventually removes it from the index.
Depending on the situation and the website, 404 errors may have a negative, positive, or neutral effect on the website’s SEO.
404 errors’ negative effect on SEO
When 404 errors impact crucial pages with traffic, rankings, and backlinks, removing them can harm the site’s SEO performance.
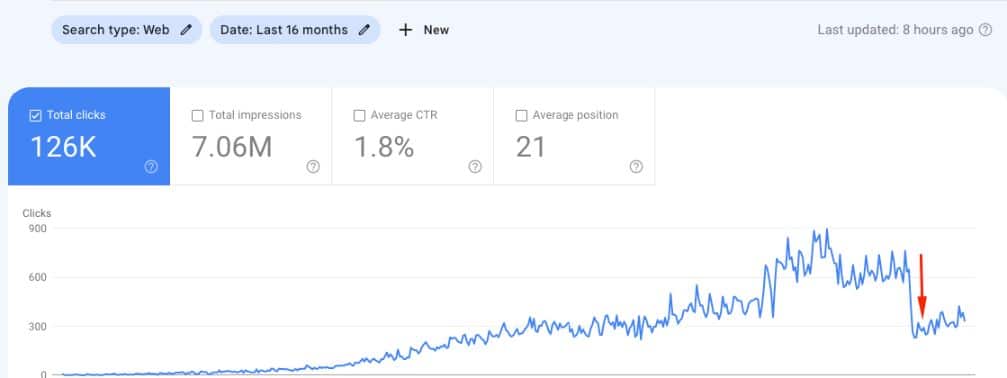
For example, if an e-commerce site accidentally deletes a popular product page that was driving significant organic traffic and had numerous backlinks from reputable sources, this could lead to a decrease in search visibility and overall performance.
404 errors’ positive effect on SEO
When low-quality, duplicate, or unnecessary pages are removed following a website content audit, 404 errors can help search engines better understand the topic and topical authority/relevance of the site.
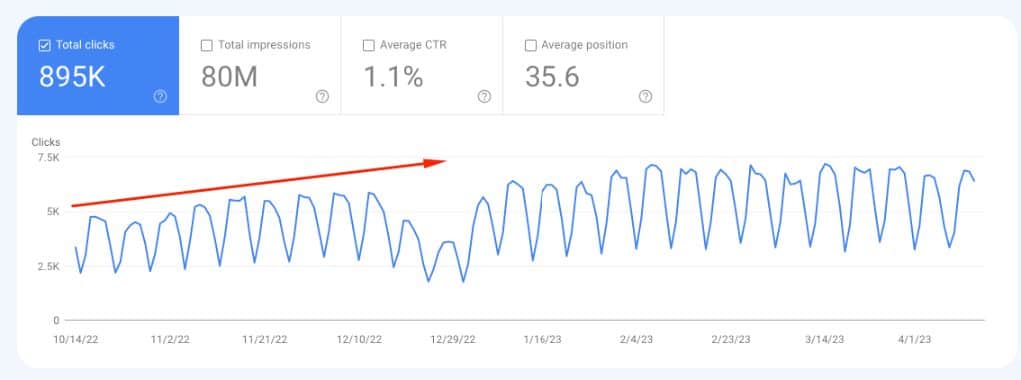
For instance, a blog that had multiple articles on the same topic with little variation might choose to remove the less relevant articles, consolidating the content into one comprehensive piece. This can improve the site’s perceived value and help it rank higher for relevant search queries.
404 errors’ neutral effect on SEO
404 errors relating to unimportant pages that didn’t rank or drive traffic may have little to no impact on a site’s overall SEO performance.
For example, if a company’s website has an outdated news release or an event page that is no longer relevant, these 404 errors would likely not impact the site’s search engine rankings or visibility, as they were not significant in the first place.
Soft 404 errors and their potential negative impact
A soft 404 error occurs when a URL returns a page indicating that the content does not exist, yet it also sends a 200 (success) status code. This could be due to a page with no main content or an empty page.
Soft 404 errors can arise from various situations involving your website’s web server, content management system, or the user’s browser, such as a broken connection to the database, an empty internal search result page, etc.
Returning a 200 (success) status code while displaying or suggesting an error message on the page leads to a poor user experience. Users may assume the page is functional, only to be confronted with some form of error.
Such pages are excluded from Google Search. If Google’s algorithms identify the page as an error page based on its content, Search Console will display a soft 404 error in the site’s Page Indexing report.
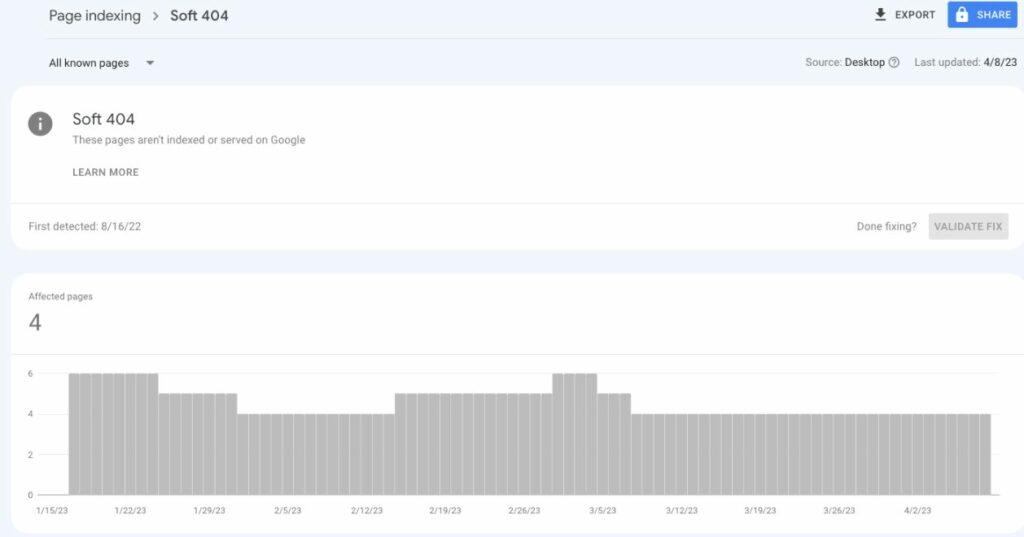
Let’s look at some examples and explore their potential consequences:
- Custom 404 page with a 200 status code: A webmaster creates a visually appealing custom 404 page with helpful information for users but configures the server to return a 200 (OK) status code instead of a 404 (Not Found) status code. This makes search engines think the page contains valid content.
- Redirecting nonexistent URLs to the homepage: When a website automatically redirects nonexistent URLs to the homepage rather than returning a 404 error, search engines may struggle to understand which pages should be indexed and which should not. This may cause potential indexing and ranking problems.
- Empty or thin content pages: A page that contains very little content, such as a page with only an image or a brief sentence, may be considered a soft 404 by search engines if it does not offer substantial value to users.
- Out-of-stock or discontinued products: E-commerce websites that display out-of-stock or discontinued product pages without proper 404 or 410 status codes might cause search engines to treat these pages as soft 404 errors.
Read the Google documentation on soft 404 errors and how to fix them.
How to identify 404 errors
The first step is always an awareness of the problem. To effectively identify 404 errors, I use the following three methods:
- Performing a full website crawl with JetOctopus or Screaming Frog
These powerful SEO tools provide comprehensive crawl reports, enabling me to discover all the 404 errors on my website. They list all detected broken links together with the list of pages where those links are. It allows me to quickly review and (if necessary) fix those 404 errors.
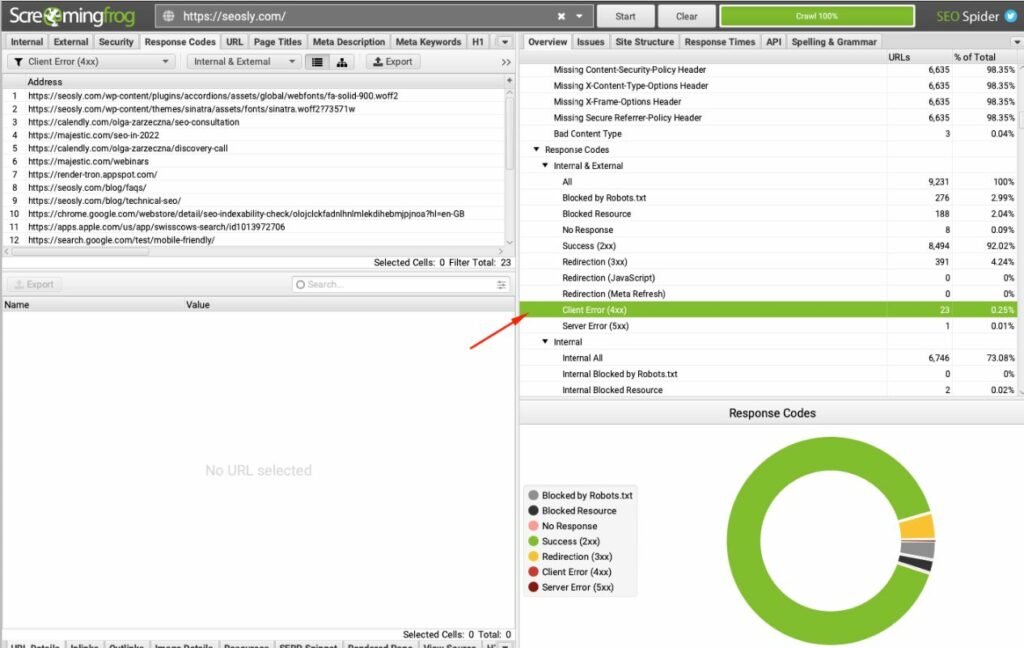
For example, a crawl report might reveal that several blog posts link to a non-existent product page.
- Checking Google Search Console Indexing report
You can check all 404 and soft 404 errors (detected by Google) in the Google Search Console Indexing report.
Just navigate to Indexing > Pages > Not indexed and review the section “Why pages aren’t indexed”.
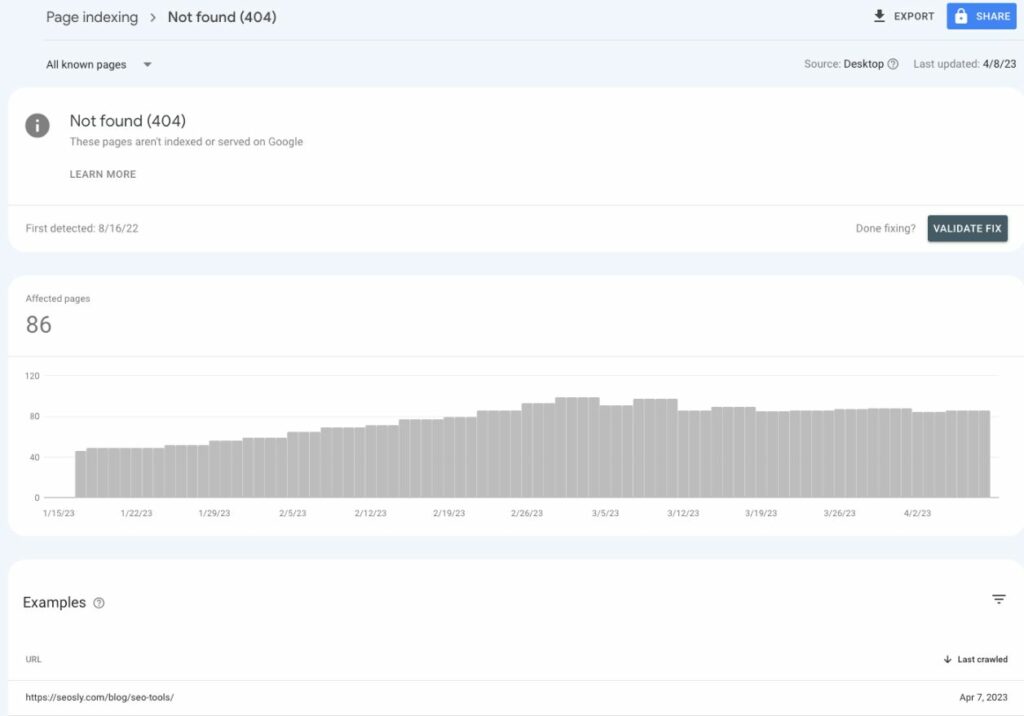
By looking for 404 and soft 404 errors, I can gain valuable insights into pages that Google has attempted to index but failed due to errors.
This information helps me identify which pages may potentially need to be fixed.
- Using Ahrefs SEO Toolbar for checking broken links on a per-page basis
The Ahrefs SEO Toolbar extension allows me to quickly assess the status of all links on a specific page.
When I find a broken link, I can promptly fix or remove it. This is, of course, only the method to analyze specific pages.
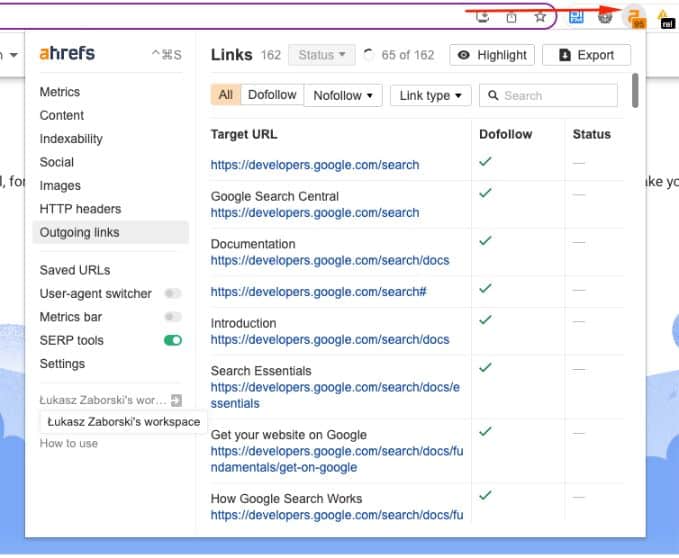
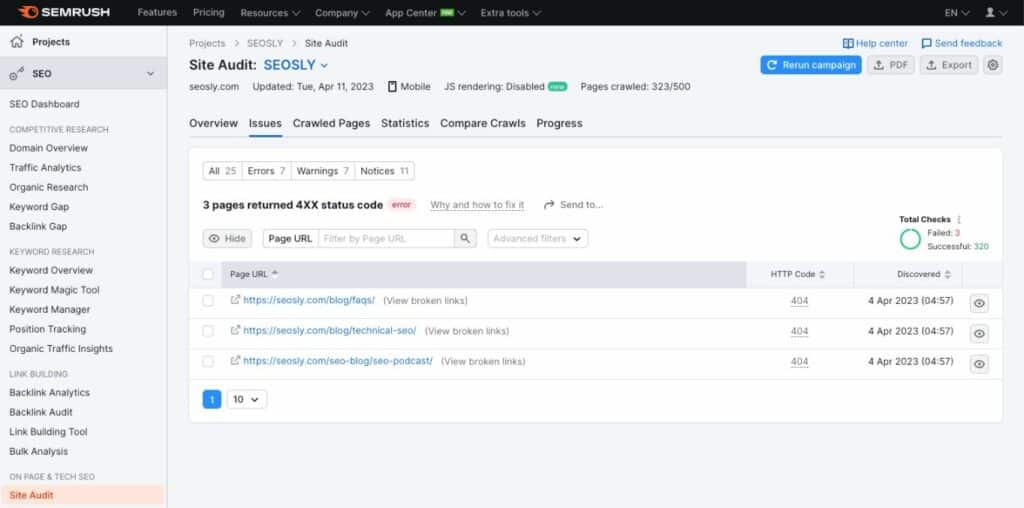
To analyze pages in bulk, you need to crawl the site with a crawler like JetOctopus or Semrush Site Audit and check the Google Search Console Indexing report.
How to assess 404 errors
Once you’ve identified the 404 errors on your website, it’s crucial to evaluate their impact and determine if they require attention.
Here’s how I approach this assessment:
- Intentionally removed pages returning 404 errors
If the pages were removed on purpose and you want them to be removed from the index, 404 errors may not be an issue. In this case, it’s better to return a 410 (Gone) status code, which signals to search engines that the page has been permanently removed and should be deindexed more quickly.
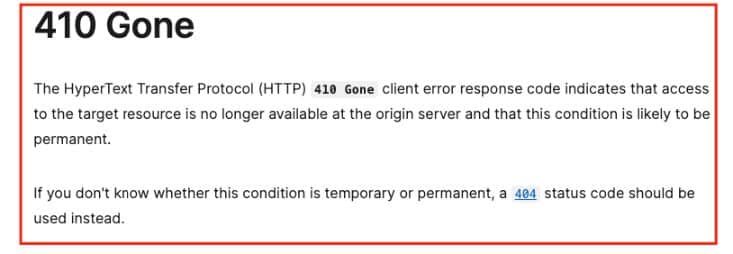
In the case of 404 pages, Google will be crawling them from time to time while for 410 pages Google should stop crawling them entirely once they are removed from the index.
- Purposefully removed pages with internal or external links pointing to them
If there are still internal links or external backlinks pointing to pages that you’ve intentionally removed, these 404 errors could be problematic. In this scenario, you should consider implementing 301 redirects to guide users and search engines to relevant, existing pages on your site.
To check if specific 404 pages have external backlinks, simply put them into the Semrush Domain Overview tool.
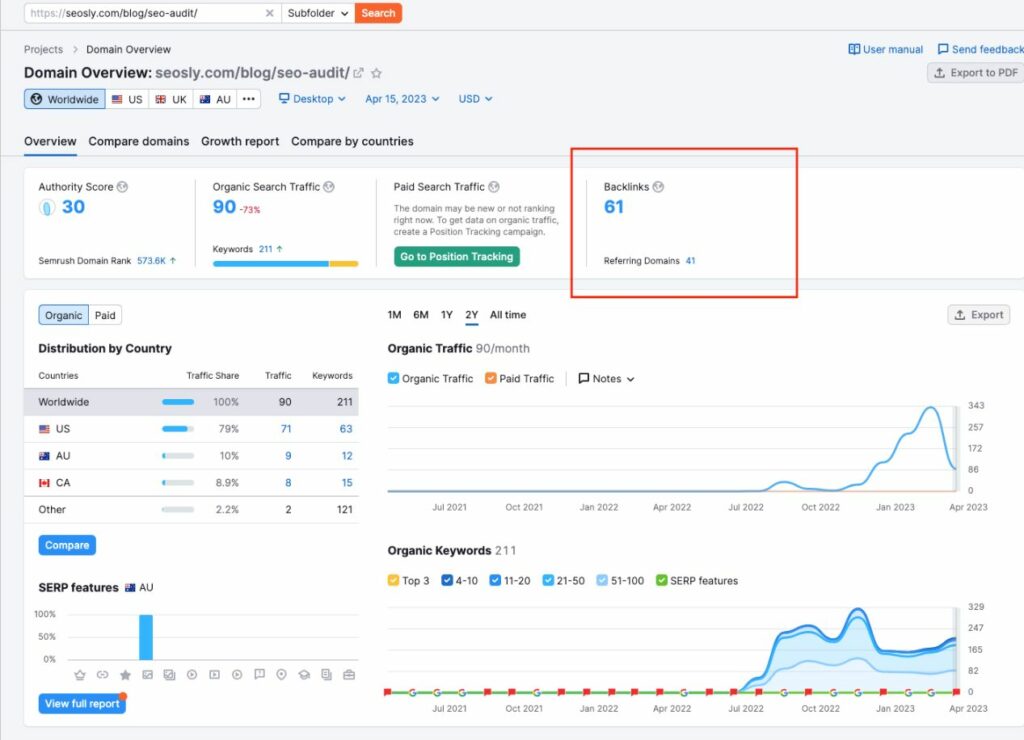
You can also use the Backlink Analytics in Semrush to review all backlinks of the domain and check the ones to point to 404 pages.
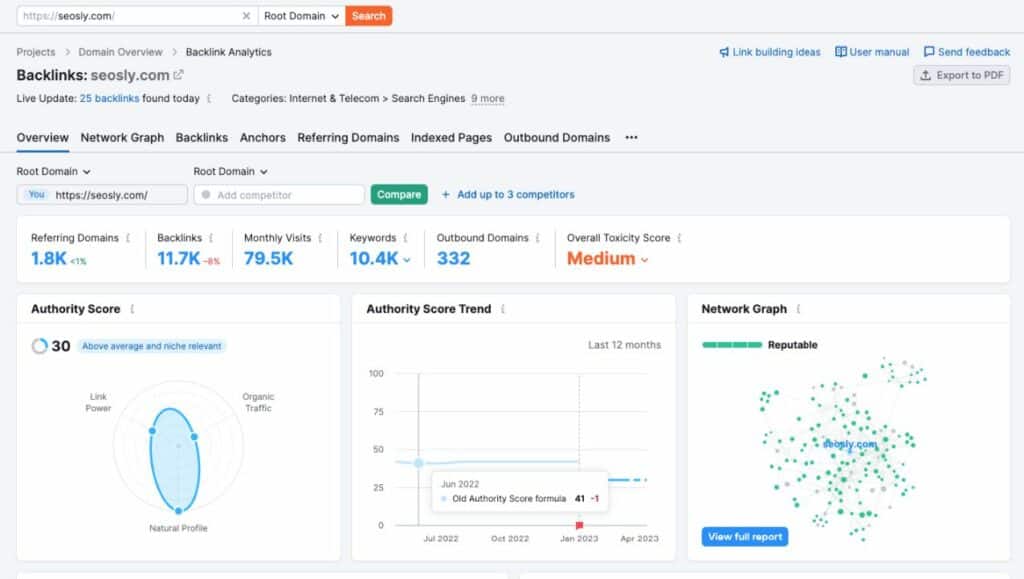
Any external link pointing to the 404 page on your site does not transfer any authority to your site, so it really worth checking if you have such links and – if you do – redirecting them to working pages.
Any unintended 404 errors always warrant a deep analysis and assessment, as they can lead to traffic and ranking drops, particularly if they involve high-traffic pages. Investigate the cause of these errors and determine the appropriate action to resolve the issue (restoring the pages or redirecting them to working pages).
- 404 errors resulting from a website migration
Often, 404 errors occur when a website migration has taken place, and the URL structure has changed without proper implementation of 301 redirects. In this case, it’s essential to correct the redirect issues to prevent any negative impact on your site’s SEO and user experience.
How to fix 404 errors
After assessing the impact of 404 errors and determining which ones need to be addressed, it’s time to take appropriate action to fix them.
Here are some steps you can take to resolve 404 errors:
- Implement 301 redirects: If a page has been moved to a new URL or if you’ve found misspelled URLs causing 404 errors, set up 301 redirects to direct users and search engines to the correct, updated URLs. This helps maintain the SEO value of the original pages and ensures a smooth user experience.
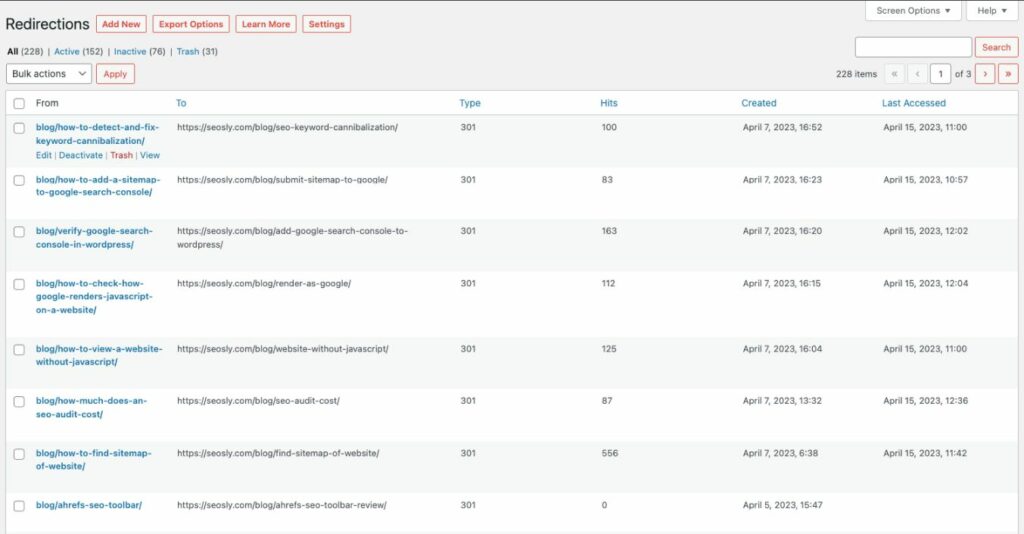
- Update internal links: Go through your website and update any internal links pointing to pages that return 404 errors. This will prevent users and search engines from encountering broken links on your site and improve overall navigation.
- Try to update external links or redirect them: If you’ve discovered valuable external backlinks pointing to 404 error pages, consider reaching out to the website owners of those sites and kindly request an update to the correct URL. If they cannot change the link, you should internally redirect the broken URL to the correct page or the closest thematically related page. This will help preserve the SEO value of those backlinks and improve the user experience for their visitors.
- Create helpful custom 404 pages: Design a custom 404 page that provides users with helpful information and links to other relevant pages on your site. This will help mitigate the impact of 404 errors on user experience and guide them to find the information they were initially looking for. And – of course – make sure that your 404 page indeed returns status code 404.
Best practices for 404 error pages
Here are some best practices for creating effective 404 pages:
- Ensure that your 404 page’s design and branding are consistent with the rest of your website. This helps users recognize that they are still on your site, despite encountering an error.
- Provide a clear and concise message that explains the 404 error and why the requested page is not available. Avoid using technical jargon and focus on a user-friendly explanation.
- Include links to your homepage, popular pages, and main navigation menu to help users quickly find their way to other sections of your site.
- Add a search bar to your 404 page, allowing users to search for specific content on your site, which may help them locate the information they were initially seeking.
- Invite users to report any broken links or other issues they encounter on your site. This feedback can help you identify and fix additional 404 errors or site problems.
- Consider adding a touch of humor or a visually appealing graphic to your 404 page. This can help lighten the mood and make the error less frustrating for users.

- Regularly monitor GSC and set up weekly crawls (for example with Semrush Site Audit) to stay up to **** if there is a spike of 404 errors on your site.
Frequently asked questions about 404 errors
And here are a few FAQs about 404 errors that will beat this topic to death.
How long does it take for Google to deindex a 404 page?
It can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for Google to deindex a 404 page. The process depends on factors like the crawl rate for your site and how frequently the page was being updated before it was removed.
What if I accidentally deleted a page and want to restore it?
If you accidentally deleted a page and want to restore it, simply re-upload the content to the same URL. Make sure that the URL returns a 200 status code, and Google should recrawl and index the page again in due course.
Can I customize the way Google handles 404 errors on my site?
You cannot directly customize how Google handles 404 errors on your site. However, you can follow the best practices outlined above to create a user-friendly 404 page and address issues that may arise from 404 errors.
Do 404 errors impact my site’s crawl budget?
Yes, 404 errors can impact your site’s crawl budget, as Googlebot still spends time crawling these non-existent pages. To make the most efficient use of your crawl budget, it’s essential to fix or redirect broken links and remove unnecessary 404 errors.
Should I use a custom 404 page or redirect all 404 errors to my homepage?
Using a custom 404 page is generally preferable, as it provides a better user experience by offering helpful navigation options and relevant content suggestions. Redirecting all 404 errors to your homepage can be confusing for users and may be seen as a soft 404 by search engines, potentially impacting your site’s SEO.
How often should I check for 404 errors on my site?
It’s a good practice to check for 404 errors on your site regularly, especially after making significant updates or changes to your site’s structure. Monitoring Google Search Console for crawl errors and using website auditing tools can help you identify and address 404 errors promptly.
What is the difference between 404 and 410 status codes, and when should I use each one?
A 404 status code indicates that the requested page was not found, while a 410 status code signals that the page has been permanently removed and will not be coming back. It’s advisable to use a 410 status code instead of a 404 when you intentionally remove content from your site and want search engines to deindex the page more quickly. Both status codes inform search engines that the content is no longer available, but a 410 response is more explicit about the permanence of the removal.
Can 404 errors impact my site’s user experience?
Yes, 404 errors can negatively impact your site’s user experience, as visitors may become frustrated or confused when they encounter a non-existent page. By creating a custom 404 page with helpful navigation options and relevant content suggestions, you can mitigate the negative impact of 404 errors on user experience.
Is there a limit to the number of 301 redirects I can use on my site?
There is no strict limit to the number of 301 redirects you can use on your site. However, it’s essential to avoid creating redirect chains or loops, as these can negatively impact your site’s performance and SEO. Aim to use 301 redirects only when necessary and ensure that they lead directly to the most relevant destination page.
How can I monitor external backlinks that lead to 404 errors on my site?
You can use backlink analysis tools, such as Ahrefs, Moz, or SEMrush, to monitor your site’s backlink profile and identify external links pointing to 404 pages. By addressing these broken links, either by reaching out to the linking site’s owner or implementing 301 redirects, you can recover any lost link equity and improve your site’s SEO.
How can I prevent 404 errors from occurring in the future?
To minimize the occurrence of 404 errors, consider the following strategies:
- Regularly audit your site for broken links and fix or remove them promptly.
- Be cautious when making changes to your site’s URL structure, and ensure that any necessary 301 redirects are in place.
- Use a content management system (CMS) with built-in functionality to prevent or automatically fix broken links (Rank Math allows you to create automatic redirections).
- Train your site’s content editors and administrators to avoid creating broken links when updating or adding new content.
I hope you found this article helpful in understanding the impact of 404 errors on SEO and how to address them effectively.
If you’re interested in learning more about SEO and website optimization, be sure to check out my other articles like:
Your continuous improvement and growth are always the focus, and I’m here to support you along the way. Happy optimizing!



