Overview
A few years ago, Adobe introduced a feature of Adobe Experience Manager as a Cloud Service which reduces the amount of time it takes to produce creative assets. This work is typically done by Creative groups and involves some manual steps and operations before having a completed, web-ready set of assets to release to market for an organization.
With Content Automation, an add-on to Assets, the manual tasks typically handled by Creatives can now be “offloaded” to Cloud Services for processing.
In this first part of a series, we will explore an overview of Content Automation in Adobe Experience Manager as a Cloud Service, specifically Assets. Our second part will discuss in further detail and provide an example of Content Automation in action.
Use Cases and Why This Should be Adopted
Bringing automation into the workflow of sourcing creative assets not only reduces the time-to-market for assets, but also reduces the churn often associated with the back-and-forth of trying to prepare content and assets for production-readiness. If workflows from a tool like Workfront are not being used to facilitate this flow, creatives will often repeat the same process over and over. This type of flow can be prone to error, delays, and diminished productivity.
Content Automation can also decrease the amount of time it takes for processing assets using microservices. This processing can be significantly quickened running in a “serverless” infrastructure as opposed to relying on Desktop applications for processing, which also means processing can run in batch.
By working with one main asset, many renditions based on processing profiles can be created which further enables marketing teams and non-technical users. Content Automation gives them the ability to create assets that are consistent, adhere to brand standards, and leverage AI capabilities of the platform.
Key Features and Benefits
- Content Automation is executed by Microservices, a modern approach to cloud processing that offloads processing and minimizes impact to the authoring experience.
- AI assistance is available for processing, further minimizing manual tasks.
- Certain processing can also be customized and configured entirely via the UI – no coding or development needed!
- Content Automation eliminates tedious tasks typically done by creatives.
How does Content Automation Work?
Content Automation works by adopting features of the new architecture in how Assets are processed in AEM as a Cloud Service. Instead of memory-heavy workflows that run for each asset that is uploaded to AEM, the processing is instead “offloaded,” or done by Microservices. These Microservices are run and in the background, which does not impact the authoring experience.
Once Content Automation is provisioned in your environment, a new “Creative” option will appear along the other processing profiles that are part of Assets.
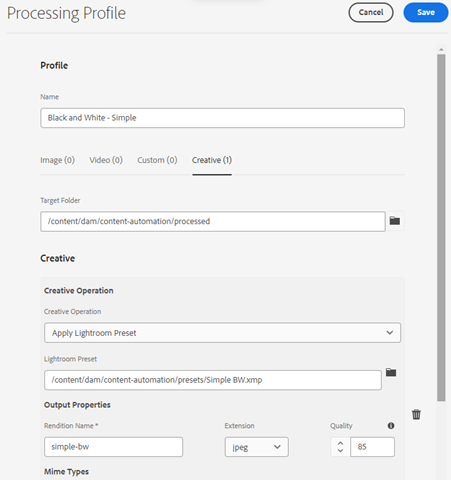
The Creative tab allows creation of processing profiles that can be added and applied to folders in AEM, so that when assets are uploaded, the processing profiles define the execution based on the asset type. Additional parameters can be configured, such as ‘which Creative Action to apply from Photoshop’ or Lightroom, quality percentages, and more.
After the one-time steps of creating the processing profile, any assets uploaded to the folder will generate the additional rendition(s), without having to go through Lightroom or Photoshop manual processing.
Available Creative Actions are detailed below:
| Creative Action: | Description: |
| Apply Photoshop Actions | Actions in Photoshop can be saved, similar to a script, and applied to one or more PSD files. |
| Image Cutout | AI can be used to remove parts of the image such as backgrounds. |
| Image Mask | Masking can apply settings to parts of an image, such as blurring the background or brightening the subject. |
| Replace Photoshop Smart Object | A smart object can be replaced within a PSD file while retaining effects and adjustments. |
| Apply Lightroom Preset | As in the example above, one or more filter presets in Lightroom can be applied to an image, in addition to 50 default presets. |
| Auto Straighten | AI can be used to auto-straighten an image, such as level horizons or vertical buildings. |
| Auto Tone | AI can be used to analyze the image and make a number of light and color adjustments. |
Considerations when Using Content Automation
- Content Automation is an add-on to AEM as a Cloud Service Assets, which requires licensing and provisioning.
- Experience Manager limits the asset processing to 300 requests per minute per environment and 700 requests per minute per organization.
- File size is limited to 4 GB for Adobe Photoshop API operations and 1 GB for Adobe Lightroom operations.
Wrap-Up and Further Reading
In addition to Content Automation, Adobe has several offerings related to integrating between AEM as a Cloud Service Assets and Creative Cloud applications. See their best practices documentation to explore some of the use cases.
There are many additional ways to configure microservices to process assets, such as creating custom FPO (For Placement Only) renditions, changing file format, and calling 3rd-party systems to update data for a PIM (Product Information Management) system. Additional configurations and settings are described in detail on Adobe’s documentation site.
We hope to have improved your understanding of Content Automation, and how it can be leveraged within your organization. Look for the second part of the series coming soon! Thank you for reading and do get in touch with us if we can help you in your current AEM project.